The Enduring Presence Of Lead In Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview
The Enduring Presence of Lead in Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Enduring Presence of Lead in Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Presence of Lead in Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Presence of Lead in Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview

Lead, a heavy metal known for its malleability and resistance to corrosion, has a long history of use in various industries. While its applications have significantly declined due to growing awareness of its toxicity, lead still finds its way into numerous products, often unknowingly. This article delves into the presence of lead in various products, exploring its potential risks and highlighting the importance of informed consumer choices and responsible manufacturing practices.
Lead in Consumer Products: A Historical Perspective
For centuries, lead has been a ubiquitous element in various industries. Its versatility and affordability made it a popular choice for diverse applications, including:
-
Paint: Lead-based paints were widely used until the late 20th century, primarily due to their durability, coverage, and resistance to fading. However, the discovery of lead’s neurotoxicity led to its gradual phase-out, with the US banning lead in residential paints in 1978.
-
Pipes and Plumbing: Lead’s corrosion resistance made it a preferred material for water pipes and plumbing fixtures for centuries. Its use in these applications declined as concerns about lead contamination of drinking water emerged.
-
Electronics: Lead was extensively used in electronics for its ability to solder components together. While its use has been significantly reduced in recent years due to environmental regulations and the development of lead-free alternatives, it still finds applications in some electronic devices.
-
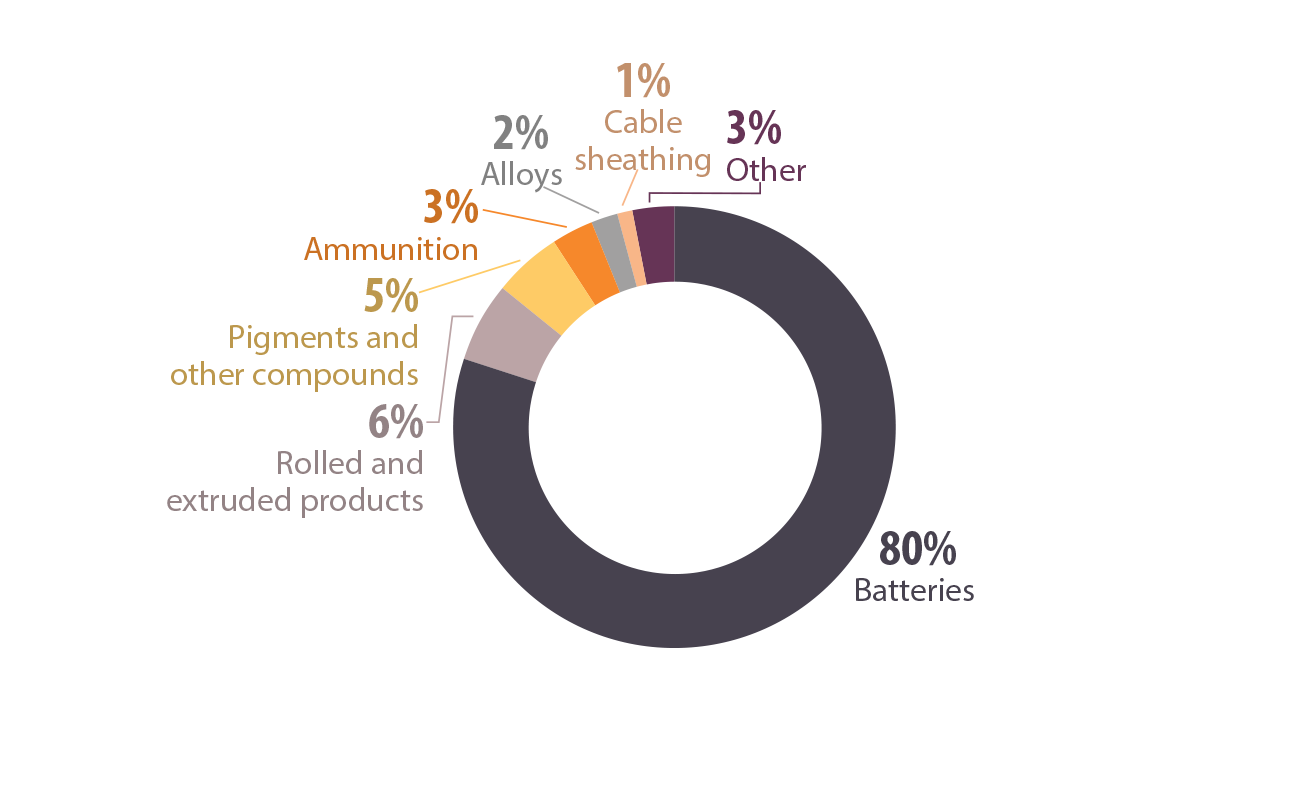
Batteries: Lead-acid batteries, commonly found in vehicles and other applications, utilize lead in their construction. While these batteries are generally safe when properly handled, lead exposure can occur during their manufacturing, recycling, and disposal.
