A Comprehensive Exploration Of Common Recycling Practices: Examining The Impact And Importance Of Material Reuse
A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse
- 3.1 Paper: The Foundation of Recycling
- 3.2 Aluminum: A Metal with a Second Life
- 3.3 Glass: A Material with Infinite Recyclability
- 3.4 Plastic: A Complex Recycling Challenge
- 3.5 The Importance of Recycling: A Collective Effort
- 3.6 FAQs about Recycling
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Recycling
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Call to Action
- 4 Closure
A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse

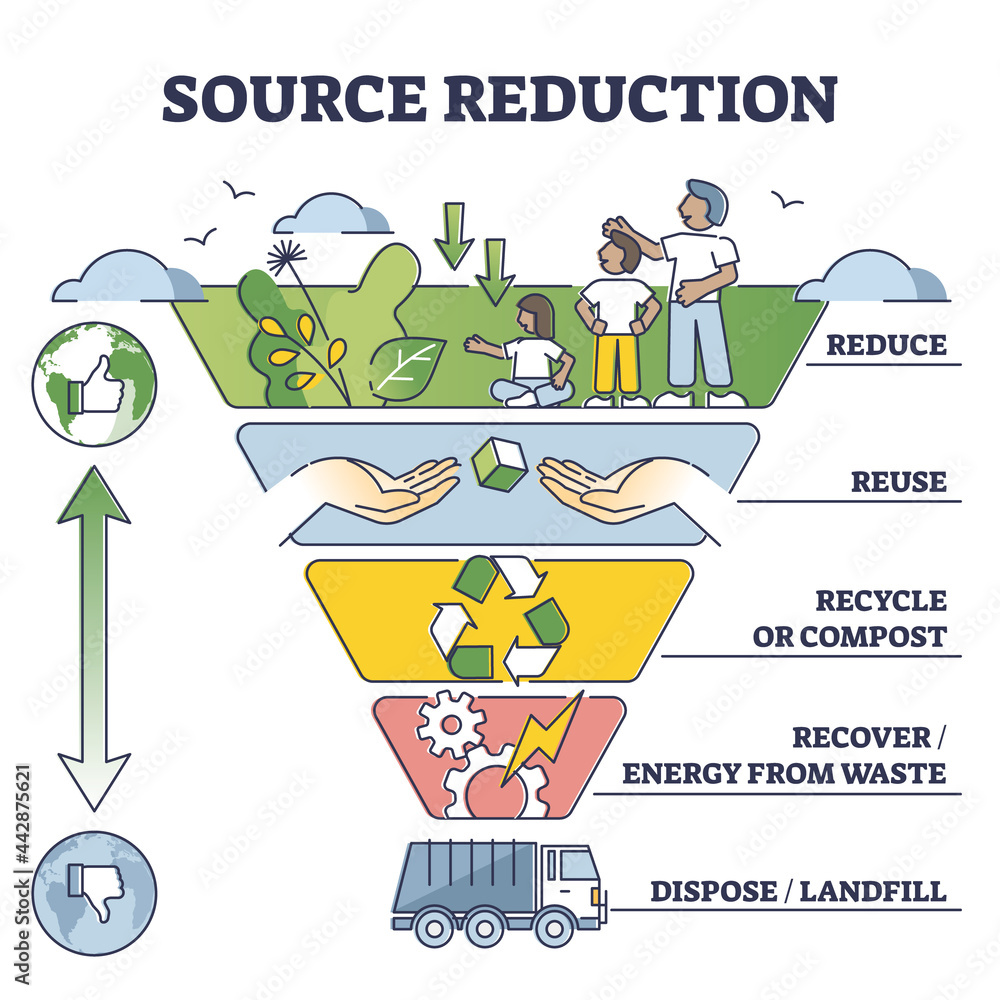
Recycling, the process of converting waste materials into reusable objects, plays a pivotal role in environmental sustainability. By diverting waste from landfills, recycling conserves natural resources, reduces pollution, and mitigates climate change. This article delves into the common items frequently recycled, highlighting their significance and the benefits they offer.
Paper: The Foundation of Recycling
Paper, a ubiquitous material in our daily lives, is one of the most commonly recycled items. Its recycling process involves collecting used paper, separating it from contaminants, and pulping it into a slurry. This slurry is then cleaned, de-inked, and reformed into new paper products. The benefits of paper recycling are multifaceted:
- Conservation of Trees: Paper production requires significant amounts of wood, a non-renewable resource. Recycling paper reduces the demand for virgin pulp, conserving forests and their vital ecological functions.
