The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding Antimicrobial Agents
Related Articles: The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding Antimicrobial Agents
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding Antimicrobial Agents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding Antimicrobial Agents
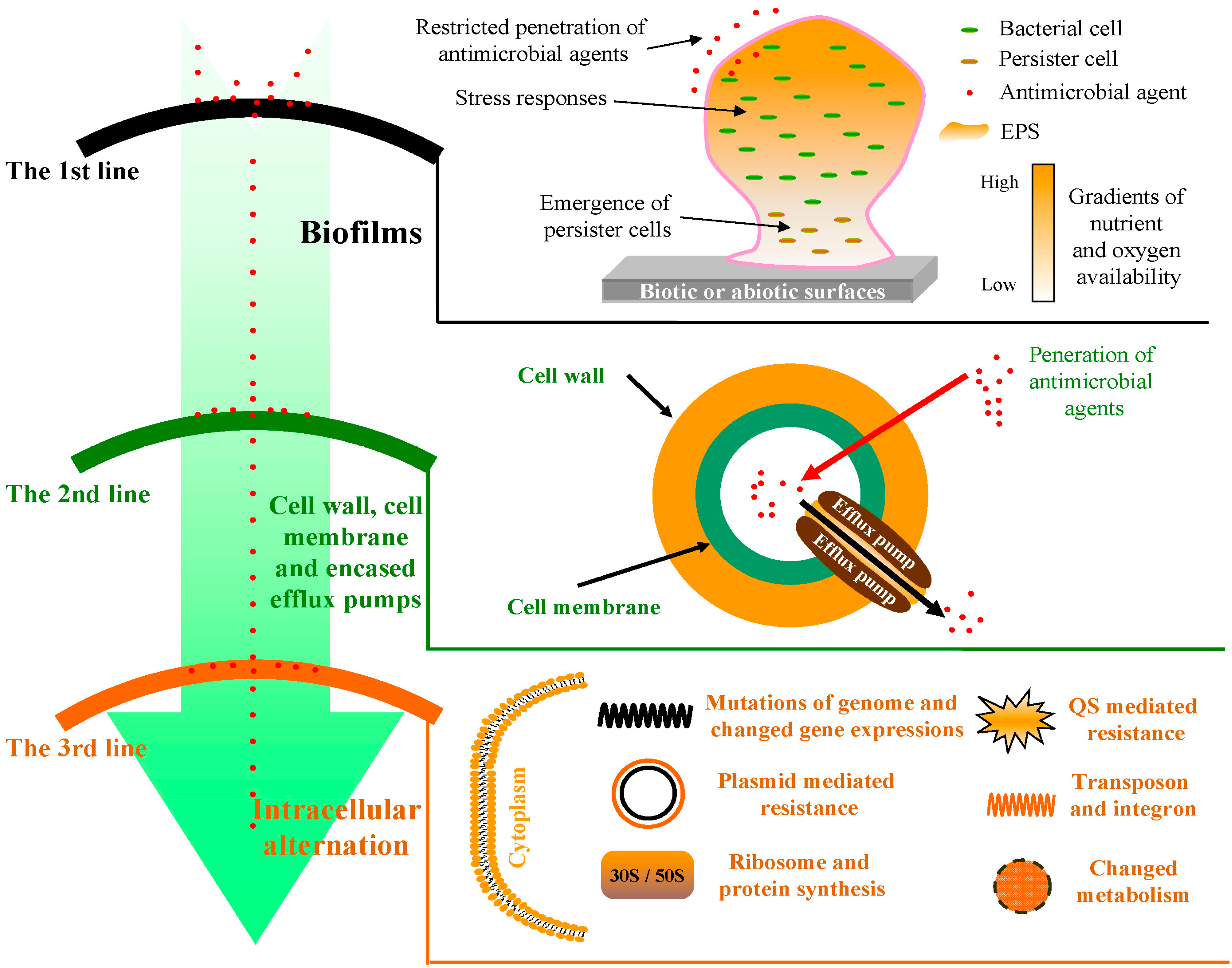
The human body exists in a constant state of equilibrium with a diverse population of microorganisms. While many of these microbes are beneficial, some pose a significant threat to our health. Bacteria, single-celled prokaryotic organisms, are among the most common and versatile of these pathogens. They can cause a wide range of infections, from mild skin irritations to life-threatening illnesses.
