The Powerhouse Within: A Deep Dive into Mitochondrial Production
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: A Deep Dive into Mitochondrial Production
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: A Deep Dive into Mitochondrial Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerhouse Within: A Deep Dive into Mitochondrial Production

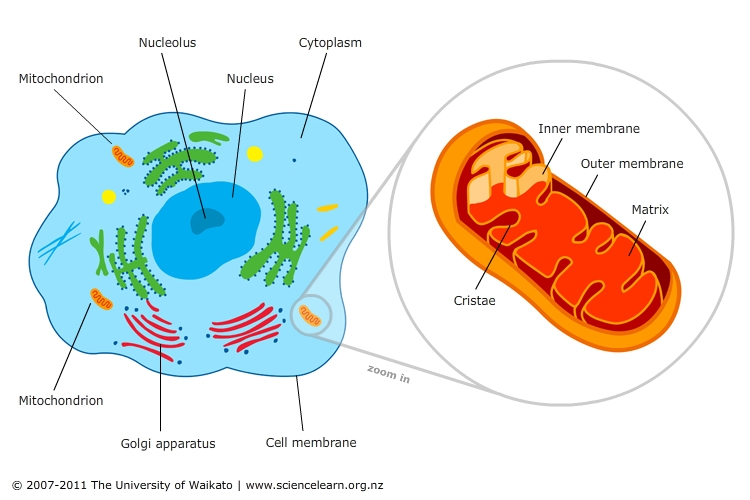
The mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are vital organelles found in nearly every eukaryotic cell. These intricate structures are responsible for a vast array of essential cellular processes, primarily centered around the production of energy. However, their role extends far beyond simple energy generation, encompassing a complex interplay of biochemical reactions that are fundamental to life itself.
The Essence of Energy: ATP Synthesis
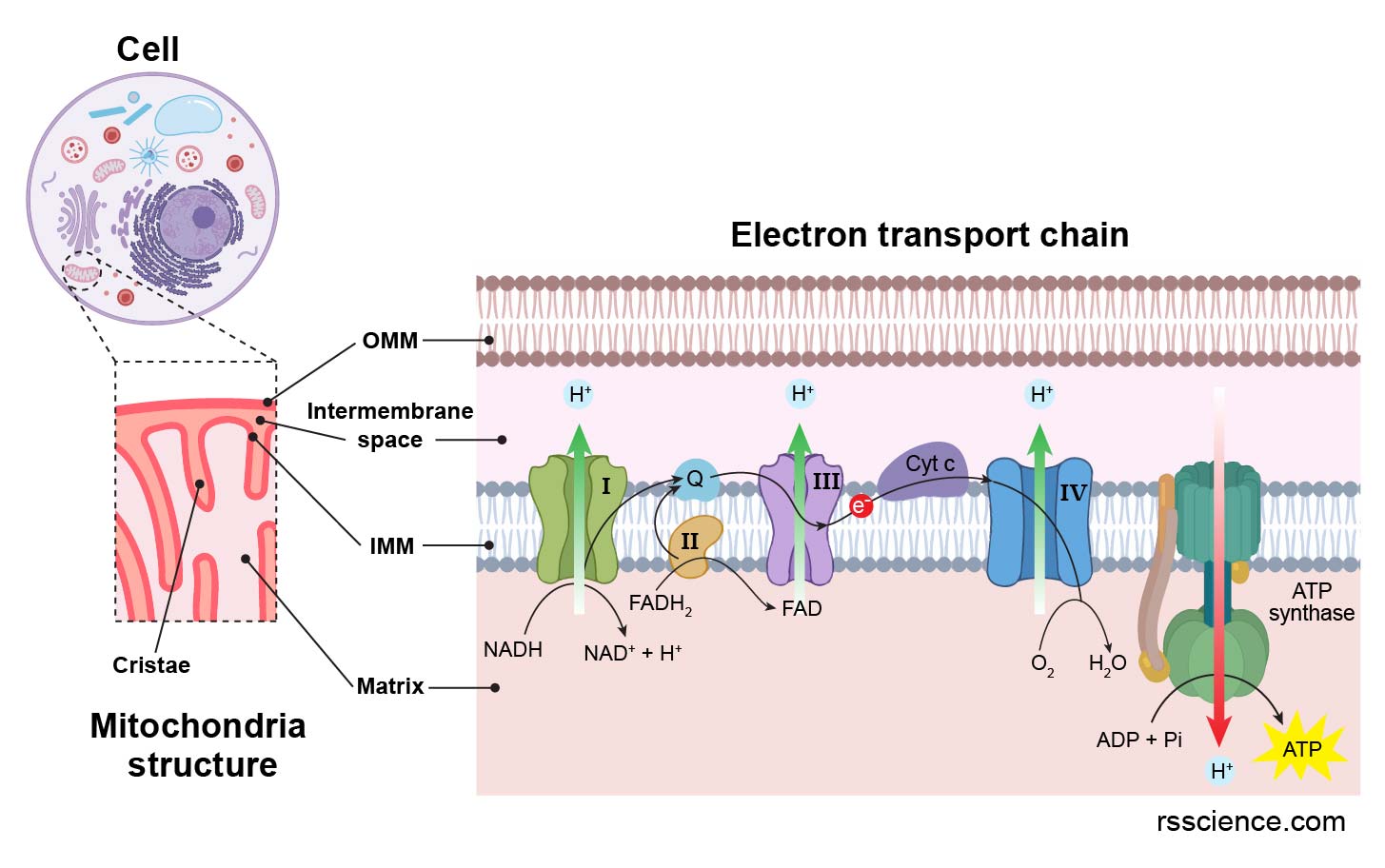
The most well-known function of mitochondria is the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. This process, known as oxidative phosphorylation, occurs within the inner mitochondrial membrane, a highly folded structure that houses a series of protein complexes known as the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain is a remarkable system that harnesses the energy released from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This creates a proton gradient, a difference in proton concentration across the membrane. The energy stored in this gradient is then used by ATP synthase, a molecular motor embedded in the membrane, to drive the synthesis of ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate.
