The World of Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The World of Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The World of Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The World of Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview

Explosives, substances capable of rapid energy release, have played a significant role in human history, shaping both advancement and destruction. From mining and construction to warfare and demolition, their applications are diverse and often essential. Understanding the various types of explosives and their properties is crucial for safety, control, and responsible utilization.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the world of explosives, exploring their classifications, characteristics, applications, and associated risks.
Classifying Explosives: A Framework for Understanding
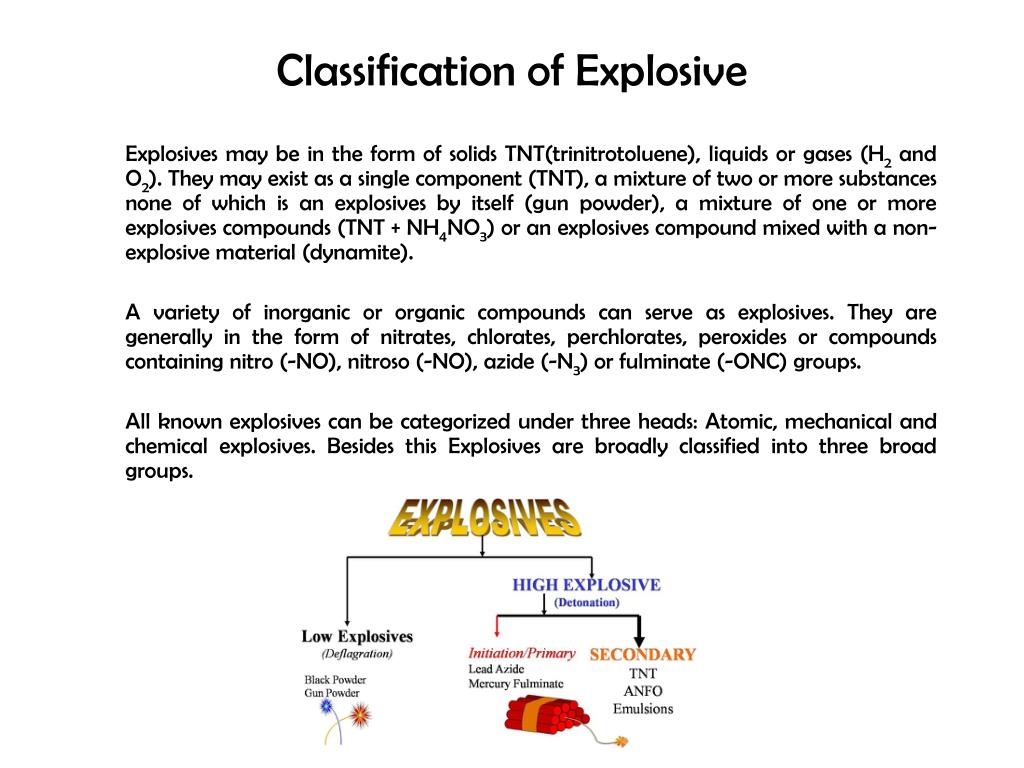
Explosives are categorized based on their chemical composition, detonation mechanism, and intended use. This categorization provides a structured approach to understanding their diverse properties and applications.
1. Primary Explosives:
Primary explosives are highly sensitive compounds that detonate readily upon initiation by heat, impact, or friction. They are often used as detonators to initiate the explosion of less sensitive secondary explosives.
- Mercury Fulminate: This classic primary explosive is known for its extreme sensitivity and is commonly used in blasting caps and detonators.
- Lead Azide: A less sensitive primary explosive than mercury fulminate, lead azide is widely used in detonators for its stability and reliability.
- Diazodinitrophenol (DDNP): This explosive is highly sensitive to impact and friction but is favored for its stability and ease of handling.
2. Secondary Explosives:
Secondary explosives require a significant energy input, such as a detonator, to initiate detonation. They are less sensitive than primary explosives and are commonly used in larger-scale applications.
- Dynamite: This iconic explosive consists of nitroglycerin absorbed into a porous material like diatomaceous earth. Its power and relative stability have made it a mainstay in mining and construction.