To combat these bacterial threats, humankind has relied upon a diverse arsenal of antimicrobial agents. These substances, which encompass a wide spectrum of chemical structures and mechanisms of action, play a critical role in modern medicine and public health.
Antimicrobial Agents: A Diverse Landscape
Antimicrobial agents are broadly classified into two categories:
- Antibiotics: These agents are primarily used to treat bacterial infections. They target specific biochemical pathways or cellular processes essential for bacterial survival.
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants: These substances are used to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms on living tissue (antiseptics) or inanimate objects (disinfectants). They are typically employed for preventing infections and controlling the spread of bacteria.
Understanding the Mechanisms of Action
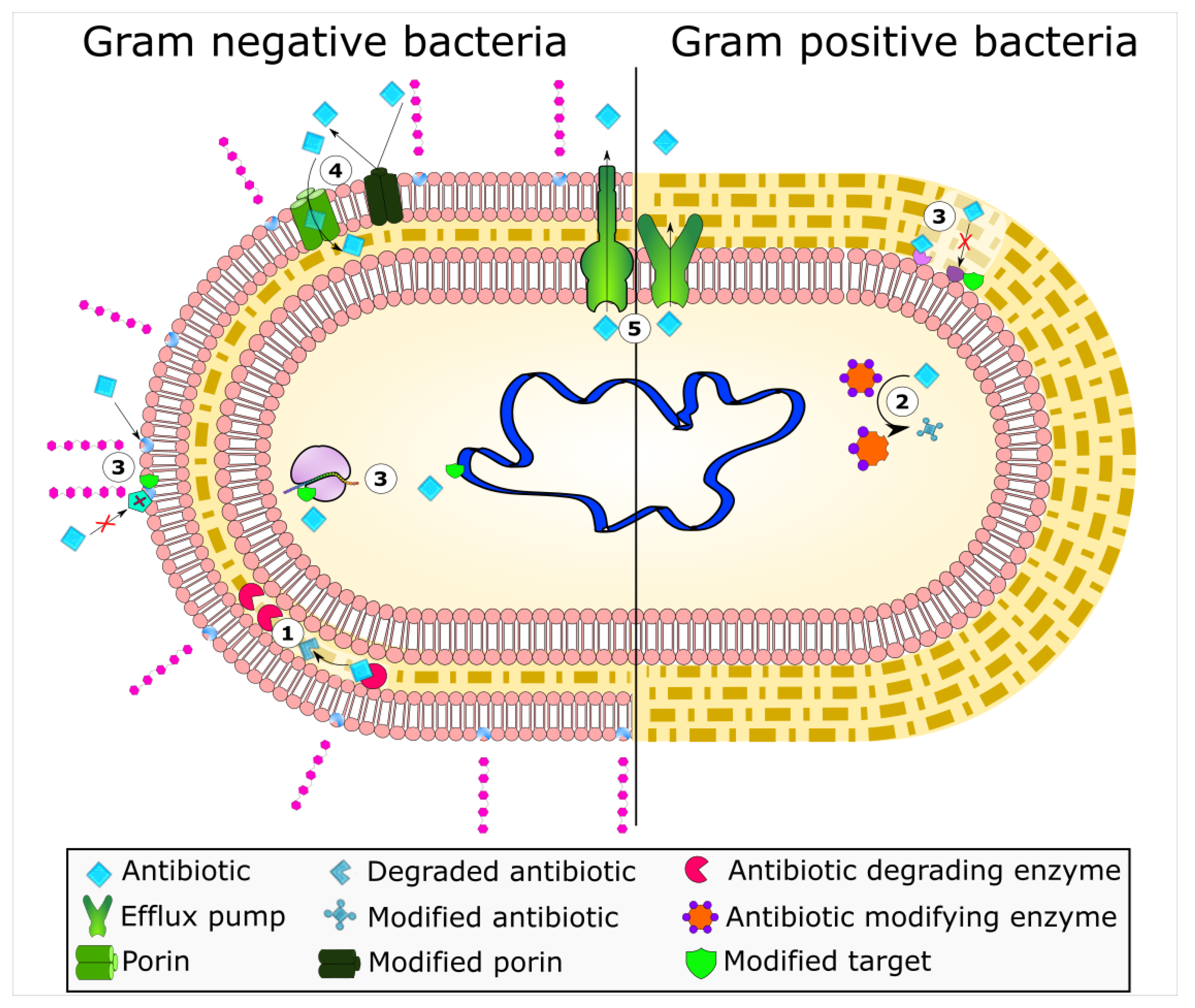
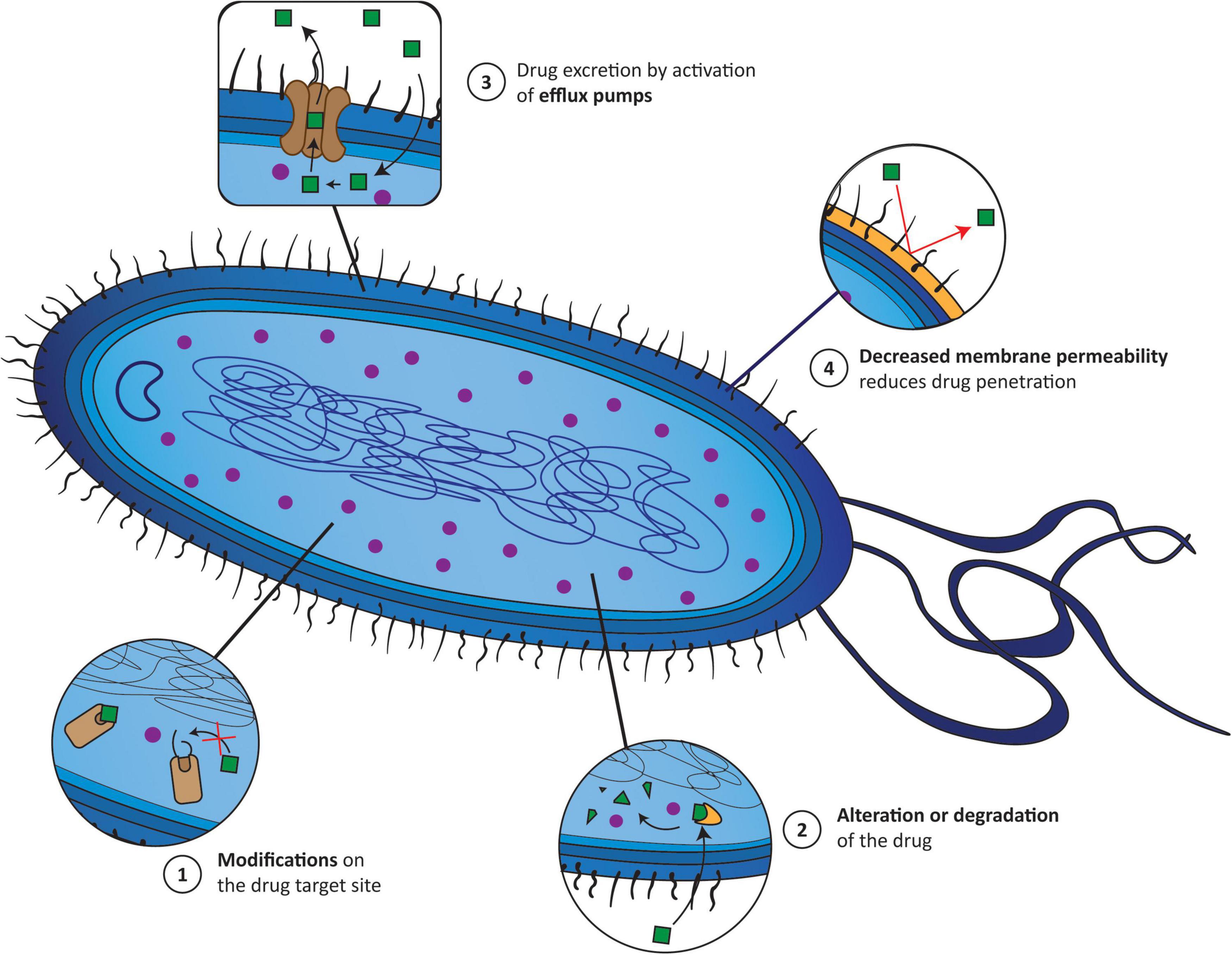
The effectiveness of antimicrobial agents lies in their ability to disrupt essential bacterial processes. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized as follows:
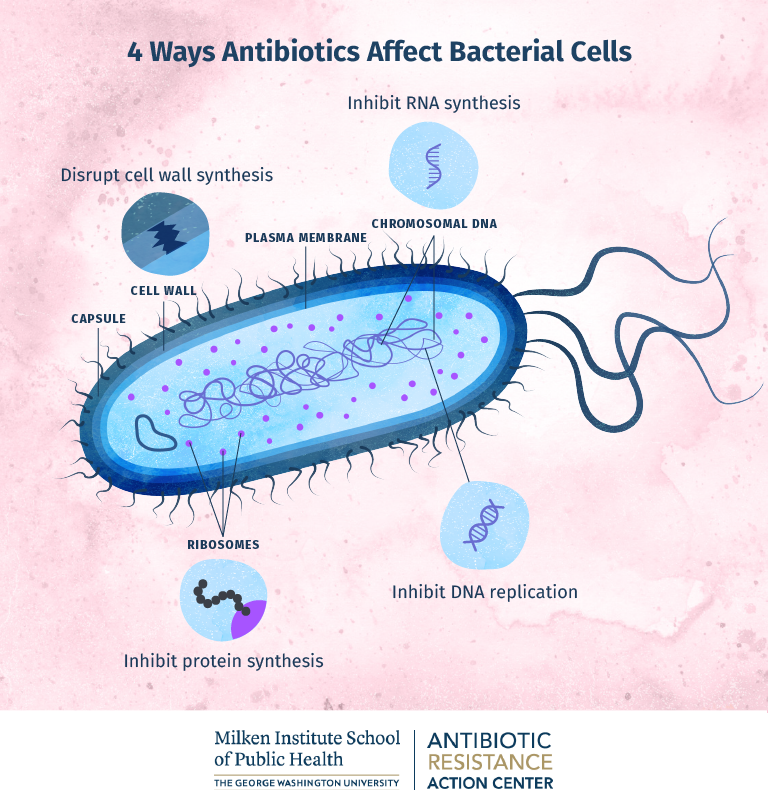
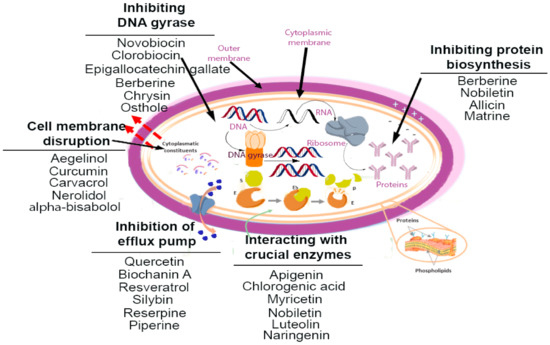
1. Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis:
Bacterial cell walls provide structural integrity and protect the cell from osmotic stress. Many antibiotics, such as penicillin and its derivatives, target enzymes involved in the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a key component of the bacterial cell wall. By inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesis, these antibiotics weaken the cell wall, leading to cell lysis and death.
