Understanding the Role of Stomach Acid in Digestion: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Role of Stomach Acid in Digestion: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Role of Stomach Acid in Digestion: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Role of Stomach Acid in Digestion: A Comprehensive Guide

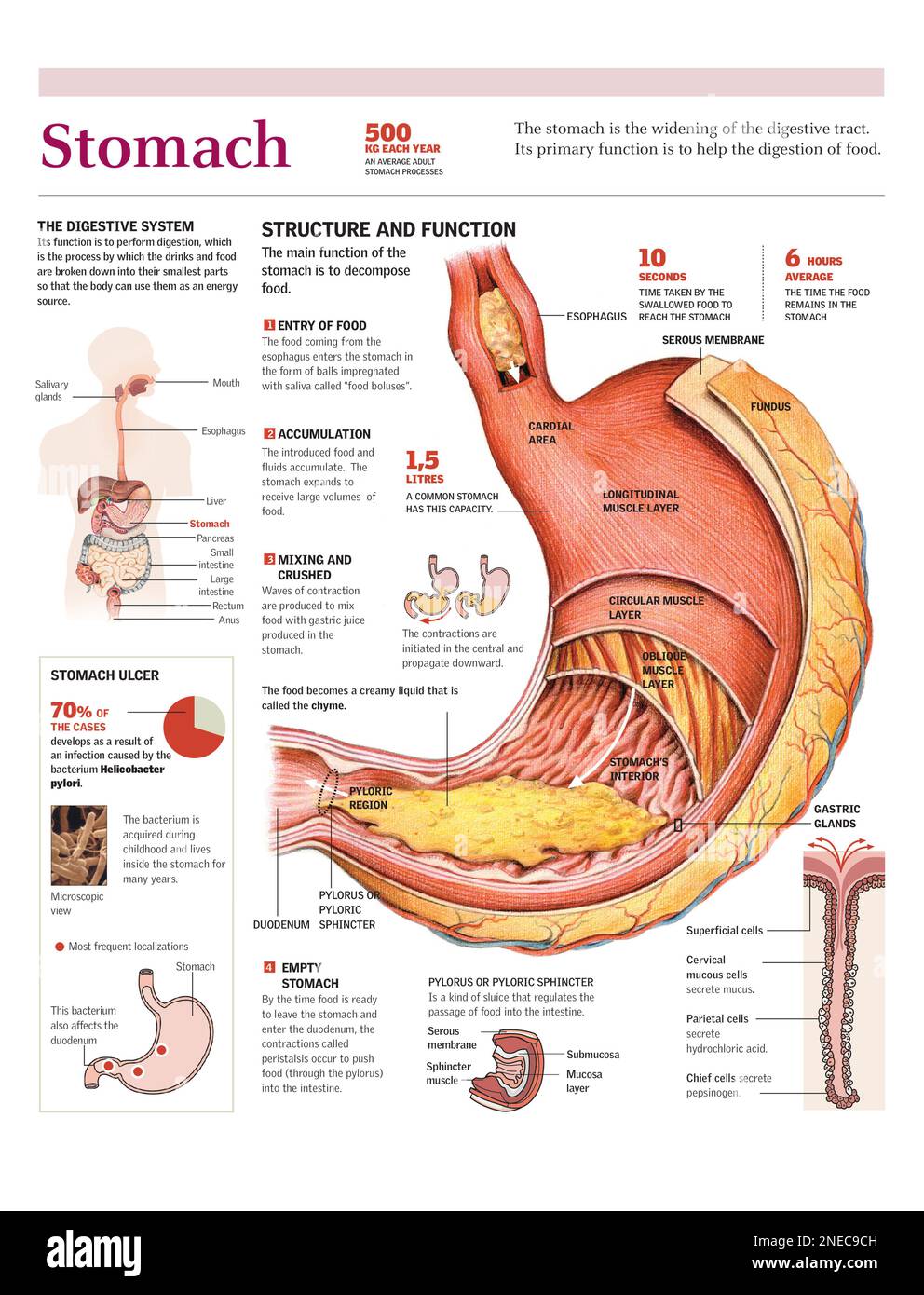
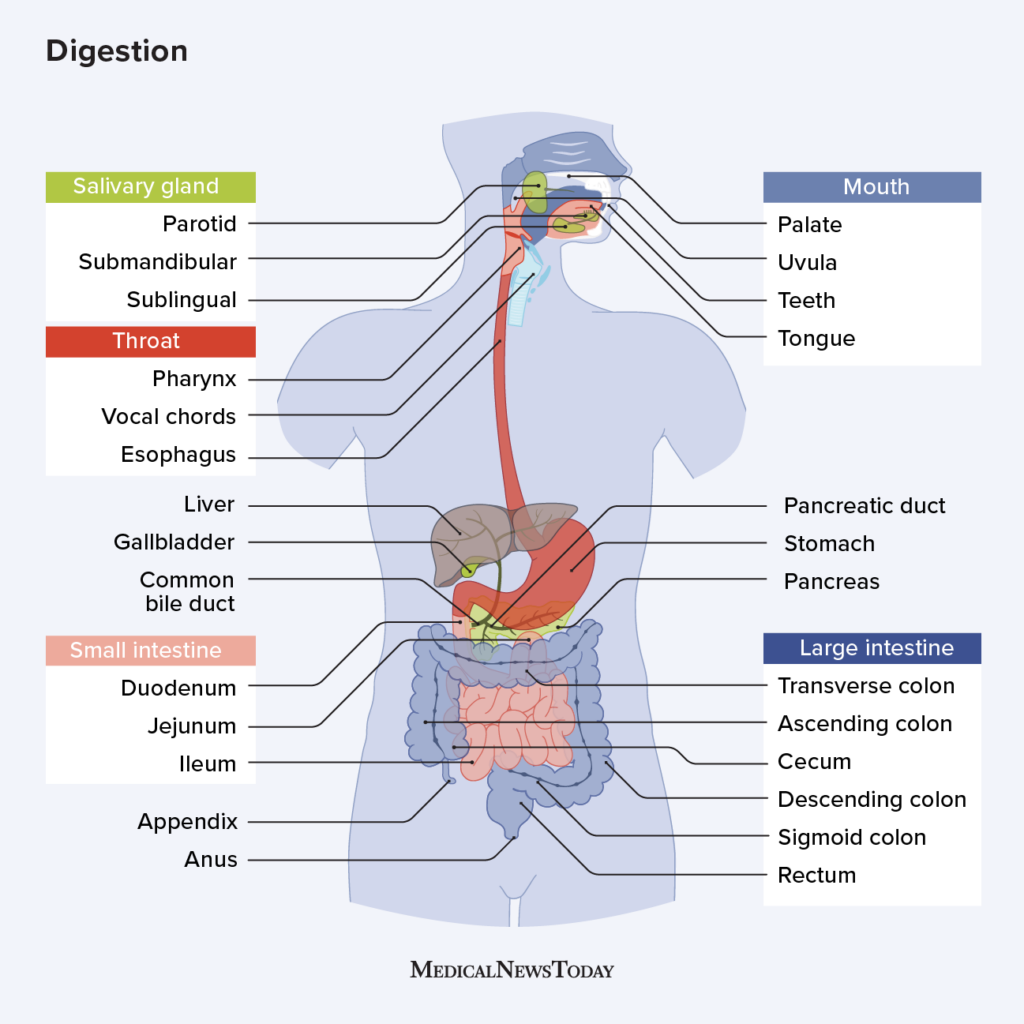
The human digestive system is a complex and intricate network of organs working in harmony to break down food into its essential components, allowing the body to absorb nutrients and eliminate waste. A crucial player in this process is stomach acid, also known as gastric acid, primarily composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl). While the term "hydrochloric acid foods" is not technically accurate, as food itself does not contain hydrochloric acid, it is often used colloquially to refer to foods that stimulate the production of this vital digestive fluid.
The Importance of Stomach Acid
Hydrochloric acid plays a critical role in several key aspects of digestion:
- Activation of Digestive Enzymes: Stomach acid activates pepsin, a primary enzyme responsible for breaking down proteins into smaller peptides. This process is essential for the efficient absorption of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
- Breakdown of Food: The acidic environment created by hydrochloric acid helps soften and break down food particles, making them easier to digest.
- Killing Bacteria: Stomach acid acts as a natural defense mechanism, killing harmful bacteria and pathogens that may be present in food. This protects the body from infections and food poisoning.
