The 1800s: A Century of Transformation
Related Articles: The 1800s: A Century of Transformation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The 1800s: A Century of Transformation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The 1800s: A Century of Transformation
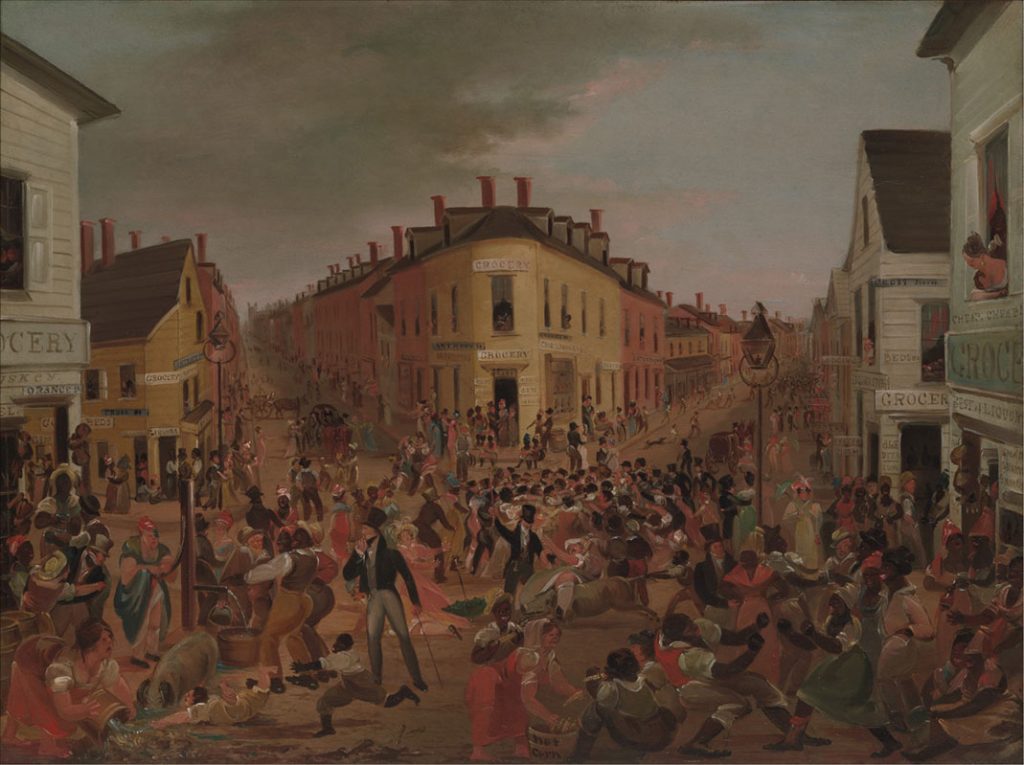
The 19th century, or the 1800s, witnessed a period of unprecedented change and upheaval across the globe. This era, often referred to as the "Age of Revolution," saw the rise of industrialization, the emergence of new ideologies, and the reshaping of political landscapes. While the 1800s were marked by significant challenges and conflicts, they also laid the foundation for the modern world we know today.
Industrial Revolution and Technological Advancements:
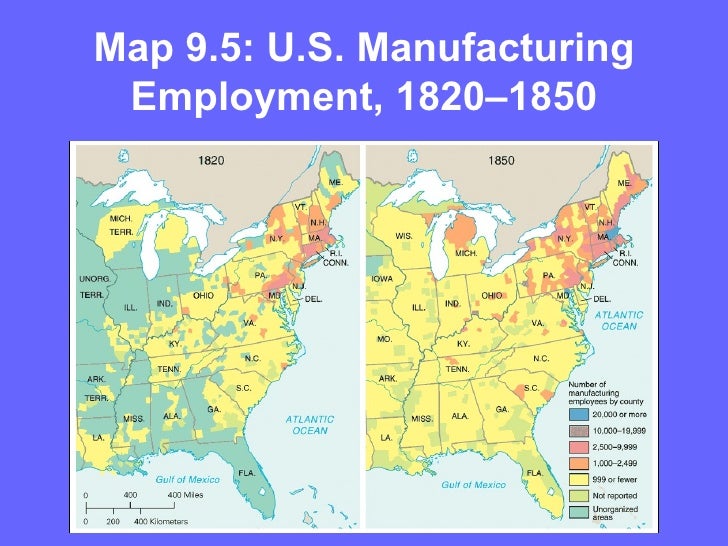
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, gained momentum in the 1800s. This period witnessed the invention and widespread adoption of new technologies that dramatically transformed production methods, transportation, and communication.
- Steam Power: The invention of the steam engine by James Watt in the late 18th century revolutionized power generation. It powered factories, mills, and steamboats, driving industrial growth and enabling the mass production of goods.
- Textile Industry: The invention of the spinning jenny and power loom in the 18th century led to the mechanization of textile production, increasing efficiency and output. This fueled the growth of factories and the rise of industrial cities.