- Ammonium Nitrate-Fuel Oil (ANFO): This highly effective explosive mixture is widely used in mining and quarrying due to its low cost and ease of production.
- TNT (Trinitrotoluene): A powerful and relatively stable explosive, TNT is commonly used in military munitions, demolition, and industrial applications.
3. Tertiary Explosives:
Tertiary explosives are insensitive materials that require a large amount of energy to detonate. They are often used in military applications and are designed to be safe during transportation and handling.
- HMX (Octogen): This powerful explosive is highly stable and is commonly used in military munitions and rocket propellants.
- RDX (Cyclonite): Another high-explosive material, RDX is used in military munitions, demolition, and rocket propellants.
4. Black Powder:
This historical explosive is a mixture of charcoal, sulfur, and potassium nitrate. While less powerful than modern explosives, black powder is still used in pyrotechnics, fireworks, and some specialized applications.
5. Propellants:
Propellants are explosives that burn rapidly and produce a large volume of gas, providing thrust for projectiles or rockets.
- Gunpowder: A low-explosive propellant used in firearms and other pyrotechnic applications.
- Smokeless Powder: A modern propellant that produces less smoke and residue than gunpowder, making it suitable for firearms and rockets.
- Solid Rocket Propellants: These propellants are used in rockets and provide sustained thrust for space exploration and military applications.
The Importance of Explosives: Shaping the World Around Us
Explosives have played a pivotal role in shaping the world around us, contributing to advancements in various fields:
- Mining and Construction: Explosives are essential for extracting minerals and resources from the earth, enabling the construction of roads, bridges, and buildings.
- Demolition: Controlled explosions are crucial for demolition projects, allowing for the safe and efficient removal of structures.
- Military Applications: Explosives are integral to military operations, used in weapons, ammunition, and demolition charges.
- Research and Development: Explosives are utilized in research and development, contributing to advancements in materials science, engineering, and other scientific fields.
Safety and Responsibility: The Crucial Role of Regulation and Education
Despite their benefits, explosives pose significant risks if not handled properly. Therefore, strict regulations and responsible practices are essential for ensuring safety and minimizing harm:
- Regulation: Governments worldwide implement stringent regulations governing the production, storage, transportation, and use of explosives. These regulations aim to control access, prevent misuse, and ensure responsible handling.
- Education and Training: Proper education and training are crucial for individuals working with explosives. This includes understanding the properties, hazards, and safe handling practices of different explosives.
- Security and Storage: Secure storage facilities and robust security measures are necessary to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the risks of accidental explosions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Explosives
Q: What is the difference between an explosion and a detonation?
A: An explosion is a rapid expansion of volume caused by a sudden release of energy. A detonation is a supersonic exothermic reaction that propagates through a material at a speed greater than the speed of sound.
Q: Are all explosives dangerous?
A: While all explosives have the potential to be dangerous, their level of risk depends on their sensitivity, stability, and intended use. Responsible handling and proper storage are essential for minimizing hazards.
Q: How are explosives used in mining?
A: Explosives are used in mining to break up rock formations, allowing for the extraction of valuable minerals and resources. They are also used for creating access tunnels and excavating large areas.
Q: What are some safety precautions for handling explosives?
A: Always handle explosives with extreme caution. Follow all safety regulations and guidelines, wear appropriate protective gear, and never experiment with explosives.
Tips for Understanding Explosives
- Research: Consult reputable sources like scientific journals, textbooks, and government websites for in-depth information on explosives.
- Learn the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the classification, properties, and applications of different types of explosives.
- Seek Expert Guidance: If you are working with explosives, consult with qualified professionals and follow their instructions.
Conclusion: A Vital Force in Our World
Explosives are powerful substances with both destructive and constructive potential. Understanding their properties, applications, and associated risks is crucial for their responsible utilization. By adhering to safety regulations, promoting education, and prioritizing responsible practices, we can harness the power of explosives for progress and advancement while mitigating their potential dangers.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The World of Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!