Lead in the Home: A Silent Threat and its Hidden Sources
Related Articles: Lead in the Home: A Silent Threat and its Hidden Sources
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Lead in the Home: A Silent Threat and its Hidden Sources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Lead in the Home: A Silent Threat and its Hidden Sources
Lead, a heavy metal naturally occurring in the Earth’s crust, has been utilized for centuries due to its malleability, durability, and resistance to corrosion. However, its widespread use has resulted in significant environmental and health concerns, particularly within the domestic sphere. Lead exposure, even at low levels, can pose serious health risks, especially to children and pregnant women. While lead-based paint and plumbing are often associated with lead contamination, the reality is that many other household items can harbor this silent threat. This article aims to illuminate the various sources of lead in the home, highlighting the importance of understanding these potential hazards and adopting preventative measures.
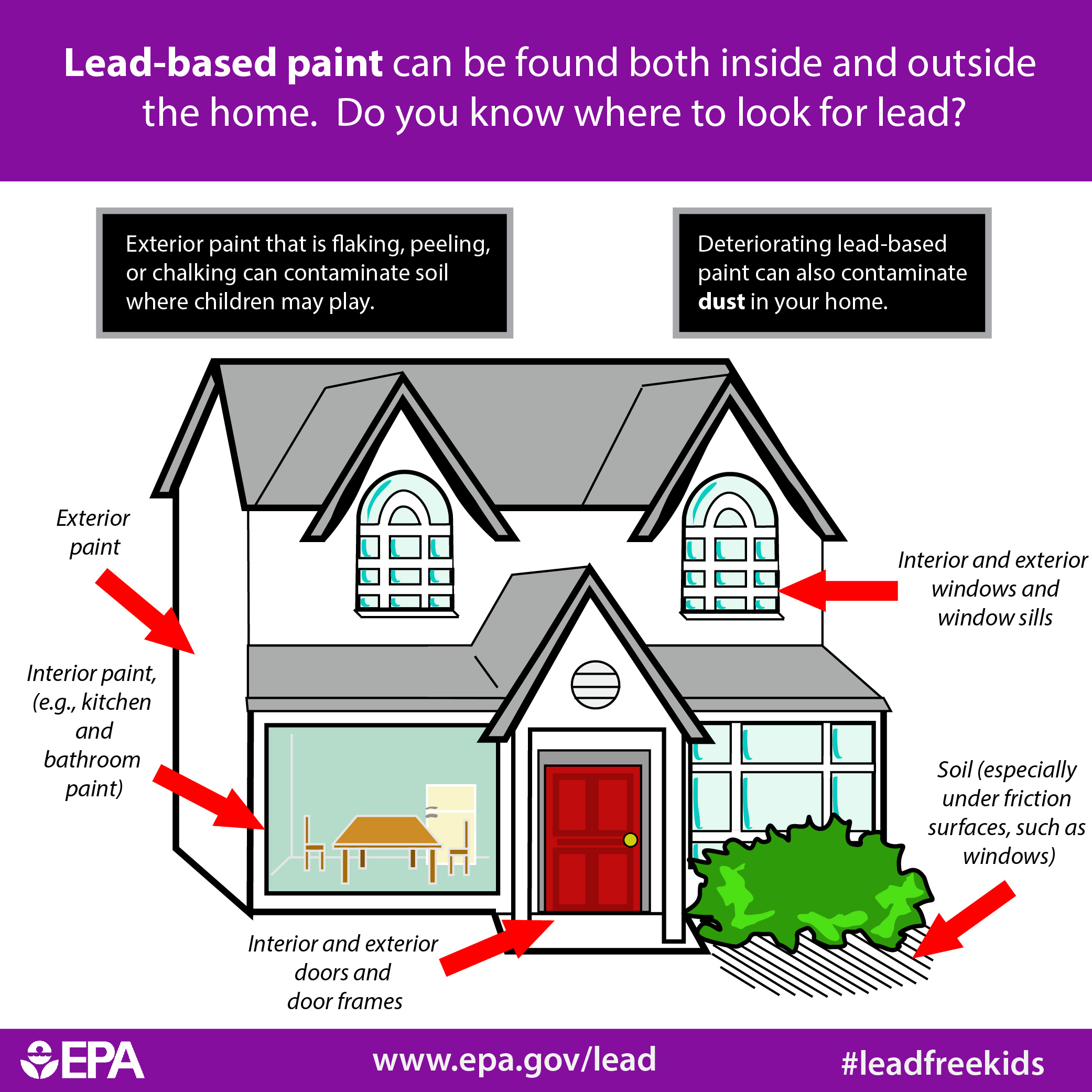
Lead in Paint:
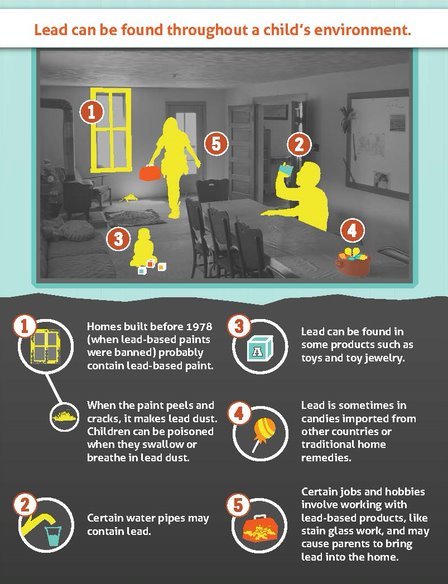
Historically, lead was a common ingredient in paint, offering durability and vibrant colors. This practice, prevalent until the 1970s, has left a legacy of lead-based paint in countless homes. Homes built before 1978, especially those in older neighborhoods, are most likely to contain lead paint.