2. Disruption of Cell Membrane Integrity:
The cell membrane acts as a barrier, regulating the passage of nutrients and waste products. Certain antimicrobial agents, such as polymyxins, disrupt the integrity of the bacterial cell membrane, leading to leakage of cellular contents and ultimately cell death.
3. Interference with Protein Synthesis:
Proteins are essential for all cellular functions. Antibiotics like aminoglycosides and macrolides target bacterial ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis. By interfering with this process, they prevent the bacteria from producing essential proteins, leading to cell death.
4. Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis:
DNA and RNA are the blueprints for cellular function. Antimicrobial agents like quinolones and rifamycins target enzymes involved in DNA replication and RNA transcription. By inhibiting these processes, they prevent bacteria from replicating their genetic material and producing essential proteins, leading to cell death.
5. Inhibition of Metabolic Pathways:
Bacteria require specific metabolic pathways for growth and survival. Sulfonamides, for example, inhibit the synthesis of folic acid, an essential coenzyme for bacterial metabolism. By disrupting these pathways, antimicrobial agents can effectively inhibit bacterial growth.
The Importance of Antimicrobial Agents
The discovery and development of antimicrobial agents have revolutionized healthcare, significantly reducing morbidity and mortality from bacterial infections. These agents are indispensable in treating a wide range of conditions, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and sepsis.
Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Threat
Despite the tremendous success of antimicrobial agents, the emergence of resistance poses a significant challenge. Bacteria can develop resistance mechanisms, such as mutations in target sites or production of enzymes that inactivate the antimicrobial agent. This resistance can render existing treatments ineffective, leading to treatment failures and potentially fatal outcomes.
Strategies for Combating Antimicrobial Resistance
Combating antimicrobial resistance requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Rational Use of Antimicrobials: Prescribing antibiotics only when necessary and completing the full course of treatment are crucial to minimizing the selective pressure that drives resistance development.
- Development of New Antimicrobials: Research and development efforts are ongoing to discover and develop new antimicrobial agents with novel mechanisms of action.
- Infection Prevention and Control Measures: Implementing effective infection control practices, such as hand hygiene and appropriate use of personal protective equipment, can prevent the spread of infections and reduce the need for antimicrobial therapy.
- Public Education: Raising awareness about antimicrobial resistance and the importance of responsible antimicrobial use is essential for promoting behavioral changes that can mitigate the threat.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between an antibiotic and an antiseptic?
Antibiotics are specifically designed to treat bacterial infections within the body. Antiseptics, on the other hand, are used to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms on living tissue.
2. How do antimicrobial agents kill bacteria?
Antimicrobial agents target specific bacterial processes, such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or DNA replication. By disrupting these essential functions, they lead to bacterial death.
3. Can overuse of antimicrobial agents lead to resistance?
Yes, overuse of antimicrobial agents can contribute to the development of resistance. When bacteria are exposed to antimicrobial agents, they can develop mutations that allow them to survive and even thrive in the presence of the drug.
4. What are some strategies for preventing antimicrobial resistance?
Strategies for preventing antimicrobial resistance include responsible use of antibiotics, development of new antimicrobial agents, and implementation of effective infection control practices.
5. What are some examples of commonly used antimicrobial agents?
Commonly used antimicrobial agents include penicillin, amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, and metronidazole.
Tips
- Always consult with a healthcare professional before using any antimicrobial agent.
- Use antimicrobial agents only when necessary and follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment.
- Practice good hygiene habits, such as regular handwashing, to prevent the spread of infections.
- Educate yourself about antimicrobial resistance and its implications.
Conclusion
Antimicrobial agents are essential tools in the fight against bacterial infections. Their discovery has revolutionized healthcare, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions. However, the emergence of antimicrobial resistance poses a significant threat to public health. Combating this challenge requires a concerted effort to promote responsible use of antimicrobials, develop new agents, and implement effective infection control measures. By understanding the mechanisms of action and the importance of these agents, we can work towards ensuring their continued effectiveness in safeguarding human health.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding Antimicrobial Agents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
