Understanding The Building Blocks Of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Assets
Understanding the Building Blocks of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Assets
Related Articles: Understanding the Building Blocks of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Assets
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Building Blocks of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Assets. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Building Blocks of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Assets

The term "household assets" encompasses a wide range of tangible and intangible possessions that contribute to a family’s financial well-being. These assets represent accumulated wealth, provide financial security, and can be leveraged for various purposes, from meeting everyday expenses to funding future goals. Understanding the different categories of household assets is crucial for individuals and families to effectively manage their finances, plan for the future, and achieve their financial aspirations.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of the diverse components that constitute household assets, highlighting their significance and the benefits they offer. It aims to provide a clear and informative understanding of the various forms of wealth individuals and families accumulate, empowering them to make informed financial decisions.
Defining the Scope of Household Assets
Household assets encompass a broad spectrum of resources, including both physical possessions and financial instruments. These assets can be categorized as follows:
1. Real Estate:
- Primary Residence: The most significant asset for many households, the primary residence provides shelter and can appreciate in value over time. It can be a source of equity that can be accessed through refinancing or home equity loans.
- Rental Properties: Investment properties generate rental income, providing a steady stream of cash flow and potential appreciation. They can be a valuable source of passive income and diversification in a real estate portfolio.
- Land: Undeveloped land can be a long-term investment, appreciating in value as the surrounding area develops. It can be used for future development or simply held as a store of value.
2. Financial Assets:
- Cash and Equivalents: This includes readily available funds in checking and savings accounts, money market accounts, and short-term investments like treasury bills. These assets provide liquidity for immediate needs and emergency funds.
-
Investments: This category encompasses a wide range of instruments, including:
- Stocks: Ownership in publicly traded companies, offering potential for capital appreciation and dividend income.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by corporations or governments, providing fixed income payments and potential for capital appreciation.
- Mutual Funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Diversified portfolios of stocks, bonds, or other assets, offering convenience and professional management.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Companies that own and operate income-producing real estate, providing exposure to the real estate market without direct ownership.
- Annuities: Contracts that provide a guaranteed stream of income for a specific period.
-
Retirement Accounts: These tax-advantaged accounts are designed to accumulate funds for retirement. Examples include:
- 401(k)s: Employer-sponsored retirement plans offering tax-deferred growth.
- IRAs: Individual retirement accounts allowing individuals to save for retirement with tax advantages.
- Life Insurance: While not strictly an asset, life insurance policies can provide a death benefit that can be used to cover expenses or provide financial support to beneficiaries.
3. Personal Property:
- Vehicles: Automobiles, motorcycles, and other vehicles are valuable assets that can be used for transportation or as investments.
- Jewelry and Collectibles: Precious metals, gemstones, artwork, and other collectibles can appreciate in value over time and offer potential for investment.
- Household Furnishings and Appliances: While not typically considered investments, these assets contribute to the overall value of a home and can provide comfort and enjoyment.
4. Intangible Assets:
- Intellectual Property: Patents, trademarks, copyrights, and other forms of intellectual property can be valuable assets, generating income or providing competitive advantage.
- Human Capital: An individual’s skills, knowledge, and experience represent a valuable asset that can contribute to earning potential and career advancement.
The Importance of Household Assets
Understanding the various components of household assets is essential for individuals and families to:
- Build Financial Security: Assets provide a safety net, enabling households to weather financial storms and achieve financial independence.
- Meet Financial Goals: Assets can be used to fund major life events, such as buying a home, paying for education, or starting a business.
- Generate Income: Some assets, like rental properties and investments, can provide a steady stream of passive income.
- Enhance Quality of Life: Assets can contribute to a more comfortable lifestyle, providing access to amenities and experiences.
- Transfer Wealth: Assets can be passed down to future generations, ensuring financial stability for loved ones.
FAQs about Household Assets
Q: How do I determine the value of my household assets?
A: The value of assets can fluctuate over time. For tangible assets like real estate and vehicles, professional appraisals or market research can provide an accurate assessment. For financial assets, online tools and brokerage statements can provide real-time valuations.
Q: What are the tax implications of owning different types of assets?
A: The tax implications of owning assets vary depending on the type of asset and applicable tax laws. For example, capital gains taxes may apply to the sale of appreciated assets, while income from investments may be subject to ordinary income tax rates.
Q: How can I diversify my household assets?
A: Diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes to mitigate risk. This can be achieved by investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets.
Q: What are some strategies for protecting my household assets?
A: Protecting assets involves implementing measures to mitigate risks, such as:
- Insurance: Homeowners, renters, and vehicle insurance policies can provide financial protection against losses.
- Estate Planning: Wills, trusts, and other estate planning tools can ensure assets are distributed according to your wishes.
- Safeguarding Documents: Storing important documents securely can prevent loss or theft.
Tips for Managing Household Assets
- Track Your Assets: Regularly review and update your asset inventory to monitor performance and identify potential adjustments.
- Set Financial Goals: Define your financial objectives, such as retirement savings, homeownership, or education funding.
