The Spectrum of Smokable Substances: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The Spectrum of Smokable Substances: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Spectrum of Smokable Substances: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Spectrum of Smokable Substances: A Comprehensive Overview

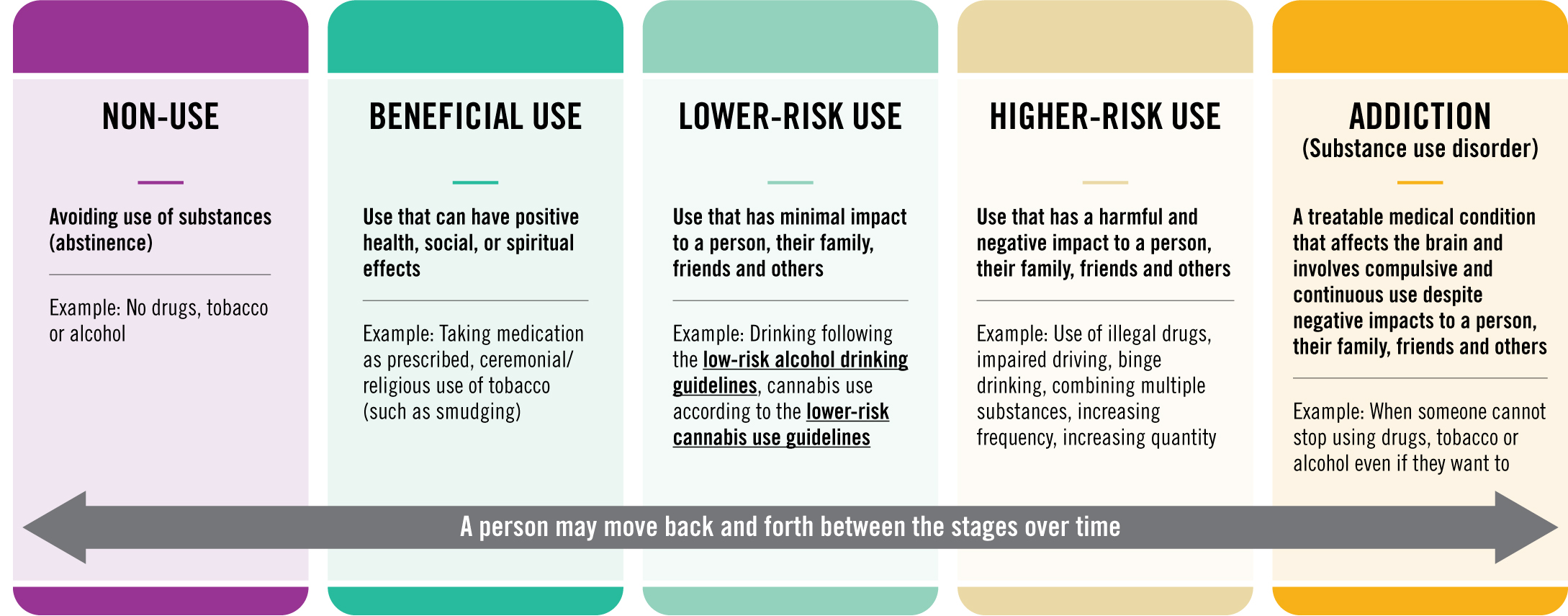
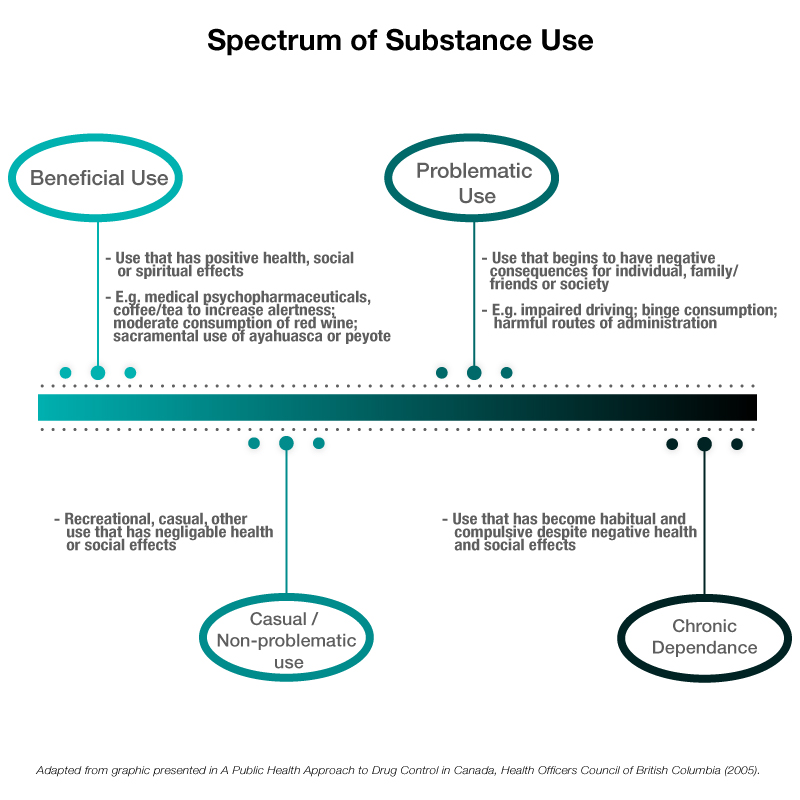
The act of smoking, historically and culturally ingrained in human societies, encompasses a wide range of substances, each with distinct properties, effects, and implications. This exploration delves into the diverse world of smokable materials, providing a comprehensive understanding of their characteristics, uses, and potential risks.