- Railways: The development of steam-powered locomotives in the early 19th century revolutionized transportation. Railways connected cities and regions, facilitating trade, travel, and the movement of goods.
- Telegraph: The invention of the electric telegraph in the 1830s enabled instant communication over long distances. This technology transformed business, government, and personal communication, creating a more interconnected world.
Social and Political Transformations:
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on society, leading to significant social and political changes.
- Urbanization: The rise of factories and industries attracted workers to urban centers, leading to rapid population growth and the emergence of industrial cities. This urbanization brought both opportunities and challenges, including overcrowding, poverty, and social inequality.
- Rise of the Middle Class: The Industrial Revolution created a new class of skilled workers and entrepreneurs, who enjoyed a higher standard of living than the traditional working class. This emergence of a middle class led to changes in social structures and values.
- Nationalism: The 1800s saw the rise of nationalism, a feeling of shared identity and pride among people within a nation. This led to the unification of several nations, such as Italy and Germany, and fueled various independence movements.
- Liberalism and Democracy: The Enlightenment ideas of individual liberty, equality, and democratic principles gained traction in the 1800s. This led to calls for political reforms and the establishment of democratic institutions in many countries.
- Abolition of Slavery: The 1800s witnessed significant movements to abolish slavery, culminating in the emancipation of slaves in the British Empire (1833) and the United States (1865). This movement challenged the existing social order and laid the foundation for greater equality.
Scientific Advancements:
The 1800s were a period of significant scientific progress, with breakthroughs in various fields:
- Biology: Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, published in 1859, revolutionized our understanding of life on Earth. This theory challenged traditional religious beliefs and had a profound impact on the study of biology.
- Chemistry: The development of atomic theory by John Dalton and the discovery of new elements like chlorine and iodine contributed to the advancement of chemistry. This led to the development of new materials and processes, impacting various industries.
- Medicine: The 1800s saw improvements in medical practices, including the development of anesthesia, the use of antiseptics, and the understanding of disease transmission. These advancements improved public health and reduced mortality rates.
- Astronomy: The discovery of Neptune in 1846 and the development of new telescopes expanded our understanding of the solar system and the universe.
Cultural and Artistic Movements:
The 1800s were a dynamic period in art, literature, and music, with the emergence of various movements:
- Romanticism: This artistic movement emphasized emotion, imagination, and individualism. Romanticism was reflected in literature, poetry, painting, and music, with prominent figures like William Wordsworth, Percy Shelley, and Ludwig van Beethoven.
- Realism: This movement focused on depicting everyday life and social issues in a realistic and objective manner. Realism emerged in literature, painting, and sculpture, with key figures like Gustave Courbet, Honoré de Balzac, and Charles Dickens.
- Impressionism: This artistic movement emerged in the late 19th century, characterized by its focus on capturing the fleeting effects of light and color. Impressionism revolutionized painting techniques, with prominent artists like Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Edgar Degas.
Challenges and Conflicts:
The 1800s were not without their challenges and conflicts:
- Industrialization and its Discontents: While industrialization brought economic growth, it also created social problems like poverty, inequality, and pollution. This led to labor unrest and the rise of socialist movements.
- Imperialism: European powers expanded their empires, colonizing vast territories in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. This led to exploitation, conflict, and the displacement of indigenous populations.
- Wars and Revolutions: The 1800s witnessed numerous wars and revolutions, including the Napoleonic Wars, the American Civil War, and the revolutions of 1848. These conflicts resulted in significant loss of life and political instability.
Legacy of the 1800s:
The 1800s were a transformative century that shaped the world we live in today. The Industrial Revolution, scientific advancements, and social and political changes laid the foundation for modern society, technology, and globalization. The challenges and conflicts of the era also serve as reminders of the need for social justice, equality, and peaceful coexistence.
FAQs
What were the key inventions of the 1800s?
The 1800s saw numerous significant inventions, including the steam engine, the spinning jenny, the power loom, the steam locomotive, the telegraph, and the internal combustion engine. These inventions revolutionized production, transportation, communication, and energy generation, driving industrial growth and transforming society.
What were the major social changes in the 1800s?
The 1800s witnessed significant social changes, including urbanization, the rise of a middle class, the emergence of new social movements, and the abolition of slavery. These changes led to a shift in social structures, values, and power dynamics.
What were the major political changes in the 1800s?
The 1800s saw the rise of nationalism, liberalism, and democracy, leading to the unification of nations, the establishment of democratic institutions, and the expansion of suffrage. These political changes challenged traditional power structures and paved the way for greater political participation.
What were the major scientific advancements of the 1800s?
The 1800s witnessed significant scientific advancements, including Darwin’s theory of evolution, the development of atomic theory, improvements in medical practices, and breakthroughs in astronomy. These advancements revolutionized our understanding of life, matter, and the universe.
What were the major artistic movements of the 1800s?
