Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look At The Biggest Energy Hogs In Our Homes
Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look at the Biggest Energy Hogs in Our Homes
Related Articles: Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look at the Biggest Energy Hogs in Our Homes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look at the Biggest Energy Hogs in Our Homes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look at the Biggest Energy Hogs in Our Homes

In today’s world, electricity is an indispensable part of our lives. It powers our homes, businesses, and the very infrastructure that sustains modern society. However, this reliance on electricity comes with a cost, both financial and environmental. Understanding the energy consumption patterns of various electrical appliances and devices is crucial for making informed choices about energy usage and minimizing our impact on the planet.
This article delves into the world of energy consumption, examining the electrical items that contribute most significantly to our energy bills and environmental footprint. By analyzing the factors that drive energy usage, we gain valuable insights into how to optimize our energy consumption and make more sustainable choices.
The Top Energy Consumers in Our Homes
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
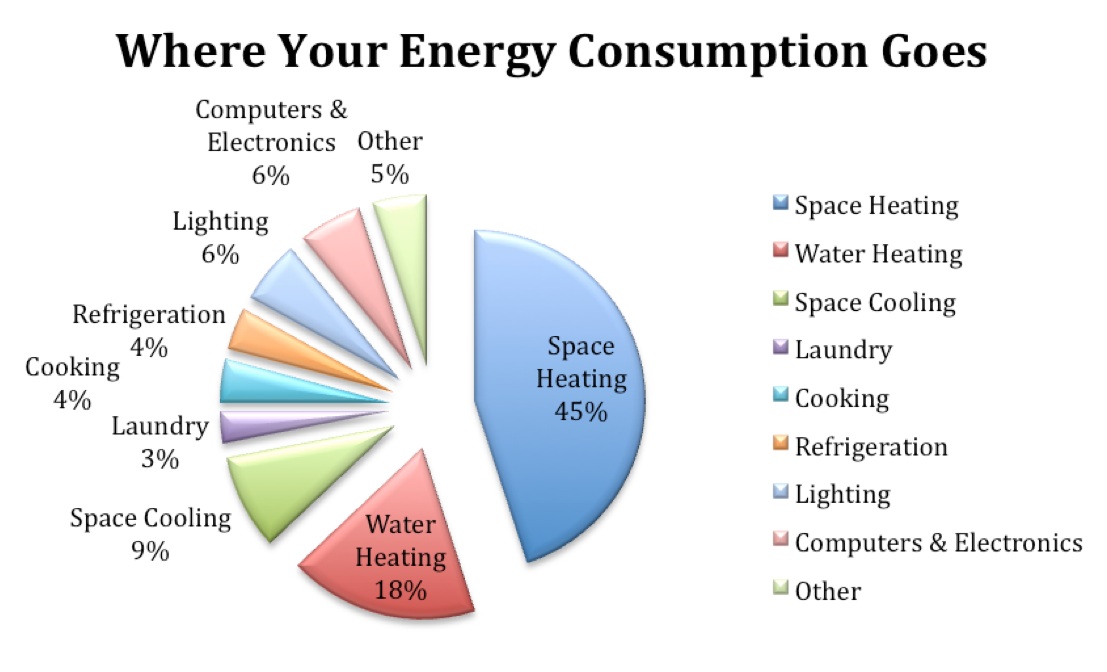
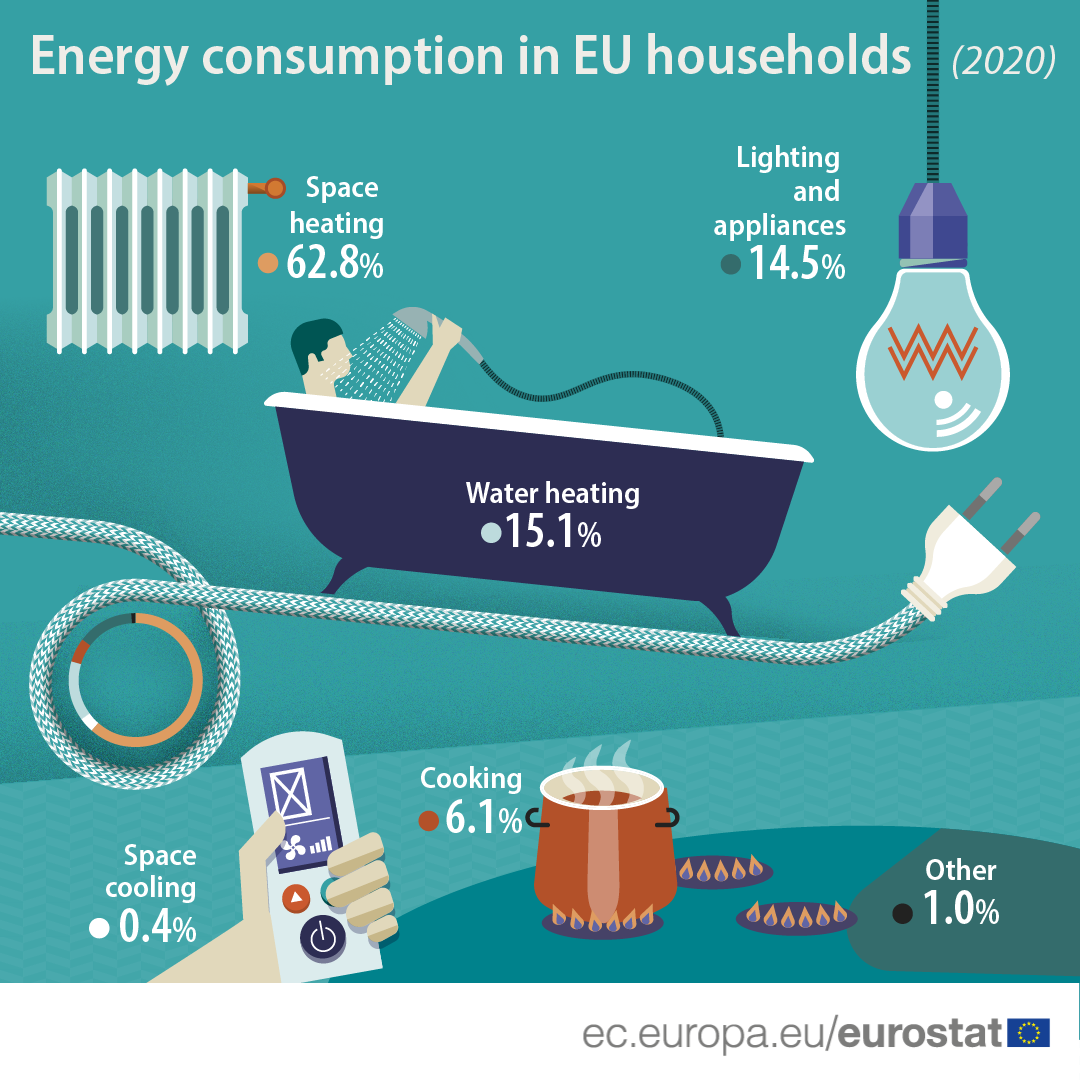
Heating and cooling systems are often the largest energy consumers in residential homes, accounting for roughly 40-50% of total energy usage. This is primarily due to the sheer amount of energy required to maintain comfortable temperatures, especially in regions with extreme climates.
