The Chemical Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: The Chemical Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Chemical Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Chemical Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
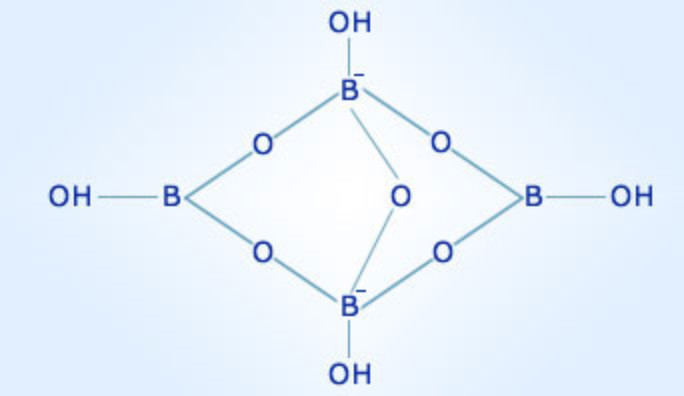
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral, has been utilized for centuries due to its diverse applications. Its chemical composition, a combination of boron, oxygen, and sodium, gives rise to its unique properties and makes it a valuable resource in various industries. This article delves into the intricate structure of borax, exploring its constituent elements and the chemical bonds that contribute to its remarkable characteristics.
Understanding the Building Blocks: Boron, Oxygen, and Sodium
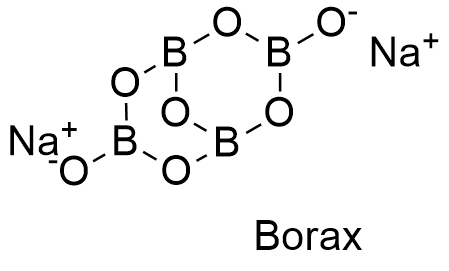
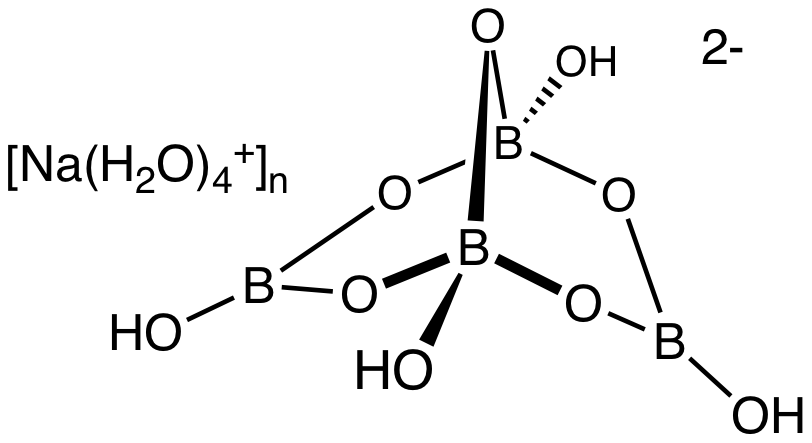
Borax, scientifically known as sodium borate, is a hydrated compound with the chemical formula Na₂[B₄O₅(OH)₄]·8H₂O. This formula reveals the fundamental components of borax:
- Sodium (Na): A highly reactive alkali metal, sodium readily forms ionic bonds with other elements. In borax, sodium ions (Na+) are attracted to the negatively charged boron-oxygen groups.
- Boron (B): A metalloid element, boron forms covalent bonds with oxygen to create complex borate anions. These anions are the heart of borax’s structure and are responsible for its unique properties.
- Oxygen (O): The most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, oxygen plays a vital role in forming the borate anions. It forms covalent bonds with boron and hydrogen, creating a network of interconnected atoms.
- Hydrogen (H): Hydrogen, present in the hydroxyl groups (OH-) and water molecules, forms hydrogen bonds with oxygen atoms within the borate anions and water molecules. These bonds contribute to the stability and hydration properties of borax.
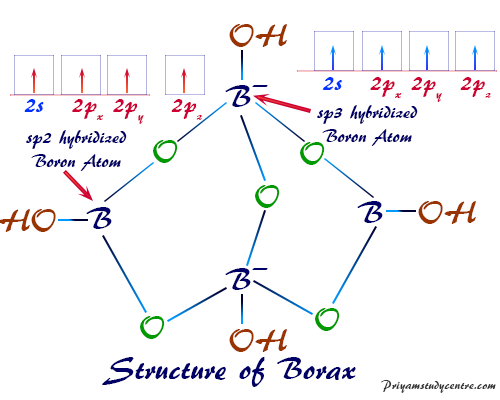
The Borate Anion: A Complex Structure
The key to understanding borax’s properties lies in its borate anion, [B₄O₅(OH)₄]²-. This complex structure consists of four boron atoms linked together by oxygen atoms. The boron atoms are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry, with each boron atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. The borate anion also incorporates hydroxyl groups (OH-) that contribute to its overall charge and reactivity.
The Role of Hydration
Borax is a hydrated compound, meaning it contains water molecules within its structure. These water molecules are essential for maintaining the stability and solubility of the borate anion. The water molecules interact with the borate anion through hydrogen bonds, forming a network of interconnected molecules. This network of hydrogen bonds contributes to the characteristic crystalline structure of borax.
Borax: A Versatile Mineral
The unique chemical composition of borax, with its complex borate anion and hydration properties, gives it a wide range of applications:
- Detergent and Cleaning Agent: Borax is a common ingredient in laundry detergents and household cleaners due to its ability to soften water and remove dirt. Its alkaline nature helps break down grease and grime, making it an effective cleaning agent.
- Industrial Applications: Borax finds use in various industrial processes, including glass production, enamel making, and the manufacture of fiberglass. Its ability to lower the melting point of glass and enhance its fluidity makes it essential in glassmaking.
- Agriculture: Borax is used as a micronutrient for plants, particularly in boron-deficient soils. It promotes healthy plant growth by aiding in the uptake and utilization of nutrients.
- Medical Applications: Borax has been used traditionally for its antiseptic and antifungal properties. In some cultures, it is used to treat skin infections and oral thrush. However, it’s crucial to note that borax should be used cautiously and under medical supervision due to its potential toxicity.
- Other Uses: Borax is also used in cosmetics, as a fire retardant, and in the production of boric acid, a valuable chemical compound with various applications.
FAQs about Borax
Q: What is the difference between borax and boric acid?
A: Borax (sodium borate) and boric acid (H₃BO₃) are related compounds, but they differ in their chemical composition and properties. Borax is a sodium salt of boric acid. Boric acid is a weak acid, while borax is an alkaline compound.
Q: Is borax safe for human consumption?
A: Borax is not intended for human consumption and can be toxic in large quantities. It’s crucial to avoid ingesting borax and to keep it out of reach of children.
Q: What are the potential health risks associated with borax?
A: Ingestion of borax can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In severe cases, it can lead to organ damage and even death. Prolonged exposure to borax dust can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
Tips for Using Borax Safely
- Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling borax.
- Avoid inhaling borax dust.
- Store borax in a cool, dry place, out of reach of children and pets.
- Use borax according to product instructions and follow safety guidelines.
- If you experience any adverse reactions after using borax, discontinue use and seek medical attention.
Conclusion
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral with a unique chemical composition, holds a significant place in various industries and applications. Its complex structure, characterized by the borate anion and hydration properties, grants it remarkable characteristics, including its ability to soften water, remove dirt, and act as a micronutrient for plants. While borax offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to handle it with caution due to its potential toxicity. Understanding the chemical composition and properties of borax is essential for utilizing it safely and effectively in various applications.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Chemical Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!