The Body’s Arsenal: Defending Against Harmful Bacteria
Related Articles: The Body’s Arsenal: Defending Against Harmful Bacteria
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Body’s Arsenal: Defending Against Harmful Bacteria. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Body’s Arsenal: Defending Against Harmful Bacteria

The human body is a complex ecosystem, teeming with trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiota. While the vast majority of these microbes are beneficial, a small fraction can cause harm, leading to infections and illness. Fortunately, our bodies possess an intricate defense system that actively combats these harmful bacteria.
The Immune System: Our First Line of Defense
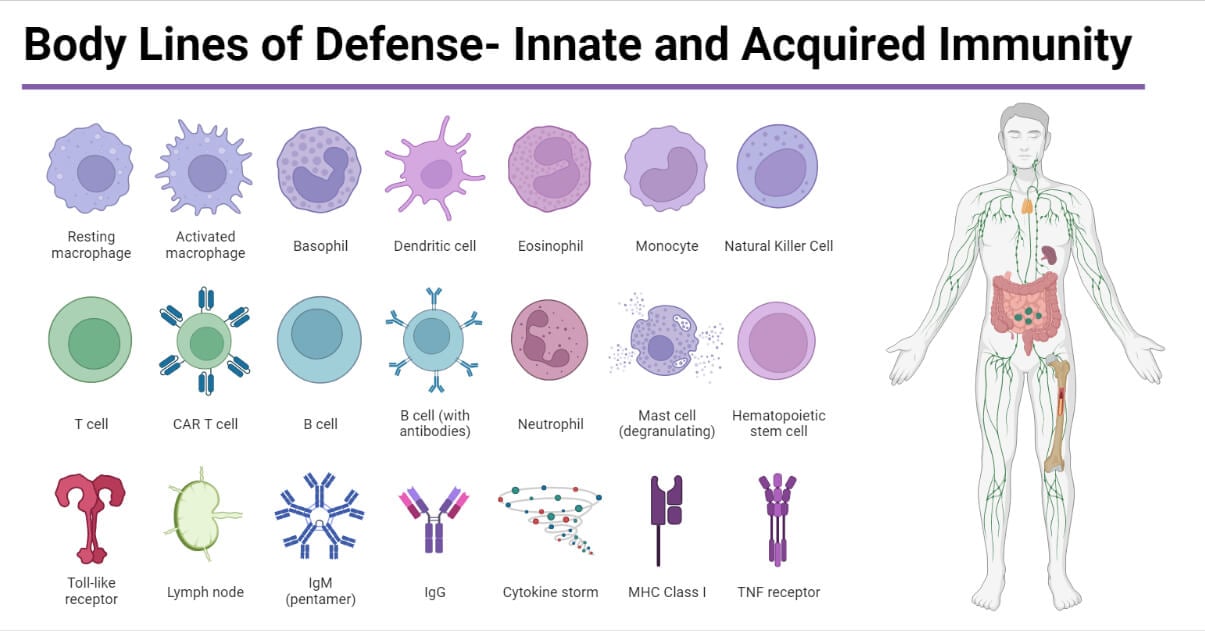
The immune system acts as the body’s vigilant guardian, constantly patrolling for and eliminating invading pathogens. This complex network of cells, tissues, and organs functions through a coordinated series of responses:
- Innate Immunity: This is the body’s immediate, non-specific defense mechanism. It involves physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes that prevent bacterial entry. Specialized cells like macrophages and neutrophils engulf and destroy invading bacteria. Chemical defenses like antimicrobial peptides and enzymes also contribute to this initial fight.
- Adaptive Immunity: This is a more targeted and specific response, developed over time through exposure to pathogens. Lymphocytes, particularly B cells and T cells, play a crucial role in this process. B cells produce antibodies that bind to specific bacterial antigens, neutralizing them or marking them for destruction by other immune cells. T cells directly attack infected cells and stimulate other immune responses.
The Gut Microbiota: A Crucial Ally
The gut microbiota, the collection of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and defending against harmful bacteria.
- Competition for Resources: Beneficial gut bacteria compete with harmful bacteria for nutrients and space, limiting their ability to establish themselves and cause harm.
- Production of Antimicrobials: Some beneficial gut bacteria produce antimicrobial substances that directly inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Immune System Modulation: The gut microbiota interacts with the immune system, influencing its development and function. This interaction helps to maintain a balanced immune response, preventing overreaction to harmless bacteria while effectively targeting harmful ones.
Beyond the Body: External Defenses
While the body’s internal defenses are paramount, external measures can significantly bolster the fight against harmful bacteria:
- Hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water is crucial in preventing the spread of bacteria. Thorough cleaning of surfaces and food preparation areas also contributes to a hygienic environment.
- Antibiotics: These medications are specifically designed to target and kill bacteria. Antibiotics are effective in treating bacterial infections, but their overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance, making infections more difficult to treat.
- Vaccines: Vaccines stimulate the immune system to develop immunity against specific bacteria, preventing future infections.
Factors Influencing Bacterial Survival
The ability of harmful bacteria to survive and cause infection is influenced by various factors:
- Virulence Factors: These are specific characteristics of bacteria that enable them to cause disease. Examples include toxins, capsules that protect them from immune cells, and enzymes that help them invade tissues.
- Host Factors: Factors related to the individual’s health, such as age, immune system function, and underlying medical conditions, can influence susceptibility to bacterial infections.
- Environmental Factors: Factors like temperature, humidity, and the presence of nutrients can affect bacterial growth and survival.
Understanding the Importance of a Balanced Microbiota
Maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiota is crucial for overall health and effective defense against harmful bacteria. Factors that contribute to a healthy microbiota include:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables provides nutrients for beneficial bacteria. Limiting processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can help to prevent the overgrowth of harmful bacteria.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiota, increasing susceptibility to infections. Practicing stress reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness can promote a healthy gut environment.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for immune function and overall health, including the maintenance of a balanced microbiota.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How do I know if I have a bacterial infection?
A: Symptoms of bacterial infections vary depending on the specific bacteria and the site of infection. Common symptoms include fever, pain, redness, swelling, and discharge. If you suspect a bacterial infection, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Q: What are the risks associated with antibiotic resistance?
A: Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop the ability to survive and multiply even in the presence of antibiotics. This makes infections more difficult to treat, increasing the risk of complications, longer hospital stays, and even death.
Q: How can I prevent antibiotic resistance?
A: Antibiotic resistance is a complex issue, but individuals can play a role in preventing it by:
- Only using antibiotics when prescribed by a doctor.
- Taking antibiotics exactly as prescribed, completing the full course even if feeling better.
- Preventing infections by practicing good hygiene.
Tips for Promoting a Healthy Microbiota
- Consume a diverse diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables.
- Limit processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Practice regular exercise.
- Manage stress levels through techniques like meditation, yoga, and mindfulness.
- Get adequate sleep.
- Consider supplementing with probiotics, which contain beneficial bacteria.
Conclusion
The human body possesses a sophisticated defense system that actively combats harmful bacteria. The immune system, the gut microbiota, and external measures like hygiene and antibiotics all contribute to this vital defense. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, stress management, and adequate sleep, is essential for promoting a balanced microbiota and strengthening the body’s defenses. By understanding the mechanisms of bacterial defense and adopting preventive measures, individuals can actively contribute to their overall health and well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Body’s Arsenal: Defending Against Harmful Bacteria. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!