The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding The Mechanisms Of Bacterial Eradication
The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding the Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication
Related Articles: The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding the Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding the Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding the Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication
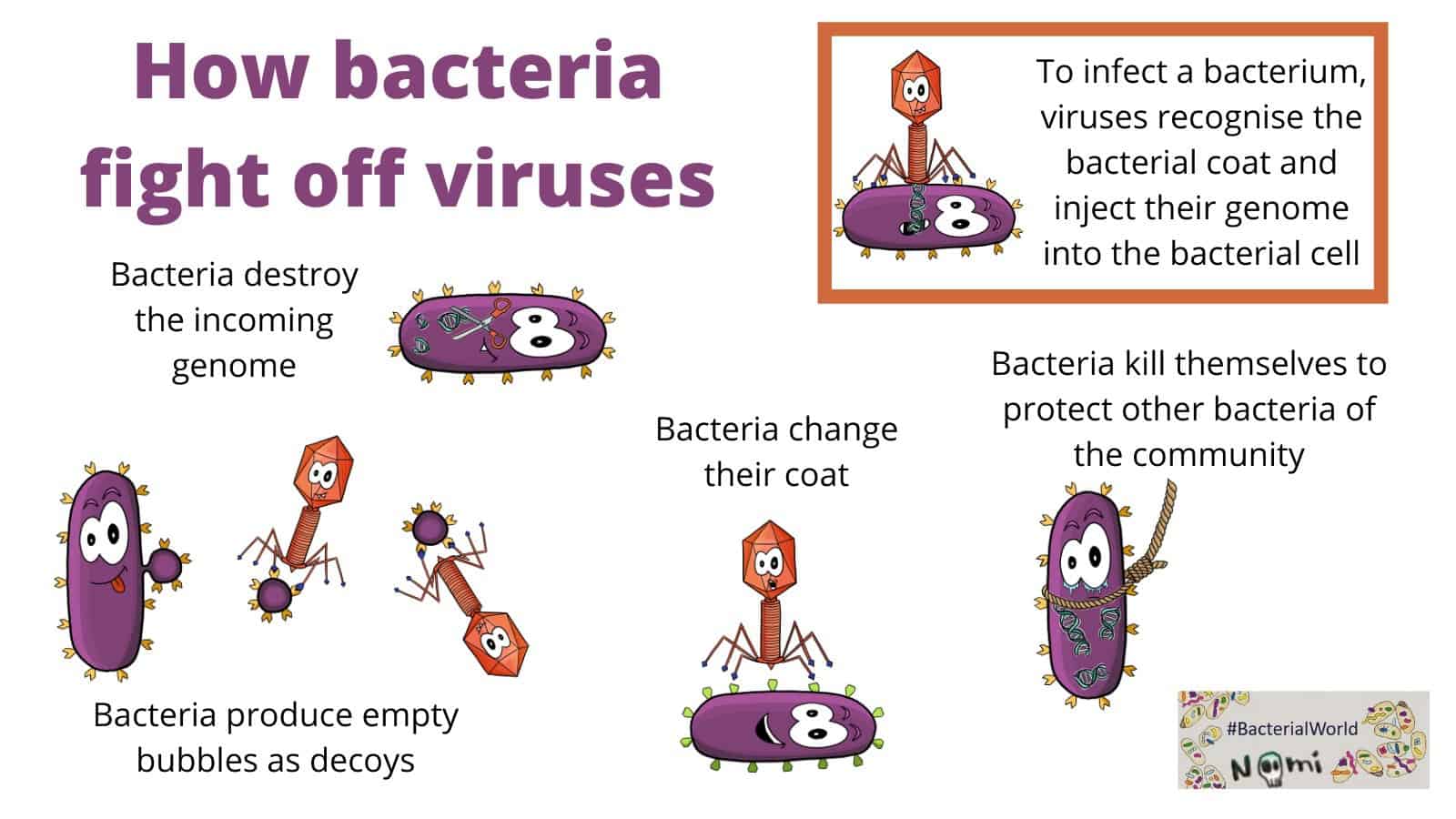
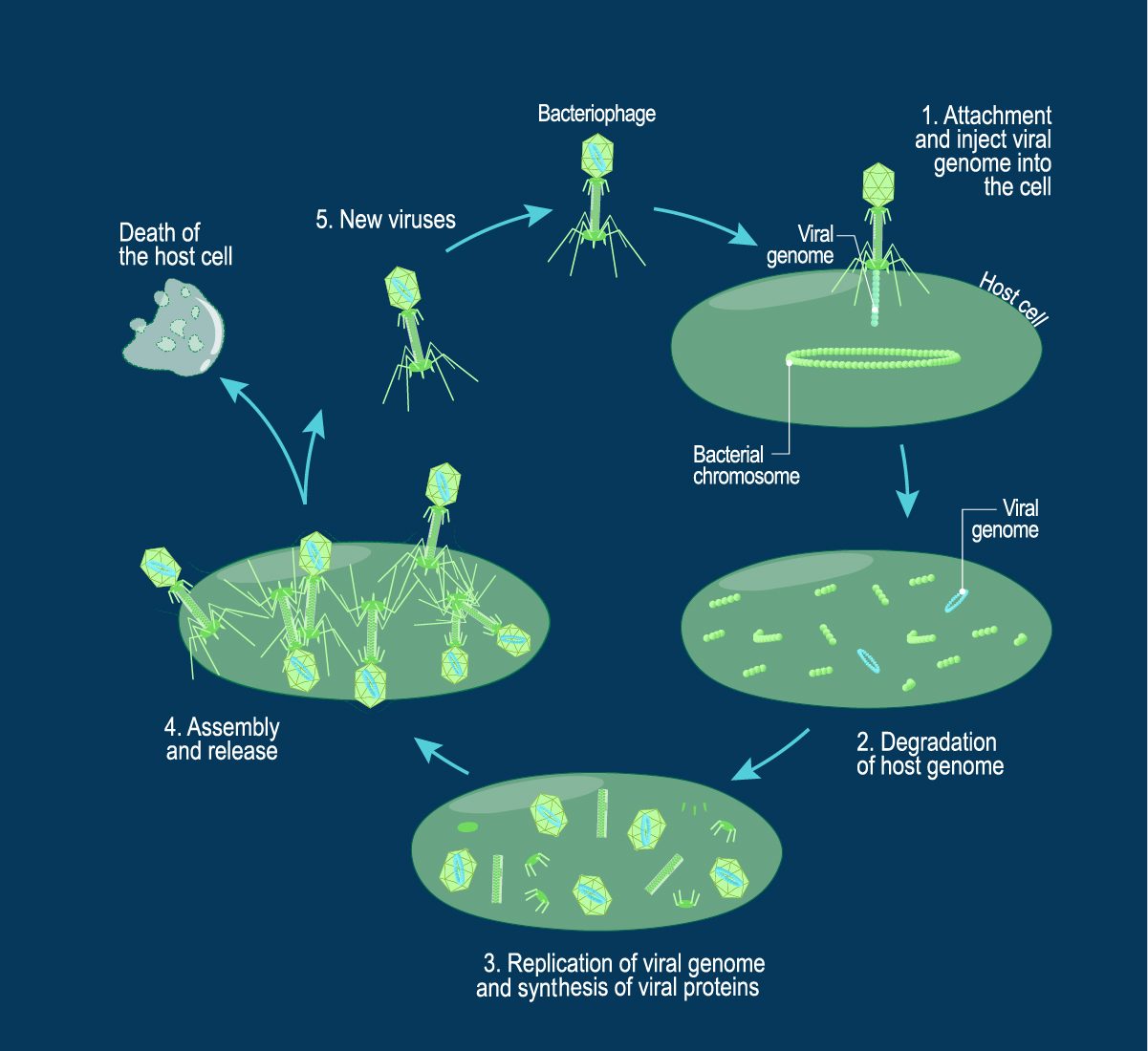
Bacteria, microscopic single-celled organisms, are ubiquitous in our environment. While many are beneficial, others can cause disease, leading to a range of illnesses from mild infections to life-threatening conditions. Understanding the mechanisms by which bacteria are eradicated is crucial for maintaining health and preventing the spread of infectious diseases.
