The Chemistry of Our Kitchens: Common Acids in Everyday Life
Related Articles: The Chemistry of Our Kitchens: Common Acids in Everyday Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Chemistry of Our Kitchens: Common Acids in Everyday Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Chemistry of Our Kitchens: Common Acids in Everyday Life

Acids are ubiquitous in our environment, playing critical roles in both natural and man-made processes. While often associated with corrosive and dangerous substances, many acids are present in our homes, contributing to the functionality and safety of everyday life. Understanding the nature and applications of these common household acids is essential for safe and informed use.
Understanding Acids: A Brief Overview
Acids are chemical compounds that release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. This characteristic defines their acidic nature, leading to a sour taste and the ability to react with bases, forming salts and water. The strength of an acid is determined by its tendency to donate hydrogen ions, with strong acids readily releasing H+ and weak acids doing so to a lesser extent.
Common Household Acids: A Diverse Range
Here’s a closer look at some of the most prevalent acids found in our homes:
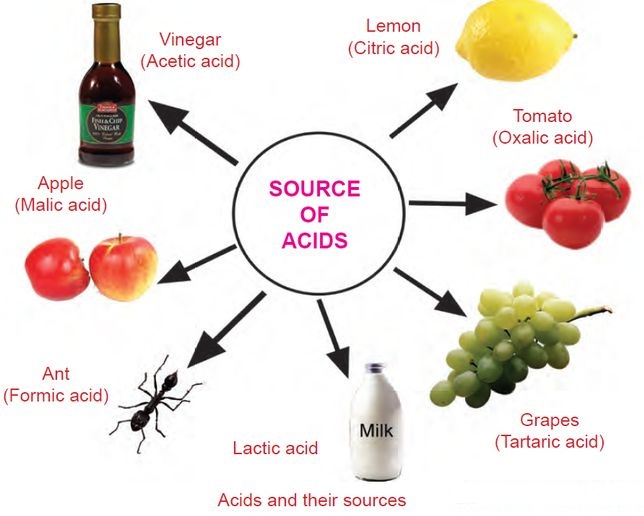
1. Acetic Acid (CH3COOH): The Vinegar Star
Acetic acid, the primary component of vinegar, is a weak organic acid with a characteristic pungent odor. Its versatile applications extend beyond culinary uses:
- Food Preservation: Vinegar’s acidic nature inhibits bacterial growth, making it an effective food preservative. From pickling vegetables to marinating meats, acetic acid helps extend shelf life and add flavor.
- Cleaning: Acetic acid’s ability to dissolve mineral deposits and grime makes it a popular cleaning agent. It can be used to clean surfaces, remove stains, and even deodorize.
- Gardening: Diluted vinegar solutions can be used as a natural weed killer and pest repellent.
2. Citric Acid (C6H8O7): The Fruitful Acid
Citric acid, abundant in citrus fruits like lemons, limes, and oranges, is a weak organic acid with a tart flavor. Its applications range from culinary delights to industrial uses:
- Food and Beverage: Citric acid serves as a natural flavor enhancer, adding a tangy note to beverages and foods. It also acts as an antioxidant, preserving the freshness and quality of products.
- Cleaning and Personal Care: Citric acid’s ability to dissolve mineral deposits makes it an effective cleaning agent for removing limescale from appliances and hard water stains. It also finds applications in personal care products like shampoos and skin cleansers.
- Industrial Applications: Citric acid is used in various industrial processes, including the production of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
3. Ascorbic Acid (C6H8O6): The Vitamin C Champion
Ascorbic acid, more commonly known as Vitamin C, is an essential nutrient found in fruits and vegetables. While not technically an acid in the same way as acetic or citric acid, it exhibits acidic properties in solution:
- Health Benefits: Vitamin C plays a crucial role in immune function, collagen synthesis, and antioxidant defense against free radicals. Its presence in fruits and vegetables makes them vital for a healthy diet.
- Food Preservation: Ascorbic acid is used as an antioxidant to prevent oxidation and browning in food products, extending their shelf life and preserving their freshness.
- Pharmaceutical Applications: Ascorbic acid is a key ingredient in various pharmaceutical formulations, including multivitamins and supplements.
4. Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4): The Cola King
Phosphoric acid is a strong inorganic acid commonly found in soft drinks, particularly cola beverages. It contributes to the characteristic tangy flavor and serves other purposes:
- Food and Beverage: Phosphoric acid acts as an acidulant, adding a tart taste to beverages. It also helps to enhance the flavor of other ingredients and preserve the product’s quality.