- Develop a Budget: Create a budget that allocates funds for essential expenses, savings, and investment.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors to develop a personalized asset management strategy.
- Stay Informed: Continuously learn about the financial markets and economic trends to make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Household assets are the building blocks of financial security and well-being. Understanding the different categories of assets, their value, and their potential benefits empowers individuals and families to make informed financial decisions, achieve their financial goals, and build a secure future. By diligently managing their assets, individuals can create a solid foundation for a comfortable and fulfilling life.
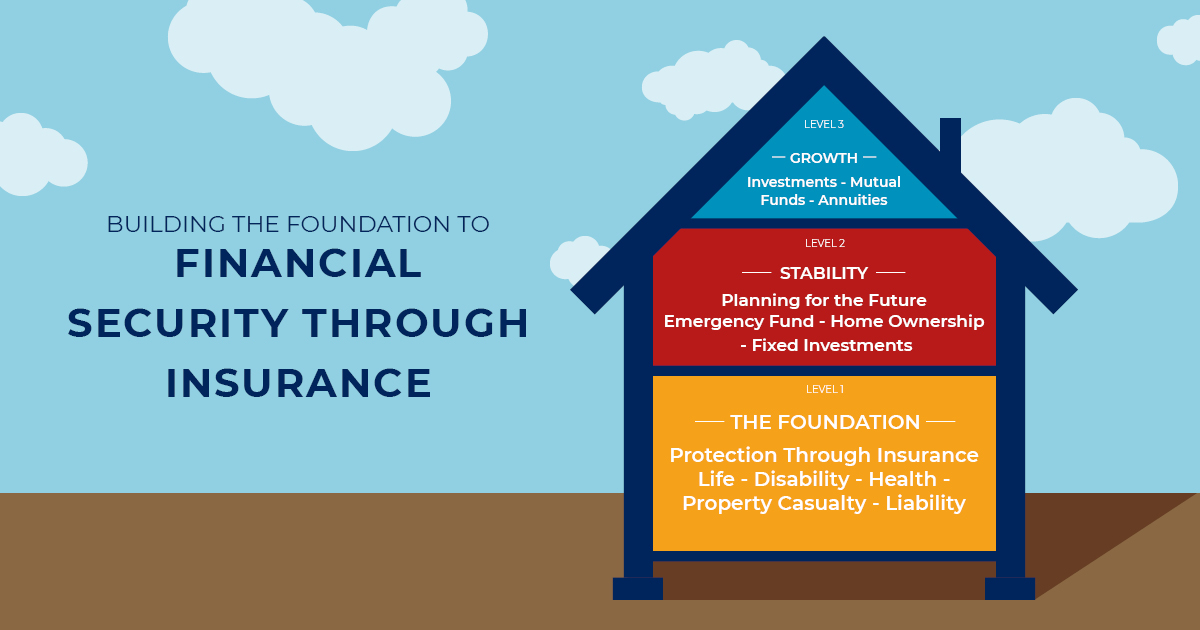
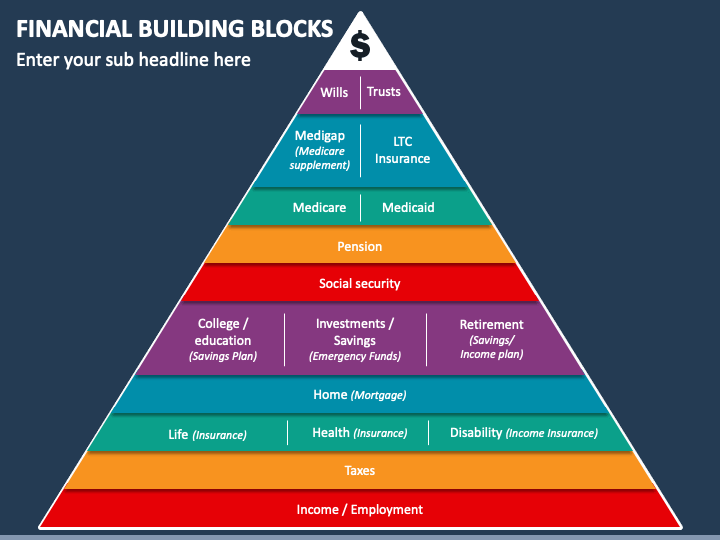




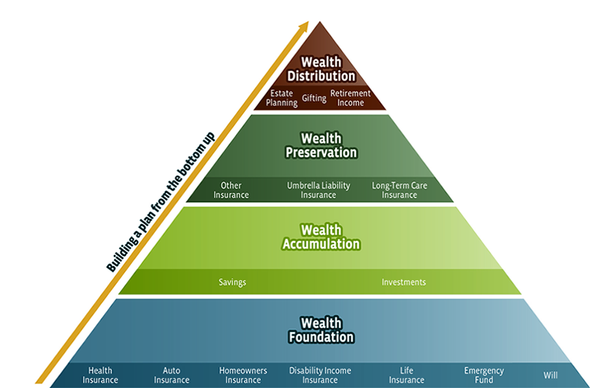
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Building Blocks of Financial Security: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Assets. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!