Tobacco:
Tobacco, in its various forms, remains the most prevalent smoked substance globally. The primary active ingredient, nicotine, is a highly addictive stimulant that triggers a cascade of physiological responses, including increased heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness.
Cigarettes: Commercially manufactured cigarettes represent the most common form of tobacco consumption. While offering a short-lived sense of relaxation and pleasure, they pose significant health risks, including lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses.
Cigars: Cigars, typically larger and containing more tobacco than cigarettes, are often associated with a slower, more ritualistic smoking experience. However, they carry similar health risks to cigarettes, with potential for even higher levels of exposure to harmful chemicals.
Pipe Tobacco: Smoked in pipes, this tobacco variety is typically blended for specific flavor profiles. Pipe smoking, while often romanticized, remains a significant risk factor for respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
Chewing Tobacco: While not technically smoked, chewing tobacco delivers nicotine through the oral mucosa. This form of tobacco use is associated with an increased risk of oral cancers, gum disease, and heart disease.
Smokeless Tobacco: Another form of oral tobacco, smokeless tobacco is often presented as a safer alternative to smoking. However, research has shown it to be linked to similar health risks, including oral cancers and cardiovascular issues.
Cannabis (Marijuana):
Cannabis, a plant containing psychoactive compounds like THC and CBD, has gained increasing acceptance for its medicinal and recreational uses.
Medical Cannabis: Used to alleviate pain, nausea, and other symptoms associated with chronic conditions, medical cannabis is often prescribed by physicians.
Recreational Cannabis: Consumed for its psychoactive effects, recreational cannabis can induce feelings of relaxation, euphoria, and altered perception. While generally considered less harmful than tobacco, cannabis use can lead to cognitive impairment, respiratory issues, and dependence.
Herbal Alternatives:
Beyond tobacco and cannabis, a diverse array of herbs and plant materials are smoked for various purposes, often for their perceived medicinal or spiritual benefits.
Damiana: Traditionally used as an aphrodisiac, damiana is known for its mildly stimulating effects and potential to enhance mood.
Catnip: Known for its effects on felines, catnip can induce a state of euphoria and relaxation in humans.
Lavender: Often used in aromatherapy, lavender is believed to possess calming and relaxing properties.
Sage: Used for centuries in traditional medicine, sage is often smoked for its purported cleansing and purifying effects.
Other Smokable Substances:
Beyond the aforementioned categories, various other substances are occasionally smoked, often for specific cultural or ceremonial purposes.
Opium: Derived from the poppy plant, opium is a highly addictive narcotic with potent pain-relieving and sedative properties.
Kratom: A Southeast Asian plant, kratom contains alkaloids with stimulant and sedative effects, often used for pain relief and mood enhancement.
Salvia divinorum: A potent hallucinogenic herb, salvia divinorum induces intense and often unpredictable psychedelic experiences.
Risks and Considerations:
Smoking, regardless of the substance, presents inherent risks to human health.
Respiratory Issues: Smoke inhalation irritates the lungs, leading to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and other respiratory ailments.
Cardiovascular Disease: Smoking increases the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular complications.
Cancer: Numerous studies have linked smoking to various types of cancer, including lung, throat, bladder, and pancreatic cancer.
Addiction: Many smokable substances, particularly tobacco and cannabis, are highly addictive, leading to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Mental Health: Smoking can exacerbate mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and psychosis.
Legal Considerations:
The legality of smoking varies widely depending on the substance, location, and individual circumstances.
Tobacco: Smoking tobacco is generally restricted in public places and subject to age restrictions.
Cannabis: The legal status of cannabis varies significantly across jurisdictions, ranging from complete prohibition to legal recreational use.
Other Substances: The possession and use of many other smokable substances, such as opium and kratom, are often illegal.
Conclusion:
The world of smokable substances is diverse and complex, encompassing a wide range of materials with distinct properties and effects. While some substances, like tobacco, pose significant health risks, others, like medical cannabis, offer potential therapeutic benefits. It is crucial to understand the potential risks and legal implications associated with each substance before engaging in any form of smoking. Informed decision-making, based on accurate information and individual circumstances, is essential for navigating the complex landscape of smokable materials.
FAQs:
Q: Is smoking safe?
A: No, smoking is not safe. All forms of smoking carry health risks, some more severe than others.
Q: What are the most common health risks associated with smoking?
A: Smoking increases the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, COPD, and other respiratory ailments.
Q: Is it legal to smoke cannabis?
A: The legal status of cannabis varies widely. It is legal for recreational use in some jurisdictions and for medical purposes in others.
Q: What are some alternatives to smoking?
A: Alternatives to smoking include vaping, edibles, and other forms of consumption that do not involve inhaling smoke.
Q: What are some tips for quitting smoking?
A: Tips for quitting smoking include seeking professional support, utilizing nicotine replacement therapy, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits.
Q: What are the long-term effects of smoking?
A: Long-term effects of smoking include chronic respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and premature aging.
Q: How can I learn more about the risks of smoking?
A: Information about the risks of smoking can be found from reputable sources such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the World Health Organization (WHO), and other health organizations.
Conclusion:
The act of smoking, while often associated with pleasure and relaxation, carries inherent risks to human health. Informed decision-making, based on a comprehensive understanding of the properties, effects, and potential risks of each substance, is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of smokable materials. Seeking professional guidance and prioritizing health and well-being should be paramount in any decisions related to smoking.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Spectrum of Smokable Substances: A Comprehensive Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!