The Science of Food Combining: A Guide to Optimizing Digestion
Related Articles: The Science of Food Combining: A Guide to Optimizing Digestion
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Science of Food Combining: A Guide to Optimizing Digestion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Food Combining: A Guide to Optimizing Digestion

The concept of food combining, a practice that suggests certain food pairings can hinder digestion and nutrient absorption, has been debated for centuries. While the idea of "good" and "bad" food combinations lacks scientific consensus, understanding the digestive process and the unique properties of various food groups can offer valuable insights into optimizing digestion and overall well-being. This article delves into the rationale behind food combining, exploring common food pairings and their potential effects on the body.
The Digestive Journey: A Symphony of Enzymes
Digestion is a complex process that involves breaking down food into smaller molecules the body can absorb and utilize. This intricate symphony relies on various digestive enzymes, each specialized for specific food types.
- Carbohydrates: Primarily broken down by salivary amylase in the mouth and pancreatic amylase in the small intestine.
- Proteins: Decomposed by pepsin in the stomach and various proteases in the small intestine.
- Fats: Emulsified by bile produced in the liver and digested by pancreatic lipase in the small intestine.
The Role of Food Combining in Digestion
Food combining theory posits that consuming certain food combinations can overwhelm the digestive system, leading to:
- Slower Digestion: Mixing foods that require different digestive enzymes can prolong the time it takes to break them down, potentially causing bloating, gas, and discomfort.
- Nutrient Malabsorption: When the digestive process is hindered, the body may not efficiently absorb vital nutrients from the food.
- Increased Risk of Fermentation: Undigested food in the gut can ferment, producing gas and potentially contributing to gut imbalances.
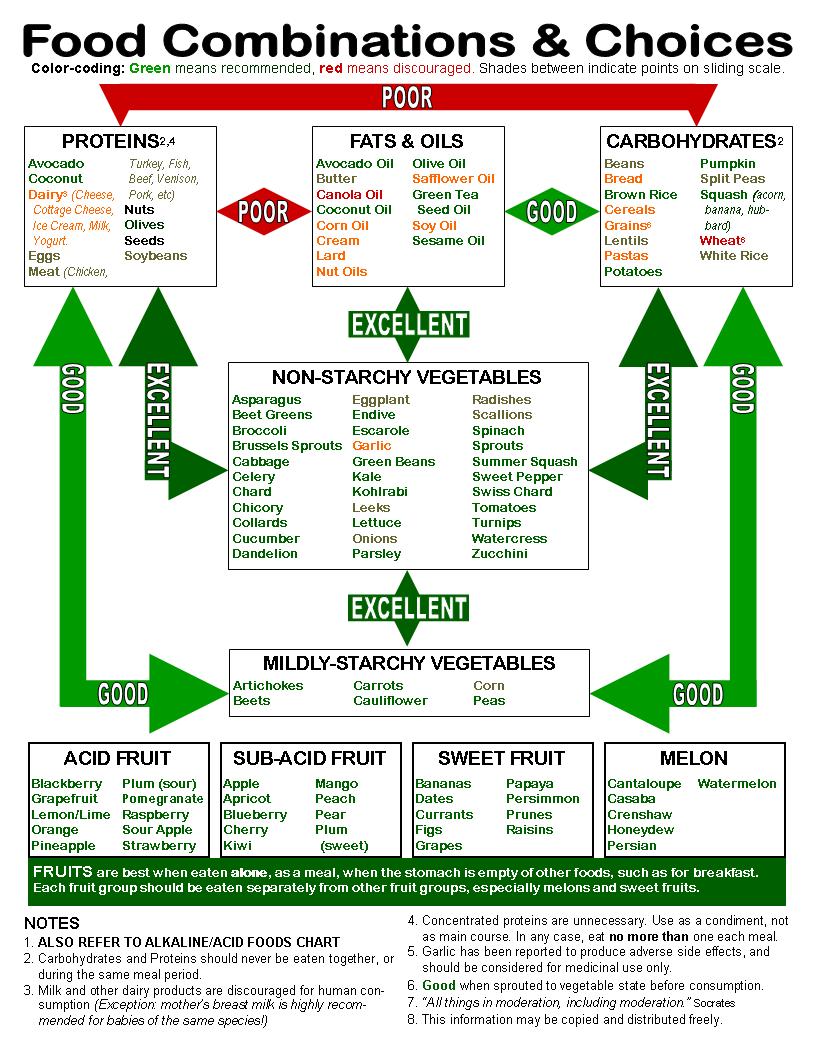
Common Food Combinations to Consider
While there is no definitive list of "forbidden" food pairings, certain combinations have been traditionally associated with digestive discomfort.
1. Protein and Carbohydrates:
- Example: Steak and potatoes, chicken and rice.
- Rationale: Proteins and carbohydrates require different digestive enzymes and environments for optimal breakdown. Consuming them together may slow down the process, potentially leading to fermentation and bloating.
2. Fruits and Other Foods:
- Example: Fruit salad with nuts and yogurt.
- Rationale: Fruits digest quickly due to their high sugar content. Combining them with other foods, especially protein-rich or high-fat options, can slow down the process, potentially leading to fermentation and discomfort.
3. Acidic and Alkaline Foods:
- Example: Citrus fruits with dairy products.
- Rationale: Acidic foods, like citrus fruits, can interfere with the digestion of alkaline foods, like dairy, by altering the pH balance in the stomach.
4. Starches and Fats:
- Example: Pasta with creamy sauces.
- Rationale: Starches require a different digestive environment than fats. Combining them can prolong digestion, potentially leading to bloating and indigestion.
Understanding the Nuances
It’s crucial to acknowledge that individual responses to food combinations vary. Factors like gut health, enzyme production, and overall dietary habits can influence digestion.
Tips for Optimizing Digestion
- Eat Mindfully: Pay attention to your body’s signals and observe how different food combinations affect your digestion.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods that are nutrient-rich and easily digestible.
- Listen to Your Body: If you experience digestive discomfort after consuming certain food combinations, avoid them or try different pairings.
- Stay Hydrated: Water plays a crucial role in digestion. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider Digestive Enzymes: If you struggle with digestion, supplementing with digestive enzymes may help break down food more efficiently.
FAQs about Food Combining
Q: Can food combining help with weight loss?
- A: While some proponents of food combining claim it can aid weight loss, there is no conclusive scientific evidence to support this claim. Weight loss is primarily determined by calorie intake and expenditure.
Q: Should I completely avoid mixing certain foods?
- A: There is no need to eliminate all food combinations. The goal is to find what works best for your body and digestive system.
Q: Can food combining help prevent allergies?
- A: Food combining does not prevent allergies. Allergies are triggered by the immune system’s reaction to specific proteins.
Q: Is food combining a fad diet?
- A: Food combining is not a diet per se, but rather a practice that aims to improve digestion and overall well-being.
Conclusion
While the science behind food combining remains inconclusive, understanding the digestive process and the properties of different food groups can be valuable for optimizing digestion. By paying attention to your body’s signals and making informed choices about food pairings, you can potentially enhance your digestive health and overall well-being. Remember, a balanced diet rich in whole foods and mindful eating habits are key to maintaining a healthy digestive system.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Food Combining: A Guide to Optimizing Digestion. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!