The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Products of the Mitochondria
Related Articles: The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Products of the Mitochondria
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Products of the Mitochondria. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Products of the Mitochondria
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)
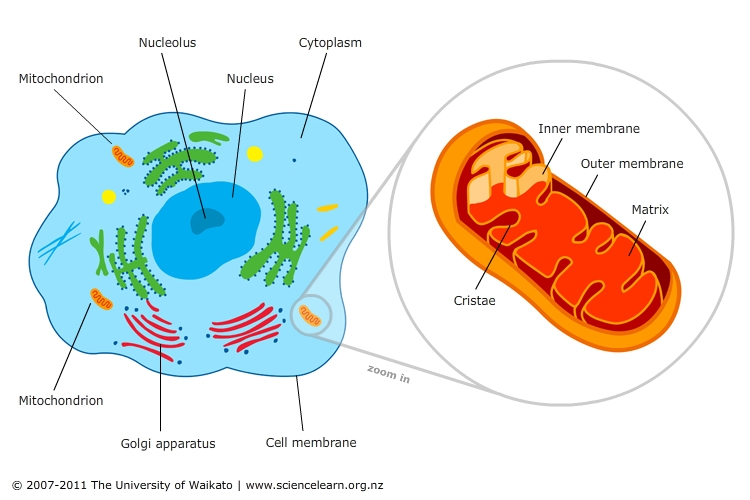
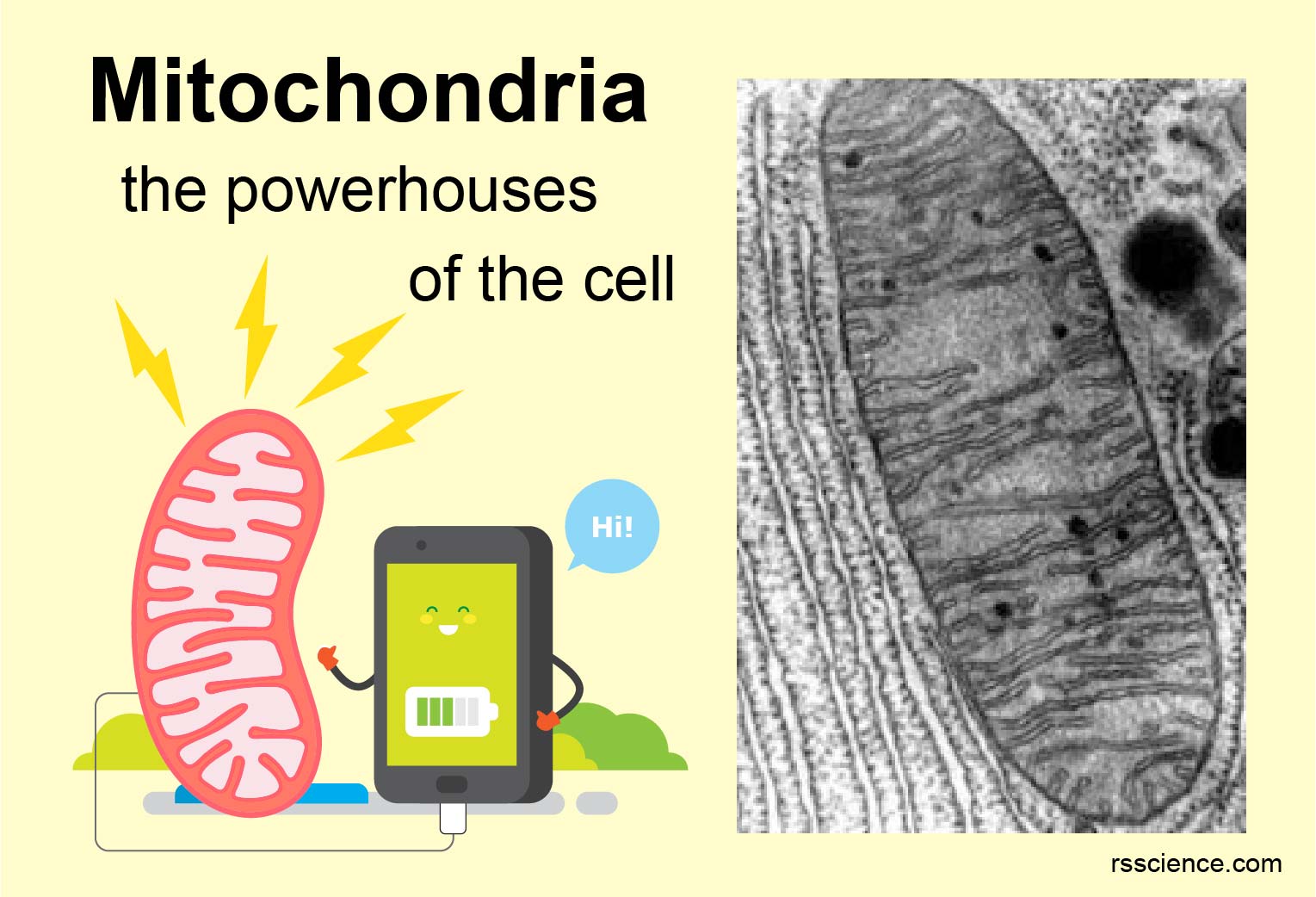
The mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are essential organelles responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This energy is crucial for a vast array of cellular processes, from muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission to protein synthesis and DNA replication. However, the role of the mitochondria extends far beyond energy production. These dynamic organelles are involved in a complex interplay of metabolic pathways, producing a diverse array of molecules that are vital for cellular function and overall organismal health.
