The Science Of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide To Effective Disinfection
The Science of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Disinfection
Related Articles: The Science of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Disinfection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Science of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Disinfection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Disinfection

Germs, ubiquitous and microscopic, are a constant presence in our lives. While many are harmless, others can cause illness, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening infections. Understanding the science behind germ elimination is crucial for maintaining personal health and preventing the spread of disease. This article delves into the most effective methods for killing germs, exploring the mechanisms behind their efficacy and highlighting their importance in various settings.
The Nature of Germs
Germs, scientifically known as microbes, encompass a vast array of single-celled organisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Each group possesses distinct characteristics and mechanisms for survival and replication.
- Bacteria: These single-celled prokaryotes are ubiquitous, thriving in diverse environments. Some are beneficial, aiding in digestion and nutrient cycling, while others are pathogenic, causing infections like pneumonia, food poisoning, and urinary tract infections.
- Viruses: These non-living entities consist of genetic material encased in a protein coat. They rely on host cells to replicate, hijacking cellular machinery to produce more viral particles. Viruses are responsible for diseases like influenza, HIV, and COVID-19.
- Fungi: These eukaryotic organisms include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. While some are beneficial, such as those used in food production, others can cause infections like athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
- Parasites: These organisms live in or on a host, deriving nourishment and shelter. Examples include protozoa causing malaria and intestinal parasites like hookworms and tapeworms.
Methods of Germ Elimination
The effectiveness of germ elimination methods depends on the type of microbe and the specific application. The most common and effective methods include:
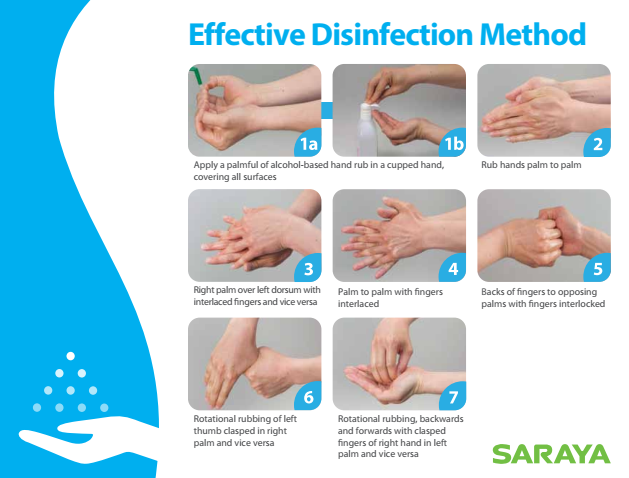
1. Handwashing with Soap and Water
Handwashing remains the cornerstone of germ prevention. Soap disrupts the lipid membranes of microbes, effectively breaking them down. The mechanical action of rubbing hands with soap and water removes germs from the skin’s surface.
2. Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizers
These sanitizers, containing at least 60% alcohol, are effective against a wide range of bacteria and viruses. Alcohol denatures proteins, disrupting the structure of microbes and preventing their replication. Sanitizers are particularly useful when soap and water are unavailable.
3. Bleach
Bleach, a powerful disinfectant, effectively kills bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It works by oxidizing cellular components, disrupting their metabolic processes and leading to cell death. Bleach is commonly used for disinfecting surfaces, laundry, and medical equipment.
4. Heat
Heat is a highly effective method for killing germs. High temperatures denature proteins and disrupt cellular structures, leading to microbial death. This principle is employed in sterilization techniques like boiling water, autoclaving, and pasteurization.
5. Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, particularly UV-C, effectively kills microbes by damaging their DNA. UV-C disinfection is commonly used in hospitals, food processing facilities, and water treatment plants.
