The Electrifying World: A Look at Energy Consumption in the 21st Century
Related Articles: The Electrifying World: A Look at Energy Consumption in the 21st Century
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Electrifying World: A Look at Energy Consumption in the 21st Century. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Electrifying World: A Look at Energy Consumption in the 21st Century
The modern world is powered by electricity, a silent force that underpins our daily lives. From the lights in our homes to the complex machinery in factories, electricity is the lifeblood of our technological society. However, the increasing demand for this vital resource raises crucial questions about its usage and the need for sustainable practices. This article explores the key sectors consuming the most electricity, providing a comprehensive overview of their energy needs and the implications for the future.
Industrial Powerhouses: The Backbone of Modern Economies
The industrial sector stands as a behemoth in terms of electricity consumption. Manufacturing, processing, and production activities across diverse industries rely heavily on electric power. From steel mills to automotive factories, these facilities utilize a vast array of electric motors, heating systems, and specialized equipment, driving the creation of goods that shape our world.
- Heavy Industry: Steel production, cement manufacturing, and mining operations are energy-intensive processes requiring substantial amounts of electricity for melting, refining, and extraction. The scale of these operations often necessitates dedicated power plants, highlighting the significant energy footprint of heavy industry.
- Manufacturing: Assembly lines, robotic systems, and sophisticated machinery in manufacturing facilities rely on electricity for operation. The production of consumer goods, electronics, and automobiles requires a constant flow of power to maintain production efficiency and quality control.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industries: The production of chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers involves complex chemical reactions that require significant energy inputs. Electric power is vital for running pumps, reactors, and other critical equipment in these industries.
A World Lit by Electricity: Residential Consumption
While industrial activities dominate overall electricity consumption, residential use is a significant contributor, driven by the increasing integration of technology and the pursuit of comfort.
- Lighting and Appliances: The ubiquitous presence of lights, refrigerators, washing machines, ovens, and air conditioners in homes contributes significantly to residential electricity consumption. The adoption of energy-efficient appliances and LED lighting has helped mitigate this impact, but the growing demand for comfort and convenience continues to drive energy usage.
- Heating and Cooling: Climate control systems, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), are major electricity consumers in residential settings. The need to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, especially in extreme weather conditions, drives significant energy demand.
- Electronics and Entertainment: The proliferation of computers, televisions, gaming consoles, and other electronic devices adds to residential electricity consumption. While these devices often have low individual power requirements, their collective impact is substantial, particularly in households with multiple users and devices.
The Data-Driven World: The Rise of Information Technology
The rapid growth of the digital economy has ushered in a new era of electricity consumption. Data centers, servers, and networks are the backbone of the internet and cloud computing, demanding vast amounts of power to process information and facilitate communication.
- Data Centers: These massive facilities house servers and other equipment that process and store vast amounts of data. The cooling requirements for these systems, coupled with the high energy demands of processing power, make data centers significant energy consumers.
- Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based services has fueled the growth of data centers and increased electricity consumption. From email and social media to streaming services and online gaming, cloud computing relies on a global network of servers that require continuous power.
- Networking and Communication: The infrastructure that connects us to the digital world, including routers, switches, and fiber optic cables, also requires electricity to function. The constant flow of data across the internet and mobile networks contributes to the growing energy footprint of the digital economy.
Beyond the Grid: Transportation’s Electrifying Future
The transportation sector is undergoing a significant transformation as electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction. While still a relatively small share of overall vehicle sales, EVs are poised to become a major force in the future, impacting electricity consumption patterns.
- Electric Vehicles: EVs rely solely on electricity for propulsion, eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel fuel. As EV adoption increases, the demand for charging infrastructure and grid capacity will rise significantly.
- Public Transportation: Electric buses and trains are becoming increasingly common in urban areas, offering a more sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-powered vehicles. This shift towards electric public transportation will contribute to increased electricity consumption.
- Charging Infrastructure: The widespread adoption of EVs necessitates the development of robust charging infrastructure. Public charging stations and home charging systems will require significant amounts of electricity to power the growing fleet of EVs.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Sources
The increasing demand for electricity necessitates a focus on energy efficiency and the adoption of renewable energy sources to mitigate the environmental impact of electricity generation.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient practices in homes, industries, and transportation can significantly reduce electricity consumption. This includes using energy-efficient appliances, optimizing building design for better insulation, and promoting sustainable transportation options.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Harnessing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation. The development and deployment of these technologies are crucial for achieving a sustainable energy future.