Lead in Plumbing:
Lead pipes, once the standard for water delivery systems, have been phased out in many areas. However, older homes may still possess lead pipes or fittings. Lead can leach into drinking water, particularly if the water is acidic or corrosive.
Lead in Toys and Jewelry:
While stricter regulations have been implemented, some toys and jewelry, particularly those manufactured in countries with less stringent safety standards, may contain lead. Lead can be found in the paint, plastic, and even the metal components of these items.
Lead in Ceramics and Pottery:
Lead glazes were commonly used on ceramics and pottery to achieve a glossy finish. However, lead can leach into food or beverages if the glaze is not properly applied or if the ceramic ware is damaged.
Lead in Electronics:
Lead is used in the manufacturing of electronics, including televisions, computers, and cell phones. While the concentration of lead in these devices is typically low, improper disposal or recycling can release lead into the environment.
Lead in Soil and Dust:
Lead can accumulate in soil and dust from various sources, including lead-based paint, automotive exhaust, and industrial emissions. Children are particularly susceptible to lead exposure through soil and dust, as they often play outdoors and put their hands and toys in their mouths.
Lead in Food:
While lead contamination in food is generally low, some foods, such as canned goods, may contain trace amounts of lead due to leaching from the can lining.
Identifying Potential Lead Hazards:
Recognizing potential lead hazards in the home is crucial for protecting health. Here are some key indicators:
- Homes built before 1978: These homes are more likely to contain lead-based paint.
- Chipped or peeling paint: This can release lead dust into the air.
- Old plumbing fixtures: Lead pipes or fittings can contaminate drinking water.
- Toys and jewelry: Check for labels indicating lead-free materials.
- Ceramics and pottery: Avoid using chipped or cracked ceramics.
- Outdoor play areas: Test the soil for lead levels if the area is near a busy road or industrial site.
Health Risks of Lead Exposure:
Lead exposure, even at low levels, can have detrimental effects on health, particularly in children.
- Children: Lead can impair brain development, affecting learning abilities, behavior, and attention span. It can also cause hearing loss, anemia, and developmental delays.
- Adults: Lead exposure can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and reproductive problems.
Mitigating Lead Exposure:
Several strategies can help reduce lead exposure in the home:
- Testing: Have your home tested for lead paint and water.
- Renovation: If lead paint is present, hire a certified lead-safe renovator.
- Dust control: Regularly clean surfaces with a damp cloth to remove lead dust.
- Water filtration: Install a certified lead-removing filter on your tap.
- Food choices: Select canned goods with BPA-free linings.
- Recycling: Properly recycle electronics to prevent lead from entering the environment.
FAQs about Lead in the Home:
Q: What are the signs of lead poisoning?
A: Symptoms of lead poisoning can include fatigue, headaches, irritability, abdominal pain, and constipation. In children, lead poisoning can also lead to developmental delays, learning difficulties, and behavioral problems.
Q: How is lead poisoning diagnosed?
A: Lead poisoning is diagnosed through a blood test.
Q: What should I do if I suspect lead poisoning?
A: If you suspect lead poisoning, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Q: How can I prevent lead poisoning in my home?
A: Follow the recommendations outlined in the "Mitigating Lead Exposure" section above.
Tips for Reducing Lead Exposure:
- Regularly clean surfaces with a damp cloth.
- Keep toys and other items that children put in their mouths clean.
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after playing outdoors.
- Don’t allow children to eat or drink from chipped or cracked ceramics.
- Avoid using lead-based paint in your home.
Conclusion:
Lead exposure in the home poses a significant health risk, especially to children. Understanding the potential sources of lead, recognizing warning signs, and implementing preventative measures are crucial for protecting families from this silent threat. By being informed and proactive, individuals can minimize lead exposure and ensure a healthier environment for themselves and their loved ones.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Lead in the Home: A Silent Threat and its Hidden Sources. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!