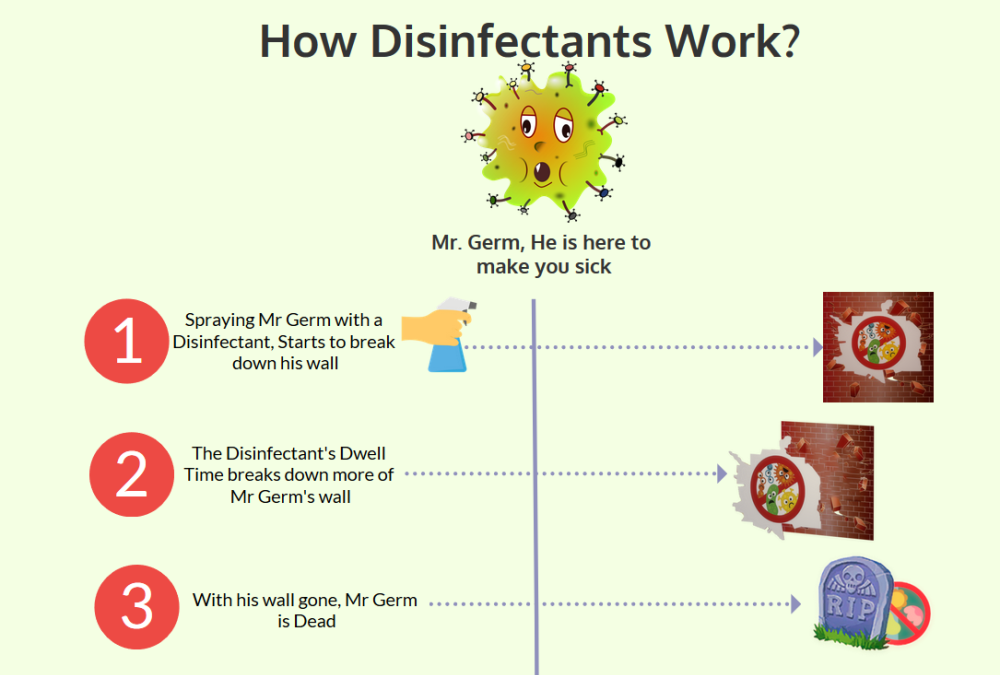
6. Disinfectant Wipes and Sprays
These products, containing various antimicrobial agents, are convenient for disinfecting surfaces and objects. They typically contain alcohol, bleach, or other disinfectants, effectively killing germs.
7. Antibacterial Soaps
These soaps contain antimicrobial agents, primarily triclosan or triclocarban, that kill bacteria. However, the effectiveness of antibacterial soaps in preventing disease is debated, and concerns exist regarding potential antibiotic resistance.
8. Antibiotics
Antibiotics are powerful medications used to treat bacterial infections. They target specific mechanisms within bacteria, inhibiting their growth and replication. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses.
9. Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications target specific viral proteins, interfering with viral replication and reducing the severity of infections. These medications are often used to treat influenza and HIV.
10. Antifungal Medications
Antifungal medications target fungal cell walls or metabolic pathways, inhibiting fungal growth and preventing infections. These medications are used to treat fungal infections like athlete’s foot and yeast infections.
Importance of Germ Elimination
Effective germ elimination is critical for:
- Preventing Illness: By reducing the number of microbes on surfaces and in the environment, we minimize the risk of infection and disease transmission.
- Promoting Public Health: Public health initiatives often focus on germ elimination to control outbreaks and prevent the spread of contagious diseases.
- Ensuring Food Safety: Proper food handling and processing techniques, including disinfection, are crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses.
- Maintaining a Clean and Healthy Environment: Germ elimination contributes to a clean and healthy environment in homes, schools, hospitals, and other public spaces.
- Protecting Vulnerable Individuals: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as infants, elderly, and those with chronic illnesses, are particularly susceptible to infections. Effective germ elimination practices are essential for their protection.
FAQs
Q: How often should I wash my hands?
A: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends washing hands frequently, especially before eating, after using the restroom, and after contact with sick individuals or contaminated surfaces.
Q: What is the difference between disinfecting and sanitizing?
A: Disinfecting aims to kill most germs on a surface, while sanitizing reduces the number of germs to a safe level.
Q: Are all disinfectants effective against all germs?
A: No, the effectiveness of disinfectants varies depending on the type of germ and the disinfectant’s active ingredients.
Q: Is it safe to use bleach on all surfaces?
A: Bleach can damage some surfaces, so it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and dilute it properly.
Q: How long should I wash my hands for?
A: The CDC recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds, making sure to lather all surfaces.
Q: Can I use hand sanitizer instead of washing my hands?
A: Hand sanitizers are a good alternative when soap and water are unavailable, but they are not as effective as washing hands.
Tips for Effective Germ Elimination
- Wash hands frequently and thoroughly.
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water are unavailable.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces regularly, especially high-touch areas like door handles, countertops, and phones.
- Wash fruits and vegetables before eating.
- Cook meat and poultry to the proper temperature.
- Avoid sharing personal items like toothbrushes and razors.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Get vaccinated against preventable diseases.
Conclusion
Germ elimination is an essential aspect of maintaining personal health and preventing the spread of disease. By understanding the science behind germ elimination methods, we can make informed choices about how to protect ourselves and others. From handwashing and disinfection to vaccination and proper hygiene practices, effective germ elimination strategies play a crucial role in creating a healthier and safer environment for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Germ Elimination: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Disinfection. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!