The Conical Form: A Versatile Shape with Diverse Applications
Related Articles: The Conical Form: A Versatile Shape with Diverse Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Conical Form: A Versatile Shape with Diverse Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Conical Form: A Versatile Shape with Diverse Applications
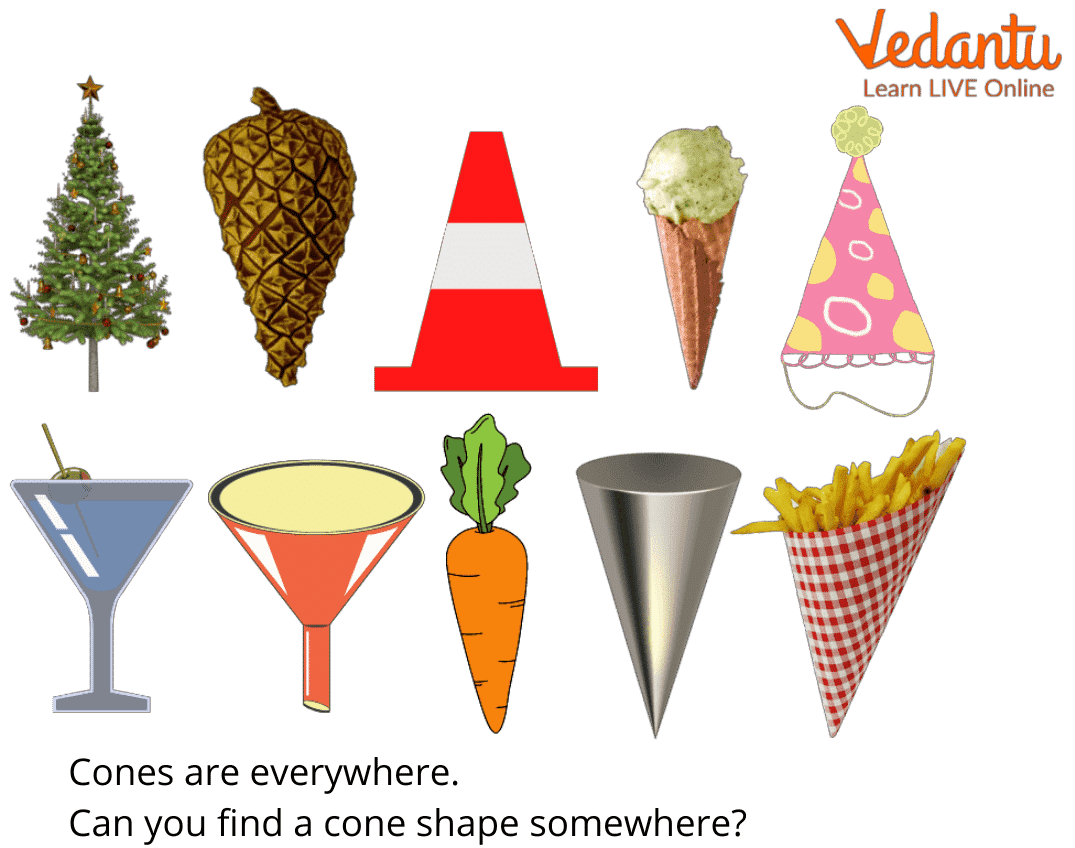
The cone, with its distinctive pointed apex and circular base, is a geometric shape that transcends the realm of pure mathematics, finding its way into countless aspects of our lives. Its simple form, characterized by a single, smooth curve, belies the remarkable versatility and significance of the cone. This article explores the prevalence of the conical form across various disciplines, examining its inherent properties and the benefits it offers in diverse contexts.
The Geometry of the Cone:
At its core, the cone is a three-dimensional shape formed by connecting all points on a circle to a single point outside the plane of the circle, known as the apex. This definition highlights the fundamental relationship between the cone and the circle, a relationship that permeates many of its applications. The cone’s simplicity allows for easy mathematical analysis, making it a foundational shape in geometry. It can be defined by a few key parameters, including its radius, height, and slant height, which simplify calculations and aid in understanding its properties.
Structural Integrity and Stability:
The conical shape exhibits inherent structural strength and stability, making it ideal for various applications. Its tapered form allows for efficient distribution of forces, ensuring that stresses are evenly distributed across its surface. This property is particularly advantageous in engineering, where conical structures are employed in bridges, towers, and other load-bearing constructions. The cone’s ability to withstand significant forces without buckling or collapsing is a testament to its structural integrity.
Aerodynamic Efficiency:
The cone’s streamlined form plays a crucial role in aerodynamics, contributing to reduced drag and improved efficiency. This characteristic makes it a preferred shape for projectiles, such as rockets and missiles, where minimizing air resistance is essential for achieving optimal performance. The cone’s pointed apex helps to cleave through air, reducing turbulence and maximizing speed. Furthermore, the cone’s smooth surface minimizes friction, further enhancing its aerodynamic efficiency.
Fluid Dynamics and Flow Control:
The cone’s shape also plays a vital role in fluid dynamics, influencing the flow of liquids and gases. Its tapering form can be used to control the direction and velocity of fluids, making it essential in various industrial processes. For instance, conical nozzles are commonly used in sprayers and other devices to direct and control the flow of liquids. The cone’s ability to direct and concentrate fluids makes it an indispensable component in many applications.