-
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Climate: Regions with colder winters and hotter summers necessitate greater heating and cooling demands, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Home Insulation: Properly insulated homes retain heat in winter and prevent heat gain in summer, reducing the need for extensive heating or cooling.
- System Efficiency: Modern heating and cooling systems with higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings consume less energy to achieve the desired temperatures.
- Usage Habits: Setting thermostats to comfortable but energy-efficient temperatures and utilizing programmable thermostats can significantly reduce energy consumption.
2. Water Heating:
Heating water for various domestic purposes, including showering, bathing, and dishwashing, is another major energy consumer in homes. Water heaters account for approximately 14% of total household energy use.
-
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Water Heater Type: Tank-style water heaters tend to consume more energy than tankless or on-demand water heaters.
- Water Heater Size: Larger water heaters consume more energy to heat the water.
- Water Usage Habits: Taking shorter showers and using energy-efficient showerheads can reduce water heating energy consumption.
3. Appliances:
Appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, and ovens are essential for modern living, but they also contribute significantly to household energy use.
-
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Appliance Efficiency: Appliances with higher Energy Star ratings are more energy efficient, consuming less energy for the same functionality.
- Usage Habits: Leaving appliances running unnecessarily or using them inefficiently can lead to higher energy consumption.
- Appliance Size: Larger appliances, like refrigerators or washing machines, generally consume more energy.
4. Lighting:
Lighting accounts for a significant portion of household energy consumption, particularly in homes with outdated lighting fixtures.
-
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Bulb Type: Incandescent bulbs are the least efficient, while LED bulbs offer the highest energy efficiency.
- Lighting Usage: Turning off lights when leaving a room and using timers or motion sensors to control lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption.
5. Electronics:
While individual electronic devices like televisions, computers, and gaming consoles may seem to consume relatively small amounts of energy, their cumulative energy usage can be substantial.
-
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Device Efficiency: Newer electronic devices often have higher energy efficiency ratings.
- Usage Habits: Leaving electronics plugged in when not in use or using them for extended periods can increase energy consumption.
- Standby Power: Even when turned off, many electronic devices continue to consume a small amount of power in standby mode.
Understanding the Importance of Energy Efficiency
The choice of electrical appliances and devices has a profound impact on our energy consumption and environmental footprint. By opting for energy-efficient models and practicing energy-saving habits, we can significantly reduce our energy bills and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Benefits of Energy Efficiency:
- Reduced Energy Bills: Energy-efficient appliances and devices consume less energy, leading to lower electricity bills.
- Environmental Protection: By reducing energy consumption, we lessen our reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions: Fossil fuel power plants are a major source of carbon emissions, and reducing energy consumption helps mitigate climate change.
- Enhanced Comfort and Convenience: Energy-efficient appliances and devices often offer improved functionality and comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What appliances use the most energy in a typical home?
A: The appliances that typically consume the most energy in a home are heating and cooling systems, water heaters, refrigerators, washing machines, and dryers.
Q: How can I reduce my energy consumption at home?
A: There are numerous ways to reduce energy consumption at home, including:
- Choose energy-efficient appliances and devices.
- Insulate your home properly.
- Use programmable thermostats and set them to comfortable but energy-efficient temperatures.
- Take shorter showers and use energy-efficient showerheads.
- Unplug appliances and electronics when not in use.
- Use LED bulbs for lighting.
- Wash clothes in cold water and air-dry them whenever possible.
- Avoid leaving the refrigerator door open for extended periods.
Q: What are some tips for saving energy while using electronics?
A: Here are some tips for reducing energy consumption from electronics:
- Turn off electronics when not in use.
- Unplug chargers and devices when not in use.
- Use energy-saving settings on your computer and other devices.
- Consider purchasing energy-efficient models.
- Avoid leaving electronics in standby mode.
Conclusion
Understanding the energy consumption patterns of our electrical appliances and devices is crucial for making informed choices about our energy usage. By opting for energy-efficient models, practicing energy-saving habits, and implementing smart energy solutions, we can significantly reduce our energy bills and environmental impact. This collective effort will contribute to a more sustainable future, ensuring a cleaner and healthier planet for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Energy Consumption: A Look at the Biggest Energy Hogs in Our Homes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!