The Importance of Bacterial Eradication
The elimination of harmful bacteria is fundamental to human health. Bacterial infections can lead to various complications, including:
- Inflammatory responses: Bacterial infections trigger the body’s immune system to fight off the invaders, leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling.
- Tissue damage: Some bacteria produce toxins that can damage surrounding tissues, causing organ dysfunction and other complications.
- Spread to other parts of the body: Infections can spread from the initial site of infection to other areas of the body, leading to systemic illness.
- Chronic conditions: Some bacterial infections can become chronic, leading to long-term health problems.
Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication
Several mechanisms can effectively eliminate bacteria, each targeting different aspects of bacterial survival and propagation:
1. Physical Removal:
- Washing hands and surfaces: This simple yet effective method physically removes bacteria from hands and surfaces. Soap and water, along with appropriate handwashing techniques, are crucial for reducing the spread of bacteria.
- Sterilization: This process involves using high heat, chemicals, or radiation to eliminate all microorganisms, including bacteria, from objects and surfaces.
- Filtration: This technique physically separates bacteria from liquids or gases using a porous membrane with pore sizes smaller than the bacteria.
2. Disruption of Bacterial Structures:
- Antibiotics: These drugs target specific bacterial processes, such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or DNA replication, inhibiting bacterial growth and ultimately leading to their demise.
- Antiseptics and disinfectants: These chemicals disrupt bacterial cell membranes or denature essential proteins, leading to bacterial death.
3. Inhibition of Bacterial Metabolism:
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics interfere with bacterial metabolic pathways, preventing the production of essential molecules for growth and survival.
- Bacteriostatic agents: These agents inhibit bacterial growth but do not necessarily kill them.
4. Activation of the Immune System:
- Vaccines: Vaccines introduce weakened or inactivated forms of bacteria into the body, stimulating the immune system to develop antibodies against specific bacterial strains. These antibodies provide long-term protection against future infections.
- Antimicrobial peptides: These naturally occurring peptides produced by the body have broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, directly killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth.
Factors Influencing Bacterial Eradication
The effectiveness of bacterial eradication methods depends on various factors, including:
- Type of bacteria: Different bacteria have varying sensitivities to different eradication methods.
- Environmental conditions: Temperature, pH, and the presence of organic matter can influence the effectiveness of eradication methods.
- Concentration of the eradication agent: Higher concentrations of antibiotics or disinfectants generally lead to faster and more complete bacterial eradication.
- Duration of exposure: Prolonged exposure to eradication agents is often necessary for complete bacterial elimination.
FAQs about Bacterial Eradication
Q: What are the most common methods for killing bacteria?
A: The most common methods include handwashing, sterilization, antibiotics, antiseptics, and disinfectants.
Q: How do antibiotics work to kill bacteria?
A: Antibiotics target specific bacterial processes, such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or DNA replication, inhibiting bacterial growth and ultimately leading to their demise.
Q: Are there any natural ways to kill bacteria?
A: Yes, there are several natural methods, including using essential oils like tea tree oil, garlic, and honey, which possess antimicrobial properties.
Q: Can bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
A: Yes, bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics through mutations that alter their susceptibility to the drug. This is a significant concern in public health, leading to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Q: What are the risks associated with using antibiotics?
A: Antibiotics can have side effects, such as allergic reactions, gastrointestinal problems, and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Tips for Preventing Bacterial Infections
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after using the restroom, before eating, and after touching surfaces that may be contaminated.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces, such as countertops, doorknobs, and phones.
- Cook food thoroughly: Ensure that meat and poultry are cooked to the recommended internal temperature to kill any harmful bacteria.
- Store food properly: Refrigerate perishable foods promptly to prevent bacterial growth.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccinations provide protection against many bacterial infections.
Conclusion
The eradication of harmful bacteria is a critical aspect of maintaining human health. Understanding the various mechanisms by which bacteria can be eliminated, from physical removal to targeted drug therapies, is essential for preventing and treating bacterial infections. By practicing good hygiene, using appropriate eradication methods, and staying informed about the latest developments in bacterial eradication, we can effectively combat these microscopic threats and protect our well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Battle Against Bacteria: Understanding the Mechanisms of Bacterial Eradication. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!