- Energy Savings: Manufacturing paper from recycled materials consumes significantly less energy than producing it from raw materials. This translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Reduced Pollution: Paper production generates considerable pollution, including air and water contamination. Recycling minimizes these environmental impacts by reducing the need for new paper production.
Aluminum: A Metal with a Second Life
Aluminum, a lightweight and versatile metal, is another widely recycled material. Its recycling process involves melting down used aluminum products and casting them into new forms. This process is highly efficient, requiring only a fraction of the energy needed to produce aluminum from raw ore. The benefits of aluminum recycling are notable:
- Resource Conservation: Aluminum is a finite resource, and its mining and extraction processes have significant environmental consequences. Recycling aluminum conserves this valuable resource.
- Energy Efficiency: Recycling aluminum requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce it from raw materials. This energy savings translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a cleaner environment.
- Reduced Landfill Space: Aluminum is a durable material that takes a long time to decompose in landfills. Recycling it reduces the amount of aluminum waste that ends up in landfills, preserving valuable space.
Glass: A Material with Infinite Recyclability
Glass, a non-biodegradable material, is highly recyclable and can be processed endlessly. The recycling process involves separating glass by color, crushing it into cullet, and melting it down to create new glass products. The benefits of glass recycling are significant:
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Glass production requires substantial amounts of sand, soda ash, and limestone, which are finite resources. Recycling glass reduces the demand for these materials, preserving them for future generations.
- Energy Savings: Recycling glass requires significantly less energy than producing it from raw materials. This energy savings contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
- Reduced Pollution: Glass production releases harmful pollutants into the air and water. Recycling glass minimizes these environmental impacts by reducing the need for new glass production.
Plastic: A Complex Recycling Challenge
Plastic, a versatile and widely used material, presents unique challenges for recycling. Not all types of plastic are recyclable, and the recycling process can be complex and energy-intensive. However, recycling plastic offers significant benefits:
- Resource Conservation: Plastic production relies on fossil fuels, a non-renewable resource. Recycling plastic reduces the demand for virgin plastic, conserving these resources.
- Reduced Landfill Space: Plastic is a durable material that takes hundreds of years to decompose in landfills. Recycling plastic reduces the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills, preserving valuable space.
- Reduced Pollution: Plastic production and disposal contribute to environmental pollution. Recycling plastic minimizes these impacts by reducing the need for new plastic production.
The Importance of Recycling: A Collective Effort
Recycling is not just a personal choice; it is a collective responsibility. By embracing sustainable practices and participating in recycling programs, individuals can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. The benefits of recycling extend beyond environmental protection; they also contribute to economic growth and social well-being.
FAQs about Recycling
1. What types of paper are recyclable?
Most paper products, including newspapers, magazines, office paper, cardboard, and paperboard, are recyclable. However, certain types of paper, such as waxed paper, tissue paper, and paper coated with plastic, are not typically recyclable.
2. How do I prepare my recyclables for collection?
Recyclables should be rinsed clean and emptied of any contents. Paper and cardboard should be flattened to save space. Glass, aluminum, and plastic containers should be sorted by type and color.
3. What happens to my recyclables after they are collected?
Recyclables are transported to sorting facilities where they are separated by type and color. They are then processed into new products, such as paper, aluminum cans, glass bottles, and plastic containers.
4. Why is it important to recycle?
Recycling conserves natural resources, reduces pollution, mitigates climate change, and creates jobs. It is an essential part of a sustainable lifestyle.