- Industrial Applications: Phosphoric acid is widely used in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and various chemical processes.
- Dental Concerns: Excessive consumption of phosphoric acid-containing beverages has been linked to tooth enamel erosion and dental health issues.
5. Tartaric Acid (C4H6O6): The Winemaker’s Friend
Tartaric acid, primarily found in grapes, is a weak organic acid that plays a significant role in winemaking:
- Wine Production: Tartaric acid contributes to the flavor and acidity of wine, influencing its balance and complexity. It also helps to stabilize the wine and prevent spoilage.
- Food and Beverage: Tartaric acid is used as an acidulant in various food and beverage products, adding a tart flavor and aiding in preservation.
- Other Applications: Tartaric acid finds applications in baking powder, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
6. Lactic Acid (C3H6O3): The Yogurt Maker
Lactic acid is a weak organic acid produced by the fermentation of lactose, the sugar found in milk. It plays a key role in the production of yogurt, cheese, and other fermented dairy products:
- Dairy Products: Lactic acid contributes to the tangy flavor and thick texture of yogurt and cheese. It also inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria, contributing to the safety and preservation of these products.
- Food Preservation: Lactic acid is used as a natural preservative in various food products, extending their shelf life and inhibiting microbial growth.
- Cosmetics and Pharmaceuticals: Lactic acid is used in skincare products as a humectant, exfoliant, and moisturizer. It also finds applications in pharmaceuticals as an antiseptic and antibacterial agent.
Importance and Benefits of Household Acids
These common household acids play a crucial role in our daily lives, offering numerous benefits:
- Food Preservation: Acids, like acetic acid in vinegar, citric acid in citrus fruits, and lactic acid in yogurt, act as natural preservatives, inhibiting bacterial growth and extending the shelf life of food products.
- Cleaning and Hygiene: Acids like acetic acid and citric acid are effective cleaning agents, dissolving mineral deposits, removing stains, and disinfecting surfaces.
- Health and Nutrition: Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is an essential nutrient, contributing to immune function, collagen synthesis, and antioxidant defense.
- Flavor Enhancement: Acids contribute to the taste and enjoyment of food and beverages, adding a tangy note and enhancing the flavor of other ingredients.
- Industrial Applications: Acids are vital components in various industrial processes, contributing to the production of fertilizers, detergents, plastics, pharmaceuticals, and other essential products.
FAQs: Common Questions about Household Acids
Q: Are all household acids dangerous?
A: While some acids can be corrosive and harmful, most common household acids are diluted and safe for everyday use. However, it’s crucial to follow safety precautions and use acids responsibly.
Q: How can I safely handle household acids?
A: Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling acids. Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. Store acids in well-ventilated areas and keep them out of reach of children.
Q: Can I mix different household acids?
A: Mixing acids can be dangerous and potentially lead to harmful reactions. It’s best to avoid mixing different acids unless specifically instructed in a safe and controlled environment.
Q: What are some common uses of household acids?
A: Household acids have diverse applications, including cleaning, food preservation, flavor enhancement, and personal care.
Q: What are some safety precautions when using household acids?
A: Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling acids. Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. Store acids in well-ventilated areas and keep them out of reach of children.
Tips for Using Household Acids Safely and Effectively
- Always dilute acids before use: Diluting acids reduces their concentration and makes them safer to handle.
- Wear gloves and eye protection: Protect your skin and eyes from contact with acids.
- Store acids in well-ventilated areas: Avoid storing acids in enclosed spaces.
- Keep acids out of reach of children: Children should never be allowed to handle acids.
- Do not mix acids unless instructed: Mixing acids can lead to dangerous reactions.
- Use acids according to manufacturer instructions: Follow the instructions on product labels for safe and effective use.
Conclusion: The Importance of Acid Awareness
Household acids are an integral part of our everyday lives, contributing to the functionality, safety, and enjoyment of various aspects of our homes. Understanding the nature, benefits, and safe handling of these common acids empowers us to use them responsibly and effectively. By embracing awareness and following safety guidelines, we can harness the power of these ubiquitous compounds for a healthier, cleaner, and more fulfilling life.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Chemistry of Our Kitchens: Common Acids in Everyday Life. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!