Understanding The Energy Hogs In Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Electricity Consumption
Understanding the Energy Hogs in Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Understanding the Energy Hogs in Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Energy Hogs in Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Energy Hogs in Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption

In today’s world, electricity is an indispensable part of our lives. It powers our appliances, lights our homes, and enables countless conveniences. However, with the increasing demand for energy and its impact on the environment, it’s crucial to understand how much electricity our homes consume and identify the major contributors to this consumption. This article delves into the intricacies of household electricity usage, highlighting the appliances and systems that draw the most power, and offering insights into minimizing energy consumption and optimizing energy efficiency.
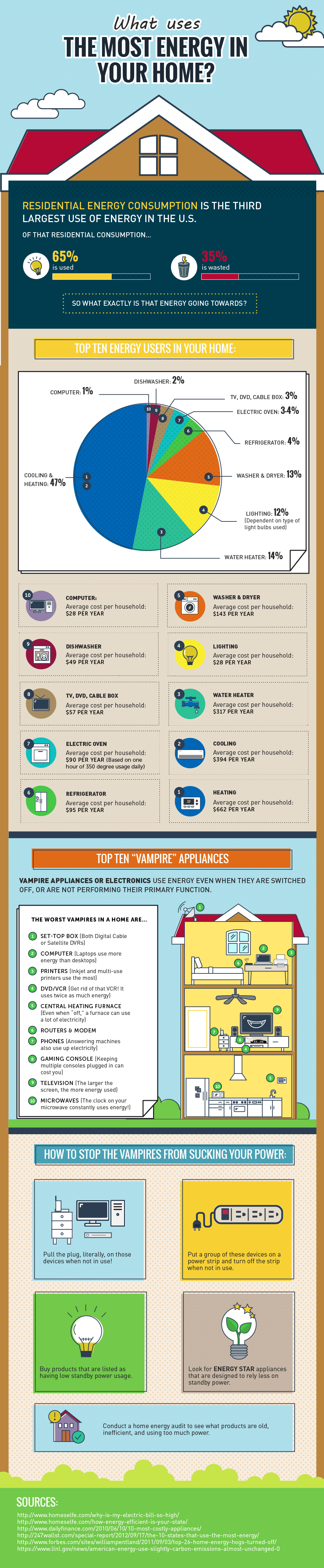
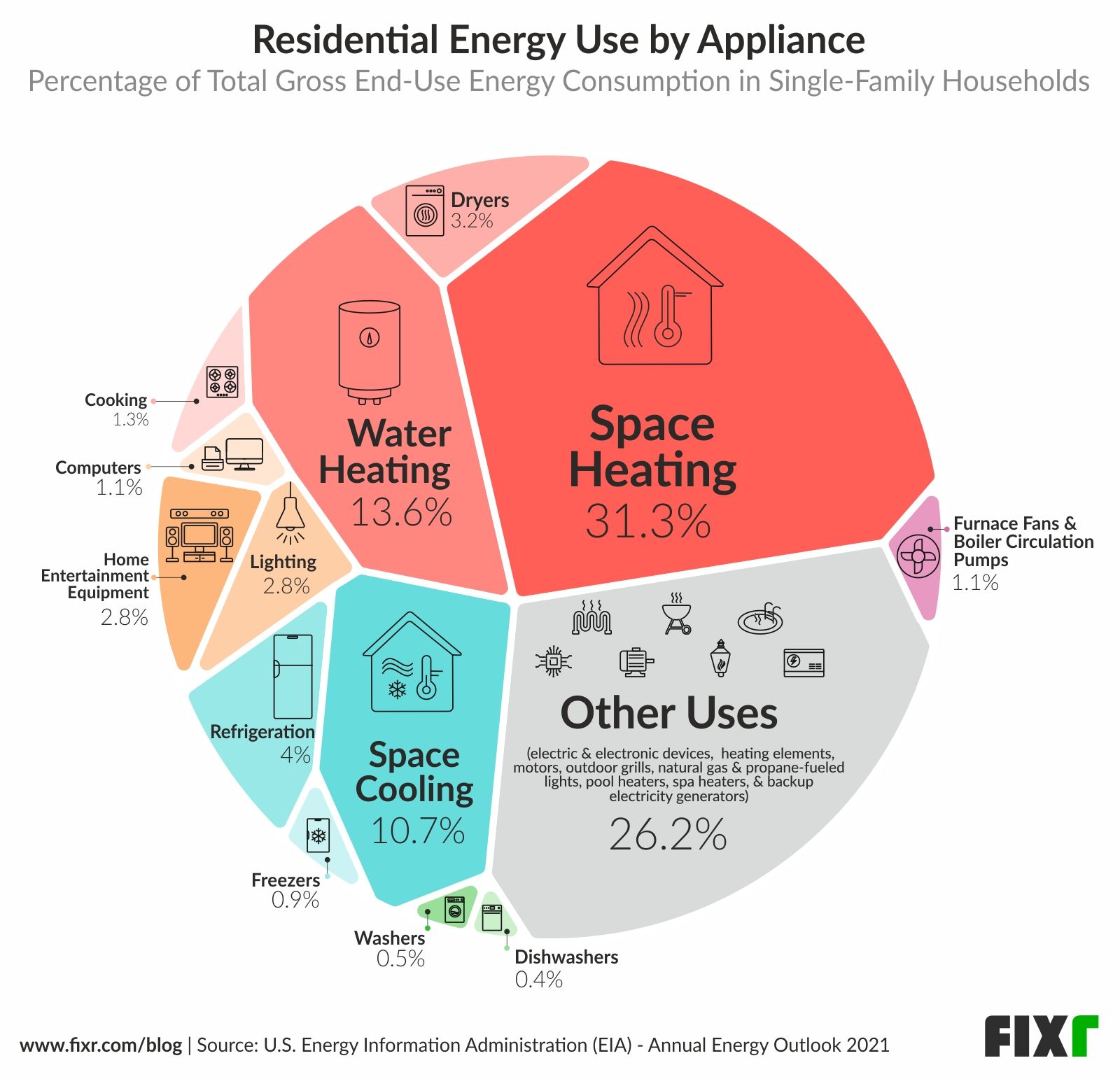
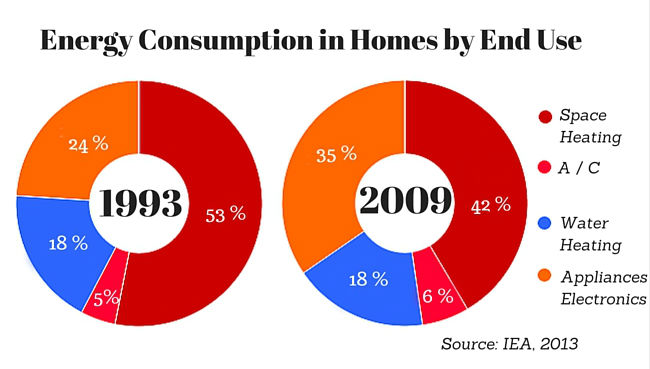
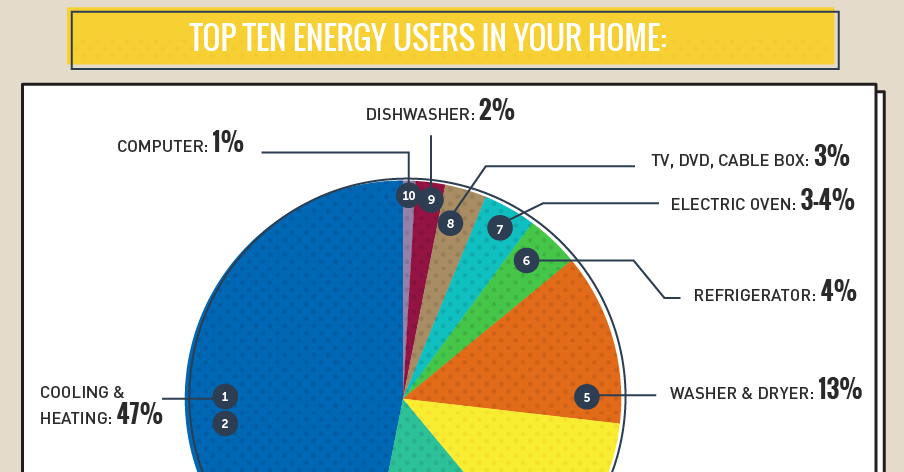
The Big Energy Consumers: Unmasking the Culprits
While every electrical device in a home consumes some energy, certain appliances and systems stand out as significant contributors to overall energy consumption. These "energy hogs" can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
Heating and cooling systems are often the biggest energy consumers in a home, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
- Heating Systems: Gas furnaces, electric furnaces, heat pumps, and boilers are responsible for a substantial portion of household energy usage, especially during the winter months.