The 1800s saw the emergence of various artistic movements, including Romanticism, Realism, and Impressionism. These movements reflected the changing social and cultural landscape, influencing literature, poetry, painting, sculpture, and music.
Tips for Studying the 1800s:
- Focus on key themes: Understand the major themes of the 1800s, such as industrialization, urbanization, nationalism, liberalism, and scientific advancements.
- Explore primary sources: Examine firsthand accounts, diaries, letters, and historical documents to gain a deeper understanding of the period.
- Connect events and movements: Analyze how different events and movements influenced each other, creating a holistic understanding of the era.
- Consider global perspectives: Recognize that the 1800s were a period of global change, and explore the experiences of different regions and cultures.
Conclusion:
The 1800s were a period of profound change and transformation, shaping the world we live in today. The Industrial Revolution, scientific advancements, social and political movements, and cultural innovations of this era left an enduring legacy. By understanding the complexities of this period, we can gain valuable insights into the forces that have shaped modern society and the challenges we face today.
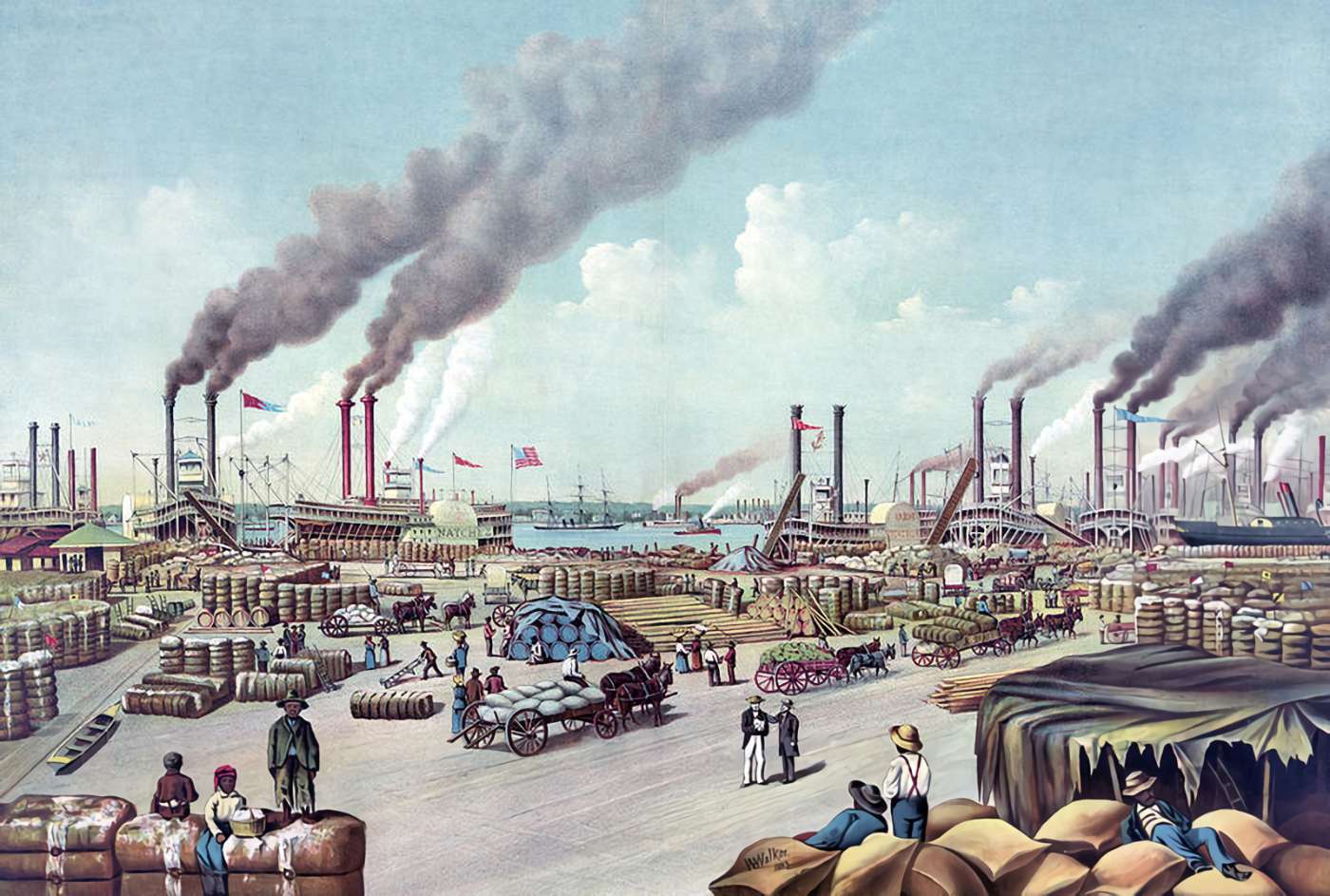



/GettyImages-951229926-5b0291908023b90036f8cf3c.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The 1800s: A Century of Transformation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!