Shielding From The Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide To Radiation Protection
Shielding from the Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide to Radiation Protection
Related Articles: Shielding from the Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide to Radiation Protection
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shielding from the Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide to Radiation Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shielding from the Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide to Radiation Protection

Radiation, an omnipresent force in the universe, can be both beneficial and harmful. While it powers medical imaging and fuels nuclear power plants, exposure to high levels of radiation can have detrimental effects on human health. Understanding how to shield ourselves from its potential hazards is crucial for safeguarding well-being.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various materials and strategies employed to block radiation, exploring their mechanisms and applications.
Types of Radiation and Their Shielding Mechanisms
Radiation encompasses a broad spectrum of energy, classified based on its origin and properties. Understanding these categories is fundamental to comprehending the effectiveness of different shielding materials:
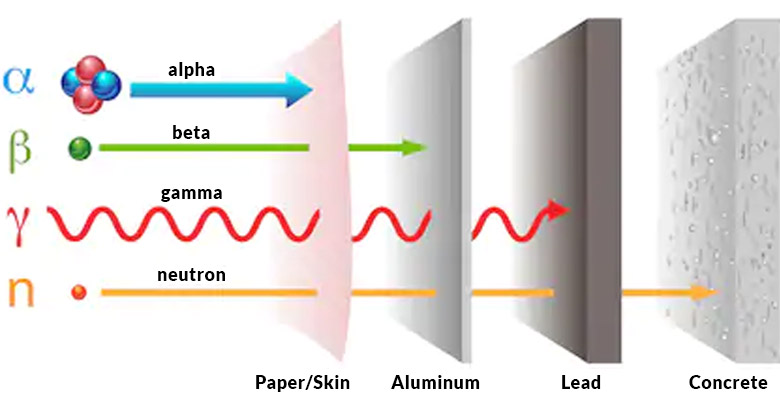
- Alpha Radiation: Consisting of helium nuclei, alpha particles are relatively heavy and possess a short range. A simple sheet of paper or even the outer layer of skin can effectively block them.
- Beta Radiation: Composed of electrons or positrons, beta particles are more penetrating than alpha particles but can be stopped by a thin sheet of metal, such as aluminum or plastic.
- Gamma Radiation: Highly energetic photons, gamma rays are the most penetrating form of radiation. They require thick layers of dense materials like lead, concrete, or water for effective shielding.
- Neutron Radiation: Uncharged particles, neutrons are highly penetrating and require specialized shielding materials like water, polyethylene, or boron.
Materials Employed for Radiation Shielding
The choice of shielding material depends on the type and energy of the radiation being blocked. Common materials used for radiation protection include:
- Lead: Due to its high density and atomic number, lead is a highly effective shield against gamma radiation. It is widely used in medical imaging equipment, nuclear power plants, and research facilities.
- Concrete: Concrete, readily available and relatively inexpensive, offers excellent protection against gamma and neutron radiation. Its effectiveness increases with thickness and density.
- Water: Water’s high hydrogen content makes it an effective shield against neutron radiation. It is commonly used in nuclear reactors and research facilities.
- Steel: Steel, while less effective than lead or concrete, provides reasonable protection against gamma and beta radiation. It is often used in industrial applications and for shielding medical equipment.
- Polyethylene: This material, containing high levels of hydrogen, is effective in slowing down neutrons. It is commonly used in combination with other materials for neutron shielding.
- Boron: Boron effectively absorbs neutrons, making it a valuable component in shielding materials. It is often incorporated into polyethylene or other materials to enhance neutron absorption.
Shielding Strategies and Applications
The application of shielding materials depends on the specific radiation source and its intended use.
- Medical Applications: Lead aprons and thyroid shields are essential for protecting healthcare workers and patients during medical procedures involving X-rays, gamma rays, and other forms of radiation.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Thick concrete walls and steel casings surround the reactor core, preventing the escape of radiation into the environment.
- Research Facilities: Shielding materials are used to protect researchers and the surrounding environment from radiation emitted during experiments.
- Space Exploration: Astronauts rely on specialized shielding materials to protect them from cosmic radiation during space missions.
- Industrial Applications: Shielding is crucial in industries involving radioactive materials, such as mining, manufacturing, and waste management.
Factors Influencing Shielding Effectiveness
The effectiveness of radiation shielding is influenced by several factors:
- Type of Radiation: Different radiation types require different shielding materials. Alpha radiation is easily blocked by a thin layer of material, while gamma radiation requires thicker, denser materials.
- Energy of Radiation: Higher energy radiation requires thicker and denser shielding materials.