FAQs: Unpacking the Complexities of Electricity Consumption
1. What sectors consume the most electricity globally?
Globally, the industrial sector accounts for the largest share of electricity consumption, followed by the residential and commercial sectors. However, the specific breakdown can vary significantly depending on the region and level of industrial development.
2. How does electricity consumption differ between developed and developing countries?
Developed countries tend to have higher per capita electricity consumption due to their advanced industrial sectors, widespread use of technology, and high living standards. Developing countries often have lower per capita consumption but are experiencing rapid growth in energy demand as they industrialize and urbanize.
3. What are the environmental implications of electricity consumption?
The generation of electricity, particularly from fossil fuels, releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Air pollution from power plants can also have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
4. How can we reduce our electricity consumption?
Reducing electricity consumption requires a multi-pronged approach, including:
- Promoting energy efficiency: Using energy-efficient appliances, optimizing building design, and adopting sustainable transportation practices.
- Shifting to renewable energy sources: Investing in solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Changing consumer behavior: Making conscious choices about energy use in homes, workplaces, and transportation.
5. What are the future trends in electricity consumption?
The global demand for electricity is expected to continue to rise in the coming decades, driven by population growth, economic development, and the increasing integration of technology. The shift towards renewable energy sources and the adoption of energy efficiency measures will be crucial for meeting this demand sustainably.
Tips for Reducing Electricity Consumption
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replace older appliances with energy-efficient models, which can significantly reduce energy consumption and save money on electricity bills.
- Optimize Building Design: Improve insulation, install energy-efficient windows, and utilize passive solar design to minimize the need for heating and cooling.
- Embrace Renewable Energy: Install solar panels or consider other renewable energy options to generate clean electricity for your home or business.
- Reduce Standby Power: Unplug electronics and appliances when not in use, as they often consume electricity even when turned off.
- Adopt Sustainable Transportation: Consider walking, cycling, or using public transportation to reduce reliance on cars and their associated energy consumption.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future Powered by Electricity
Electricity is a fundamental force in our modern world, powering our homes, businesses, and transportation systems. While the demand for electricity continues to grow, it is essential to prioritize energy efficiency and renewable energy sources to ensure a sustainable future. By embracing these practices, we can harness the power of electricity responsibly, ensuring a brighter future for generations to come.

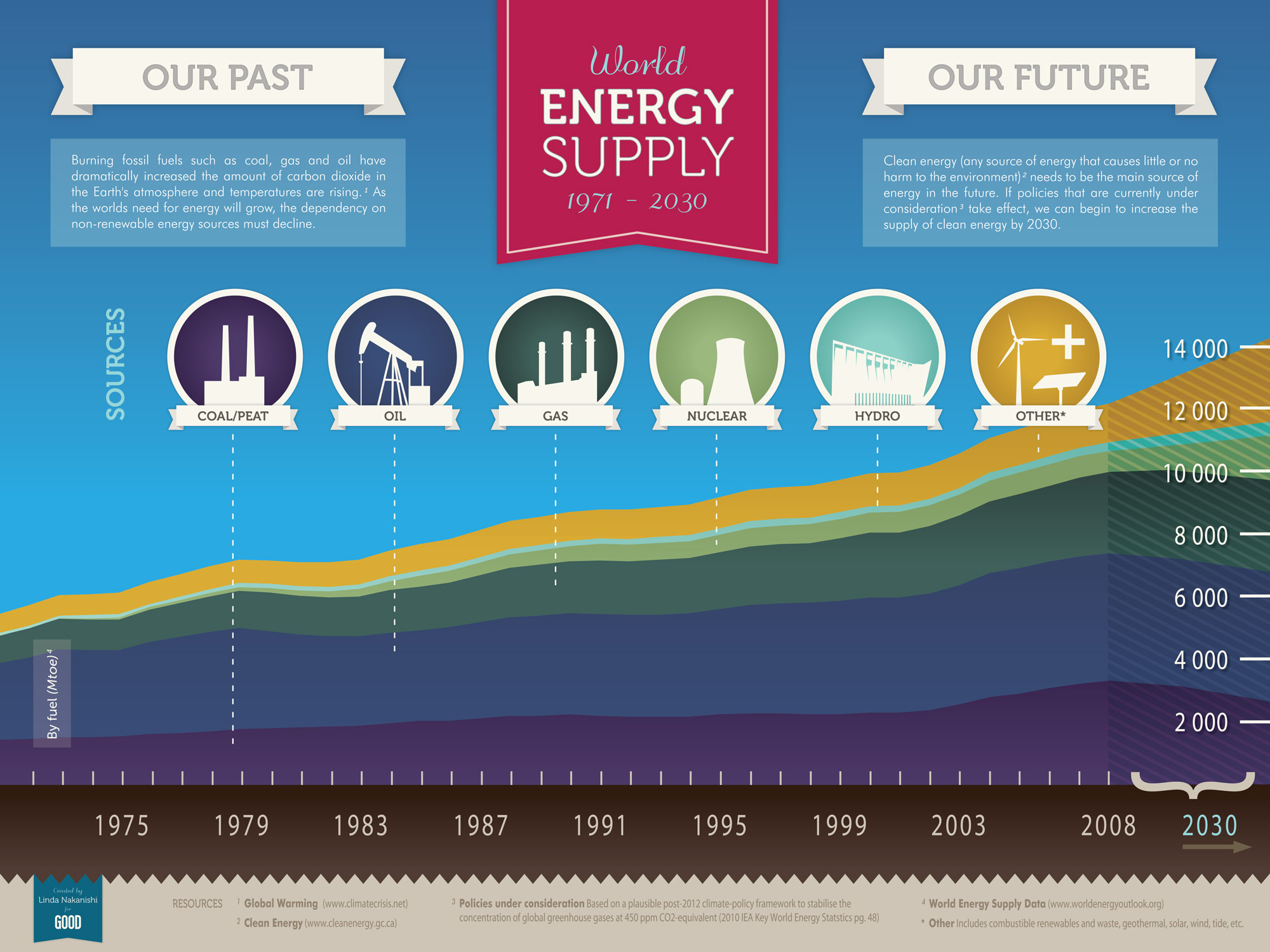
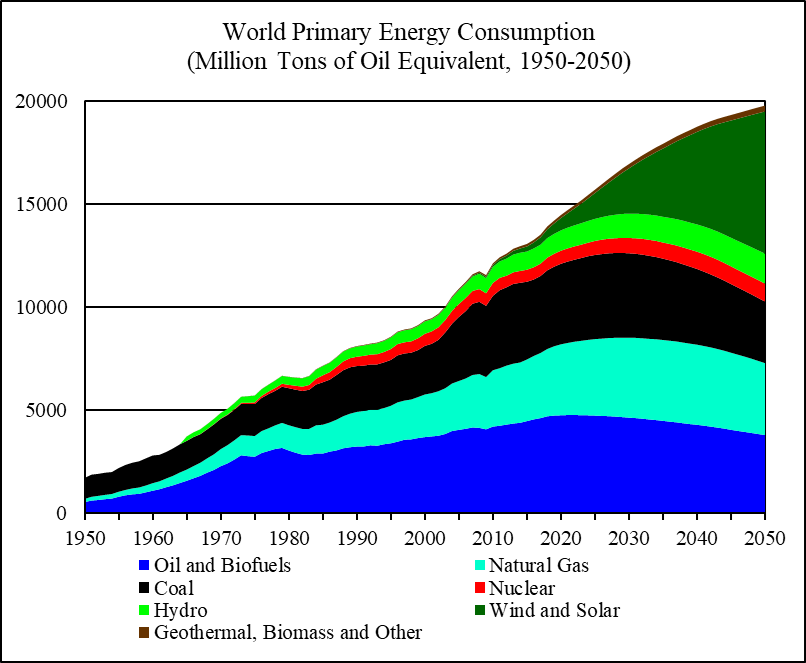





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Electrifying World: A Look at Energy Consumption in the 21st Century. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!