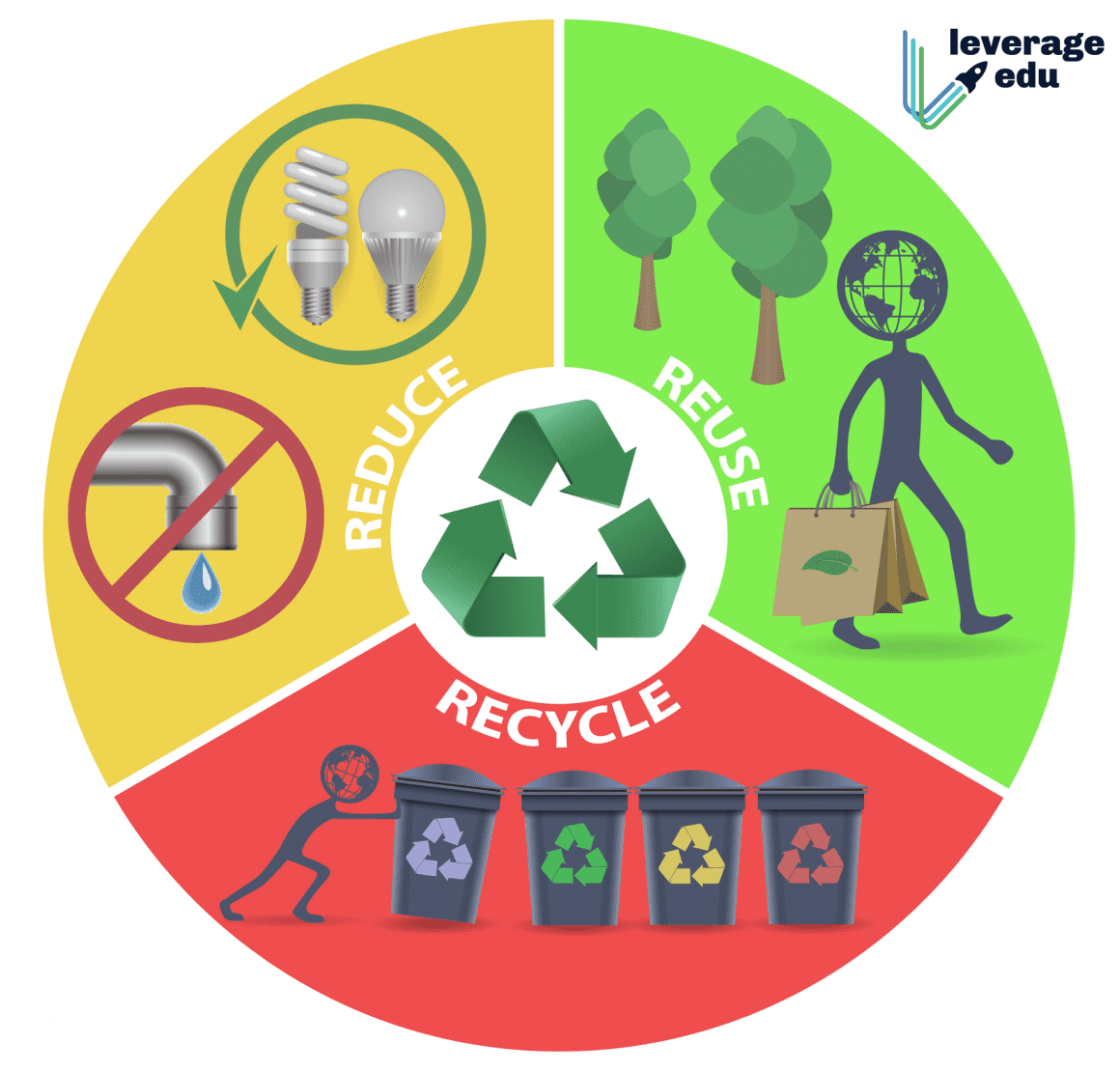
5. What are some tips for reducing waste and increasing recycling?
- Choose reusable products over disposable ones.
- Avoid single-use plastics.
- Compost food scraps and yard waste.
- Reduce packaging by purchasing products in bulk.
- Participate in local recycling programs.
Tips for Effective Recycling
- Separate recyclables from trash. Ensure that only recyclable items are placed in the recycling bin.
- Rinse and empty containers. Remove any food residue or liquid from containers before recycling.
- Flatten cardboard boxes. Flatten cardboard boxes to save space in the recycling bin.
- Remove plastic lids and labels. These items are often not recyclable and should be disposed of separately.
- Recycle glass by color. Separate clear, green, and brown glass containers for proper recycling.
- Check for recycling symbols. Look for the recycling symbol on packaging to determine if it is recyclable.
- Support local recycling programs. Participate in community recycling events and initiatives.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
Recycling is a vital component of a sustainable future. By embracing responsible waste management practices, we can conserve resources, reduce pollution, and create a cleaner and healthier environment for generations to come. It is a collective responsibility that requires the active participation of individuals, communities, and businesses. By adopting a circular economy approach, we can minimize waste, maximize resource utilization, and ensure a more sustainable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Common Recycling Practices: Examining the Impact and Importance of Material Reuse. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!