-
Ceramics and Glassware: Lead was historically used in glazes for ceramics and glassware to enhance their shine and durability. However, its presence in these products can lead to lead leaching into food and beverages, posing health risks.
The Toxicity of Lead: A Growing Concern
Lead is a potent neurotoxin that can adversely affect human health, particularly in children and developing fetuses. Exposure to lead can lead to various health issues, including:
-
Neurological Disorders: Lead can damage the brain, affecting cognitive development, learning abilities, and behavior. It can also contribute to attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other neurological problems.
-
Cardiovascular Issues: Lead exposure can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes.
-
Reproductive Health Problems: Lead can impair reproductive health, affecting fertility and increasing the risk of miscarriage.
-
Kidney Damage: Prolonged exposure to lead can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
-
Bone Weakness: Lead can interfere with calcium absorption, leading to bone weakness and osteoporosis.
Lead in Products: A Continued Challenge
Despite the growing awareness of lead’s toxicity, its presence in various products remains a concern. While regulations and consumer awareness have led to a decline in lead use in some applications, it continues to be found in:
-
Imported Products: Lead contamination is a significant concern in products imported from countries with less stringent regulations. This includes toys, jewelry, and other consumer goods.
-
Older Homes and Infrastructure: Homes built before 1978 may contain lead-based paint, while older plumbing systems may still contain lead pipes.
-
Certain Food Products: Lead can contaminate food through soil and water, particularly in areas with high levels of lead pollution.
-
Traditional Medicines: Some traditional medicines, particularly those containing herbal ingredients, may contain lead due to contamination from soil or manufacturing processes.
Mitigating Lead Exposure: A Collective Responsibility
Addressing the issue of lead exposure requires a multi-pronged approach involving:
-
Government Regulations: Stringent regulations and enforcement are crucial to minimize lead use in products and ensure safe levels in the environment.
-
Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about the potential risks of lead exposure and encouraging them to make informed choices is essential.
-
Responsible Manufacturing Practices: Implementing stricter quality control measures and promoting the use of lead-free alternatives in manufacturing processes are crucial.
-
Recycling and Disposal: Proper recycling and disposal of lead-containing products are essential to prevent lead from entering the environment.
FAQs: Lead in Products
Q: What are the symptoms of lead poisoning?
A: Symptoms of lead poisoning can vary depending on the level of exposure and the individual’s susceptibility. Common symptoms include headaches, fatigue, abdominal pain, constipation, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. In severe cases, lead poisoning can lead to seizures, coma, and even death.
Q: How can I test my home for lead?
A: You can purchase lead testing kits from hardware stores or online retailers. You can also contact a certified lead inspector to conduct a thorough inspection of your home.
Q: What should I do if I find lead in my home?
A: If you find lead in your home, it is essential to consult with a qualified lead abatement contractor to develop a safe and effective removal plan.
Q: Are lead-free alternatives available for all products?
A: Lead-free alternatives are available for many products, but not all. In some cases, lead may still be used due to its unique properties or the lack of readily available alternatives.
Q: What is the best way to prevent lead exposure?
A: The best way to prevent lead exposure is to avoid contact with lead-containing products and materials. This includes:
- Using lead-free paint for home renovations.
- Testing water for lead contamination and using a water filter if necessary.
- Choosing lead-free toys and jewelry for children.
- Avoiding traditional medicines that may contain lead.
Tips: Lead in Products
-
Inspect older homes and buildings: If you are purchasing or renovating an older home, have it inspected for lead-based paint and lead pipes.
-
Test drinking water: Regularly test your drinking water for lead contamination, especially if you have older plumbing.
-
Use lead-free paint: If you are painting your home, use lead-free paint and ensure proper ventilation during the painting process.
-
Choose lead-free toys and jewelry: When buying toys and jewelry for children, select products that are labeled as lead-free.
-
Dispose of lead-containing products properly: Dispose of lead-containing products, such as batteries and electronics, at designated recycling centers.
Conclusion
Lead remains a persistent environmental and health concern, despite significant progress in reducing its use. Its presence in various products, from paint to electronics, underscores the importance of ongoing vigilance and responsible practices. By understanding the risks associated with lead exposure, promoting consumer awareness, and implementing effective regulations, we can work towards minimizing its impact on human health and the environment. Continued research and development of lead-free alternatives will be crucial in further reducing lead’s presence in our daily lives and protecting future generations from its harmful effects.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Presence of Lead in Everyday Products: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!