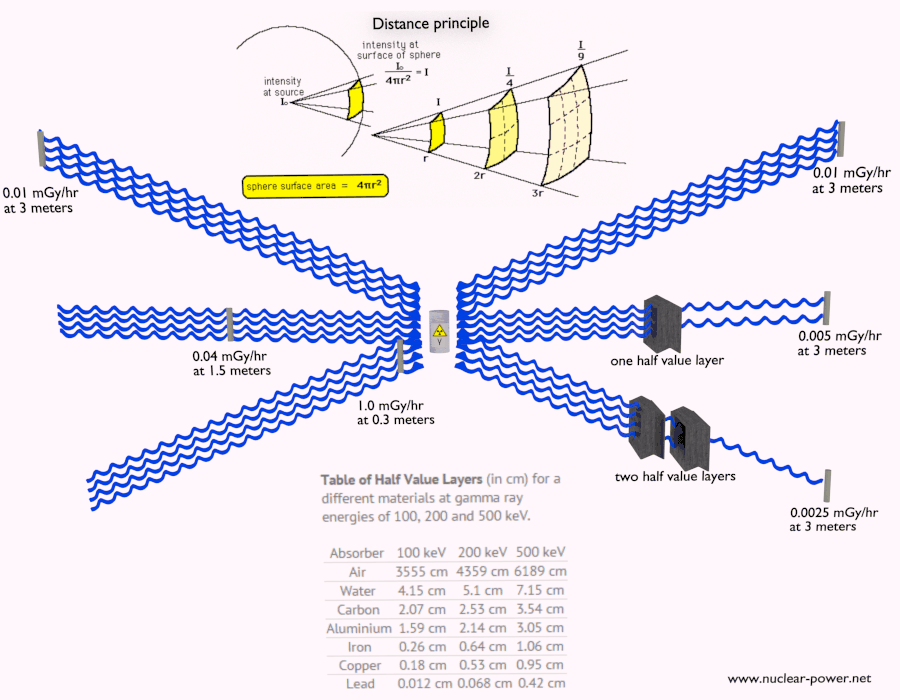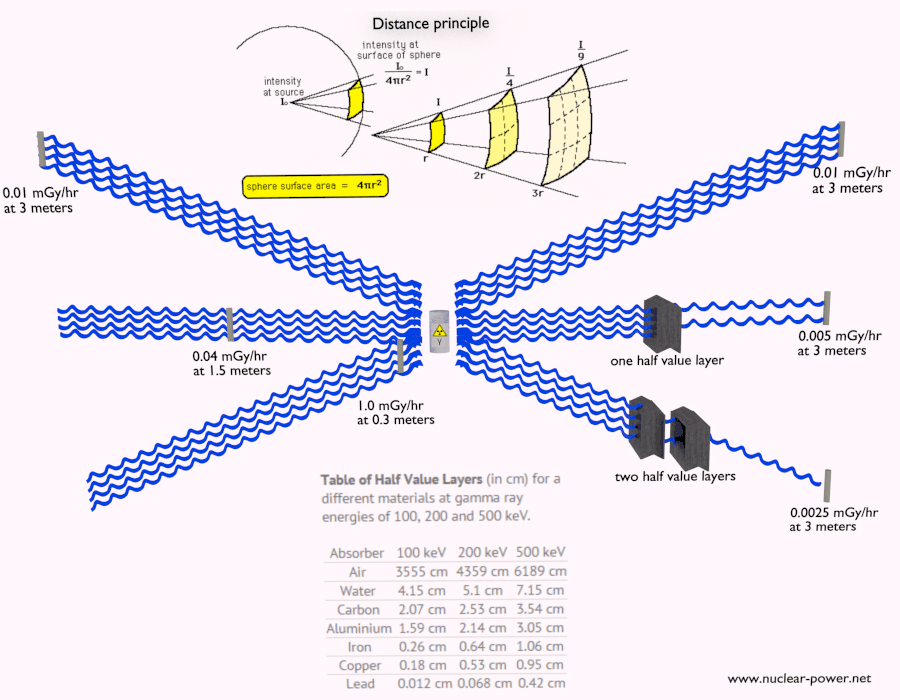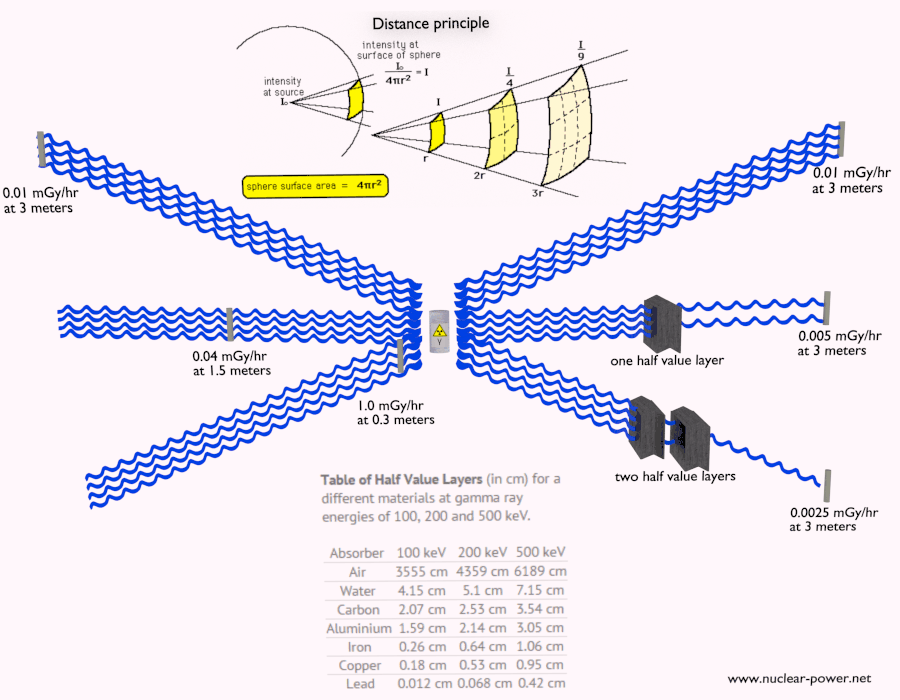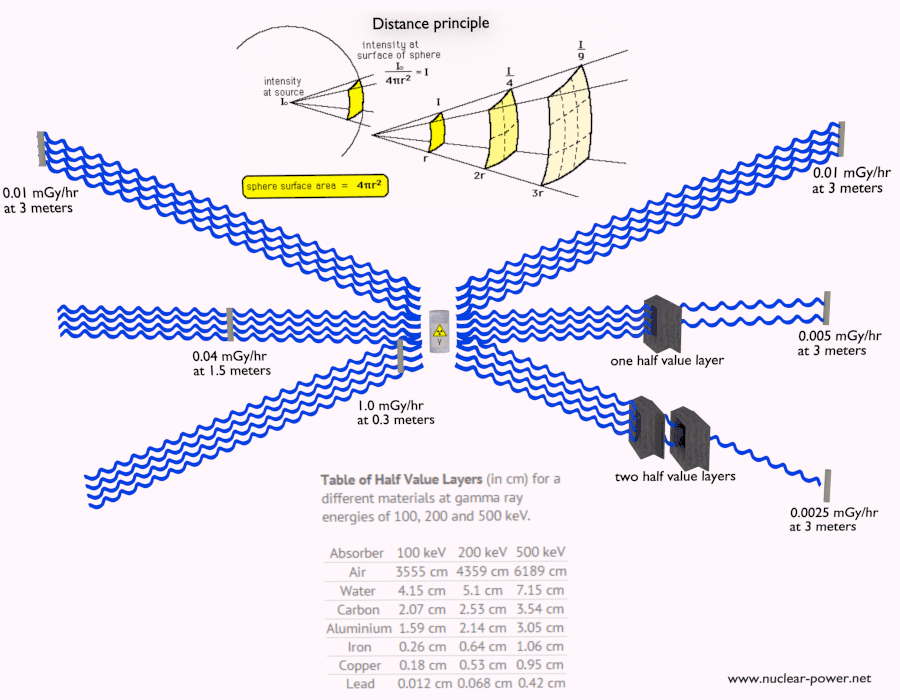
- Distance from Source: The intensity of radiation decreases rapidly with distance from the source. Increasing the distance between the source and the shielded area significantly reduces radiation exposure.
- Time of Exposure: The longer the exposure time, the greater the cumulative radiation dose. Limiting exposure time is crucial for minimizing radiation risks.
FAQs about Radiation Shielding
Q: Is it possible to block all radiation?
A: It is impossible to completely block all radiation. However, appropriate shielding materials can effectively reduce radiation exposure to safe levels.
Q: What is the most effective shielding material?
A: The most effective material depends on the type and energy of the radiation being shielded. Lead is highly effective against gamma radiation, while water is a good shield against neutrons.
Q: Can I use household materials for radiation shielding?
A: While some household materials like concrete or lead can offer some protection, it is not recommended to rely on them for radiation shielding. Consult with experts for proper shielding solutions.
Q: Is it safe to be near a cell phone?
A: Cell phones emit low levels of electromagnetic radiation, which are far lower than those associated with medical imaging or nuclear power plants. The radiation levels from cell phones are generally considered safe.
Q: How can I protect myself from radiation in everyday life?
A: Minimize exposure to sources of radiation like X-rays and sun exposure. Use sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors. Follow safety guidelines when working with radioactive materials.
Tips for Radiation Protection
- Limit exposure time: Minimize the duration of exposure to radiation sources.
- Increase distance: Stay as far away from radiation sources as possible.
- Use shielding materials: Employ appropriate shielding materials based on the type and energy of the radiation.
- Follow safety guidelines: Adhere to safety protocols when working with radioactive materials or undergoing medical procedures involving radiation.
Conclusion
Radiation shielding is an essential aspect of protecting human health and the environment from the potential hazards of radiation. By understanding the different types of radiation, their shielding mechanisms, and the factors influencing shielding effectiveness, individuals and organizations can take appropriate measures to ensure safety and minimize exposure to radiation. While complete elimination of radiation is impossible, effective shielding strategies can significantly reduce exposure levels and mitigate potential risks. By prioritizing safety and implementing appropriate measures, we can harness the benefits of radiation while safeguarding ourselves from its potential dangers.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shielding from the Invisible: A Comprehensive Guide to Radiation Protection. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!