ATP: The Universal Energy Currency
The primary product of mitochondrial activity is ATP. This molecule acts as the universal energy currency of the cell, providing the energy required for virtually all cellular processes. ATP is generated through a series of biochemical reactions known as oxidative phosphorylation, which occurs within the inner mitochondrial membrane. This process utilizes the energy released from the breakdown of glucose, fatty acids, and other fuel molecules to drive the synthesis of ATP.
Beyond Energy: A Diverse Range of Mitochondrial Products
While ATP is the most prominent product of the mitochondria, these organelles also produce a range of other essential molecules, including:
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Although often associated with oxidative stress and damage, ROS also play crucial signaling roles within the cell. They are involved in regulating various cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. The mitochondria are a major source of ROS, generated as a byproduct of electron transport during ATP production.
-
Heat: The mitochondrial electron transport chain is not perfectly efficient, and some energy is lost as heat. This heat generation is particularly important in maintaining body temperature in warm-blooded animals.
-
Amino Acids: Mitochondria play a role in the synthesis of certain amino acids, including glutamate and aspartate. These amino acids are essential building blocks for proteins and other vital molecules.
-
Heme: This iron-containing molecule is a key component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport in red blood cells. Mitochondria are involved in the biosynthesis of heme, ensuring adequate oxygen delivery throughout the body.
-
Steroid Hormones: Mitochondria contribute to the synthesis of steroid hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. These hormones play crucial roles in regulating various physiological processes, including growth, development, and reproduction.
-
Iron-Sulfur Clusters: These clusters are essential cofactors for many enzymes involved in key metabolic pathways, including those involved in energy production and DNA replication. Mitochondria are responsible for the assembly and delivery of iron-sulfur clusters to various cellular compartments.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Products
The diverse array of products generated by the mitochondria highlights their central role in cellular function and organismal health. These products are essential for:
-
Energy Production: ATP provides the energy required for all cellular processes, ensuring proper function of tissues and organs.
-
Signal Transduction: ROS act as signaling molecules, regulating cellular processes and influencing cell fate.
-
Metabolic Regulation: Mitochondria are involved in the synthesis of essential molecules like amino acids, heme, and steroid hormones, contributing to metabolic homeostasis.
-
Cellular Defense: The mitochondria play a role in cellular defense mechanisms, including apoptosis and the detoxification of harmful substances.
-
Maintaining Cellular Health: The proper functioning of mitochondria is crucial for maintaining cellular health and preventing the development of various diseases.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Disease
Disruptions in mitochondrial function can lead to a range of diseases, collectively known as mitochondrial disorders. These disorders can affect various tissues and organs, leading to a wide spectrum of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, neurological problems, and developmental delays.
FAQs
Q: What are the main products of the mitochondria?
A: The primary product of mitochondrial activity is ATP, the universal energy currency of the cell. However, mitochondria also produce a diverse range of molecules, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), heat, amino acids, heme, steroid hormones, and iron-sulfur clusters.
Q: How do mitochondria produce ATP?
A: ATP is generated through oxidative phosphorylation, a process that occurs within the inner mitochondrial membrane. This process utilizes the energy released from the breakdown of glucose, fatty acids, and other fuel molecules to drive the synthesis of ATP.
Q: Why are mitochondrial products important?
A: Mitochondrial products are essential for energy production, signal transduction, metabolic regulation, cellular defense, and maintaining cellular health.
Q: What happens when mitochondrial function is disrupted?
A: Disruptions in mitochondrial function can lead to a range of diseases, known as mitochondrial disorders. These disorders can affect various tissues and organs, leading to a wide spectrum of symptoms.
Tips
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can help maintain mitochondrial function.
-
Managing stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact mitochondrial function. Techniques like meditation and yoga can help manage stress levels.
-
Supplementation: Certain supplements, such as CoQ10 and alpha-lipoic acid, may support mitochondrial function. Consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Conclusion
The mitochondria are dynamic organelles that play a central role in cellular function and organismal health. Their diverse array of products, from ATP to ROS and heme, are essential for a wide range of cellular processes, including energy production, signal transduction, metabolic regulation, and cellular defense. Understanding the intricate workings of the mitochondria and their products is crucial for developing strategies to prevent and treat mitochondrial disorders, ensuring optimal health and well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Powerhouse Within: Unveiling the Products of the Mitochondria. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!