- Cooling Systems: Central air conditioners, window air conditioners, and evaporative coolers are essential for comfort in hot weather, but their energy consumption can be significant.
2. Water Heating:
Water heating is another major energy consumer, particularly in households with large families or those who frequently use hot water for bathing, laundry, and dishwashing.
- Tank Water Heaters: Traditional tank-style water heaters continuously heat water, leading to substantial energy consumption.
- Tankless Water Heaters: Tankless water heaters heat water only when needed, offering greater efficiency compared to tank-style heaters.
3. Appliances:
Modern appliances, while convenient, can contribute significantly to household energy consumption.
- Refrigerators and Freezers: These appliances run continuously, making them major energy consumers. Older models are particularly energy-intensive.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers can use a considerable amount of energy and water, especially if used inefficiently.
- Washing Machines and Dryers: Clothes washing and drying are energy-intensive tasks, particularly with older models.
- Ovens and Ranges: Electric ovens and ranges use a significant amount of energy, especially during baking and roasting.
- Microwaves: Microwaves are generally more energy-efficient than traditional ovens, but their usage can still contribute to overall energy consumption.
4. Lighting:
While lighting may seem like a minor energy consumer, the cumulative effect of numerous lights throughout a home can be significant.
- Incandescent Bulbs: Incandescent bulbs are notoriously inefficient, converting only a small portion of energy into light, the rest being wasted as heat.
- Fluorescent Bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs are more efficient than incandescent bulbs, but they contain mercury and require proper disposal.
- LED Bulbs: LED bulbs are the most energy-efficient lighting option, offering significant energy savings and a longer lifespan.
5. Electronics and Entertainment Systems:
Modern homes are filled with electronic devices that contribute to overall energy consumption, even when not in use.
- Televisions: Large-screen TVs, particularly older models, can consume a significant amount of energy.
- Computers and Laptops: While energy consumption varies depending on usage, computers and laptops can be substantial energy consumers.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles, especially those with high-resolution graphics, can consume a considerable amount of power.
- Home Theater Systems: Home theater systems, including soundbars and surround sound speakers, can contribute to overall energy consumption.
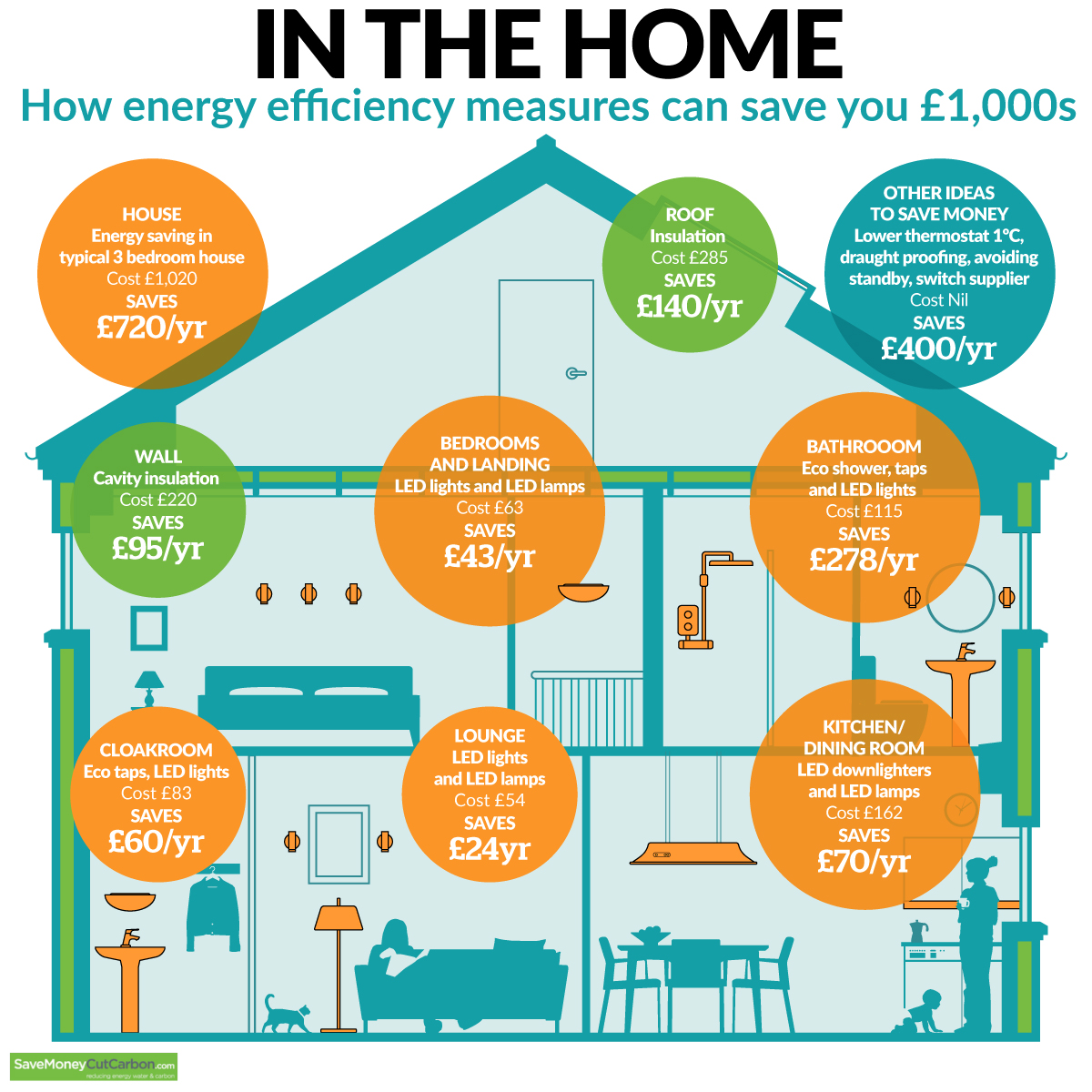
Understanding the Importance of Energy Efficiency
The understanding of energy consumption patterns in homes is crucial for several reasons:
- Financial Savings: Reducing energy consumption translates to lower electricity bills, saving money on household expenses.
- Environmental Sustainability: Lowering energy consumption reduces reliance on fossil fuels, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Resource Conservation: Efficient energy usage promotes responsible resource management, minimizing the strain on natural resources.
FAQs: Demystifying Household Electricity Consumption
Q: What are the most energy-efficient appliances?
A: Energy-efficient appliances are generally marked with an Energy Star label, indicating they meet specific energy efficiency standards. This includes refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, dryers, and water heaters.
Q: How can I reduce my home’s energy consumption?
A: Several strategies can help reduce energy consumption:
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replace older, inefficient appliances with Energy Star-rated models.
- Optimize Heating and Cooling Systems: Install programmable thermostats, ensure proper insulation, and seal air leaks.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Switch to LED bulbs for maximum energy savings.
- Practice Water Conservation: Install low-flow showerheads and faucets, and use water-efficient washing machines and dishwashers.
- Unplug Electronics When Not in Use: Unplug chargers, TVs, and other electronics when not in use to prevent phantom energy consumption.
- Use Natural Light: Maximize natural light during the day to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
Tips for Optimizing Energy Efficiency
- Conduct an Energy Audit: A professional energy audit can identify areas for improvement and provide tailored recommendations.
- Install a Smart Meter: Smart meters provide real-time feedback on energy consumption, enabling better energy management.
- Utilize Renewable Energy Sources: Consider installing solar panels or wind turbines to generate clean energy.
- Practice Energy Conservation Habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, use fans instead of air conditioning when possible, and avoid using energy-intensive appliances during peak hours.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sustainable Future
By understanding the energy consumption patterns of our homes and implementing energy-efficient practices, we can significantly reduce our electricity bills, minimize environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future. The key lies in making informed choices about appliances, embracing energy-saving habits, and prioritizing energy efficiency in every aspect of our lives. Through collective action, we can create a future where energy consumption is responsible, sustainable, and beneficial for both individuals and the planet.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Energy Hogs in Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!