Beyond Energy: The Diverse Functions of Mitochondria
While ATP production is crucial, mitochondria play a far more multifaceted role in cellular life. They are involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, including:
- Amino Acid Metabolism: Mitochondria are key players in the breakdown and synthesis of amino acids, essential building blocks for proteins. They participate in the urea cycle, which removes excess nitrogen from the body, and in the production of essential amino acids like glutamine.
- Lipid Metabolism: These organelles are involved in the breakdown of fatty acids through beta-oxidation, a process that generates energy and produces acetyl-CoA, a key intermediate in cellular metabolism. They also contribute to the synthesis of lipids, including cholesterol and phospholipids, which are essential for cell membranes.
- Heme Synthesis: Mitochondria are the site of heme synthesis, a critical component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport in red blood cells. They also produce other heme-containing proteins involved in electron transport and cellular respiration.
- Iron-Sulfur Cluster Synthesis: These clusters, composed of iron and sulfur atoms, are essential cofactors for many enzymes involved in vital metabolic processes, including DNA replication, repair, and electron transport.
- Steroid Hormone Synthesis: Mitochondria play a role in the synthesis of steroid hormones, including testosterone and estrogen, which regulate a wide range of physiological processes.
- Calcium Signaling: Mitochondria act as intracellular calcium stores, playing a crucial role in regulating calcium levels within the cell. This is essential for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression.
A Deeper Dive into Mitochondrial Production
The production of ATP, amino acids, lipids, heme, iron-sulfur clusters, and steroid hormones are just a few examples of the diverse and vital functions performed by mitochondria. These processes are interconnected, forming a complex web of biochemical reactions that sustain life.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Production
The products of mitochondrial activity are essential for the survival and proper functioning of every cell in the body. These products are vital for:
- Energy Production: ATP provides the energy needed for all cellular processes, from muscle contraction to protein synthesis.
- Cellular Building Blocks: Amino acids and lipids are the building blocks of proteins and cell membranes, respectively, essential for cell structure and function.
- Oxygen Transport: Heme, a component of hemoglobin, enables red blood cells to transport oxygen throughout the body.
- Metabolic Regulation: Iron-sulfur clusters are essential for the function of many enzymes involved in crucial metabolic processes.
- Hormonal Regulation: Steroid hormones regulate a wide range of physiological processes, including growth, development, and reproduction.
- Cellular Signaling: Calcium signaling is essential for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and gene expression.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Disease
The importance of mitochondrial production is underscored by the fact that defects in mitochondrial function can lead to a wide range of diseases, known collectively as mitochondrial disorders. These disorders can affect various organs and systems, leading to a wide spectrum of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, neurological problems, and developmental delays.
FAQs: A Deeper Understanding of Mitochondrial Production
Q: What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
A: Mitochondria are the primary site of oxidative phosphorylation, the final stage of cellular respiration, where ATP is produced. This process involves the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy that is used to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Q: How are mitochondria involved in the synthesis of proteins?
A: Mitochondria play a role in the synthesis of proteins by producing amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. They also participate in the urea cycle, which removes excess nitrogen from the body, and in the production of essential amino acids like glutamine.
Q: What is the significance of heme synthesis in mitochondria?
A: Heme is a crucial component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport in red blood cells. Its synthesis within mitochondria ensures the efficient production and function of hemoglobin, enabling the delivery of oxygen to all tissues in the body.
Q: Why are iron-sulfur clusters important for cellular function?
A: Iron-sulfur clusters are essential cofactors for many enzymes involved in vital metabolic processes, including DNA replication, repair, and electron transport. Their production within mitochondria ensures the proper function of these enzymes, critical for cellular growth and survival.
Q: How do mitochondria contribute to steroid hormone synthesis?
A: Mitochondria play a role in the synthesis of steroid hormones, including testosterone and estrogen, which regulate a wide range of physiological processes. They provide the necessary enzymes and intermediates for these critical hormone production pathways.
Q: What are some of the implications of mitochondrial dysfunction?
A: Defects in mitochondrial function can lead to a wide range of diseases, known collectively as mitochondrial disorders. These disorders can affect various organs and systems, leading to a wide spectrum of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, neurological problems, and developmental delays.
Tips for Optimizing Mitochondrial Function
While mitochondria are essential for life, their function can be influenced by various factors. Here are some tips for optimizing mitochondrial function:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves mitochondrial function, increasing the number and efficiency of mitochondria in cells.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats supports mitochondrial health.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for mitochondrial repair and function.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact mitochondrial function. Techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress levels.
Conclusion: The Unsung Heroes of Cellular Life
Mitochondria are the unsung heroes of cellular life, playing a crucial role in energy production, metabolism, and countless other essential processes. Their complex and interconnected functions underscore their importance for the survival and well-being of all organisms. Understanding the intricate workings of mitochondria provides a deeper appreciation for the complexity and elegance of life itself.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: A Deep Dive into Mitochondrial Production. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!