Optical Properties and Light Concentration:
The conical shape exhibits unique optical properties, particularly its ability to concentrate light. This characteristic is exploited in various optical devices, including lenses, mirrors, and light concentrators. The cone’s curved surface can be used to refract or reflect light, focusing it onto a specific point. This principle is employed in telescopes, microscopes, and other optical instruments, enabling precise manipulation and control of light.
Applications Across Disciplines:
The conical form finds its way into diverse disciplines, reflecting its remarkable versatility and suitability for various applications.
Engineering and Construction:
- Bridges and Towers: Conical structures are employed in bridges and towers to enhance their structural integrity and stability. The tapered form allows for efficient distribution of forces, ensuring that stresses are evenly distributed across the structure.
- Piles and Foundations: Conical piles are used as foundations in various construction projects, providing a strong and stable base for structures. The conical shape allows for easy penetration into the ground, while its tapered form ensures a secure grip.
- Tanks and Silos: Conical sections are often incorporated into tanks and silos to facilitate the flow of materials, preventing clogging and ensuring efficient storage and retrieval.
Aerospace and Aviation:
- Rockets and Missiles: Conical noses are commonly used in rockets and missiles, as their streamlined shape minimizes air resistance and enhances aerodynamic efficiency. The pointed apex helps to cleave through air, reducing turbulence and maximizing speed.
- Aircraft Wings: Some aircraft wings incorporate conical sections to optimize lift and reduce drag. The tapered form helps to distribute air pressure effectively, enhancing the wing’s performance.
Fluid Dynamics and Industrial Processes:
- Nozzles and Sprayers: Conical nozzles are used in various applications, including sprayers, sprinklers, and other devices, to direct and control the flow of liquids. The cone’s ability to concentrate fluids makes it an essential component in many industrial processes.
- Filters and Separators: Conical filters and separators are used to remove impurities from liquids and gases. The tapered shape facilitates the separation of particles, ensuring efficient filtration.
Optics and Illumination:
- Lenses and Mirrors: Conical lenses and mirrors are used in various optical devices, including telescopes, microscopes, and cameras, to focus and manipulate light. The cone’s curved surface can be used to refract or reflect light, concentrating it onto a specific point.
- Light Concentrators: Conical light concentrators are used in solar energy applications to capture and concentrate sunlight, enhancing the efficiency of solar panels.
Other Applications:
- Funnels and Measuring Cups: Conical funnels are used to guide liquids into containers, while conical measuring cups facilitate precise measurement of liquids.
- Ice Cream Cones: The iconic ice cream cone exemplifies the cone’s ability to provide a convenient and enjoyable way to consume a popular treat.
- Art and Design: The cone is a common motif in art and design, inspiring various sculptures, paintings, and architectural structures.
FAQs about the Conical Form:
Q: What are the advantages of using a conical shape in engineering and construction?
A: The conical shape offers several advantages in engineering and construction, including:
- Enhanced structural integrity: The tapered form allows for efficient distribution of forces, ensuring that stresses are evenly distributed across the structure, minimizing the risk of buckling or collapse.
- Improved stability: The cone’s wide base provides a stable foundation, enhancing the structure’s resistance to overturning or shifting.
- Ease of construction: The cone’s simple geometry allows for relatively easy construction and fabrication, using readily available materials.
Q: How does the conical shape contribute to aerodynamic efficiency?
A: The cone’s streamlined form reduces air resistance, improving aerodynamic efficiency. Its pointed apex helps to cleave through air, reducing turbulence and maximizing speed. The cone’s smooth surface minimizes friction, further enhancing its aerodynamic efficiency.
Q: What are some examples of how the conical shape is used in optics and illumination?
A: The conical shape is used in various optical devices, including:
- Lenses: Conical lenses are used to focus and manipulate light, concentrating it onto a specific point.
- Mirrors: Conical mirrors are used to reflect light, directing it to a desired location.
- Light concentrators: Conical light concentrators are used in solar energy applications to capture and concentrate sunlight, enhancing the efficiency of solar panels.
Q: What are some everyday examples of objects shaped like cones?
A: The conical shape is present in various everyday objects, including:
- Ice cream cones
- Funnels
- Traffic cones
- Measuring cups
- Some types of hats
Tips for Utilizing the Conical Form:
- Consider the structural requirements: When designing conical structures, ensure that the shape is appropriate for the intended load and stress distribution.
- Optimize for aerodynamic efficiency: For applications requiring minimal air resistance, ensure that the cone’s shape is streamlined and smooth.
- Control fluid flow: For applications involving fluid dynamics, use the cone’s tapering form to direct and control the flow of liquids or gases.
- Maximize light concentration: For optical applications, use the cone’s curved surface to refract or reflect light, focusing it onto a desired point.
Conclusion:
The cone, with its simple yet versatile form, has found its way into countless aspects of our lives, demonstrating its remarkable adaptability and significance across various disciplines. From engineering and construction to aerospace and optics, the cone’s inherent properties, including its structural integrity, aerodynamic efficiency, and optical characteristics, have made it an indispensable shape in numerous applications. Its prevalence across diverse fields is a testament to its remarkable versatility and the benefits it offers in solving complex problems and enhancing performance in various contexts. The cone’s enduring presence underscores its importance as a foundational shape, shaping our world in countless ways.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Conical Form: A Versatile Shape with Diverse Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!