- Absorption of Minerals: Hydrochloric acid facilitates the absorption of certain minerals, including iron and calcium, by converting them into forms that can be readily absorbed by the body.
Factors Influencing Stomach Acid Production
Several factors can influence the production of stomach acid, including:
- Food Intake: The presence of food in the stomach triggers the release of gastrin, a hormone that stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid.
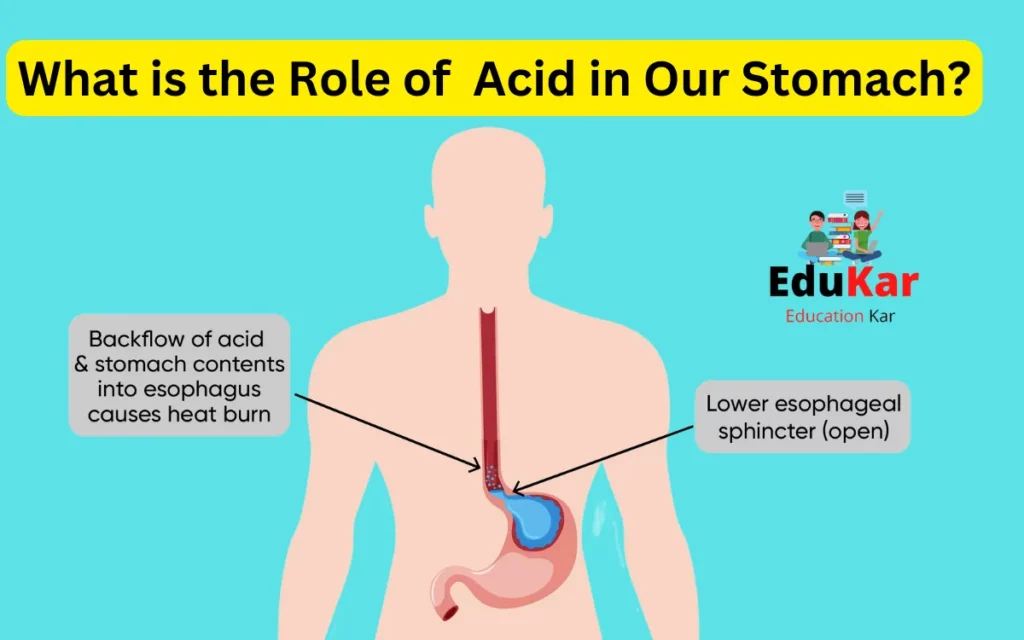
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can lead to increased stomach acid production, sometimes resulting in heartburn or indigestion.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antacids and proton pump inhibitors, can suppress stomach acid production.
- Age: As individuals age, their stomach acid production may naturally decrease.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like gastritis and ulcers can affect stomach acid production.
Foods that Stimulate Stomach Acid Production
While there is no singular "hydrochloric acid food," certain foods are known to stimulate the production of gastric acid, contributing to optimal digestion. These include:
- Citrus Fruits: Lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruits are rich in citric acid, which can stimulate the production of stomach acid.
- Vinegar: Apple cider vinegar and other vinegars contain acetic acid, a natural acid that can help with digestion.
- Fermented Foods: Sauerkraut, kimchi, and yogurt contain beneficial bacteria that can aid in digestion and potentially stimulate stomach acid production.
- Spicy Foods: Chili peppers and other spicy foods contain capsaicin, a compound that can stimulate the production of stomach acid.
- High-Protein Foods: Meat, fish, poultry, and eggs are rich in protein, which triggers the release of gastrin and promotes stomach acid production.
- Broths and Soups: Broth and soups, particularly those made with bone-in meats, can stimulate the production of stomach acid and aid in digestion.
Signs of Low Stomach Acid
While excess stomach acid can cause discomfort, low stomach acid can also lead to digestive issues. Some signs of low stomach acid include:
- Indigestion: Difficulty digesting food, especially fatty foods.
- Bloating and Gas: Excess gas and bloating after meals.
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stool due to incomplete digestion.
- Heartburn: Although counterintuitive, low stomach acid can sometimes lead to heartburn due to the inability to break down food properly.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Low stomach acid can hinder the absorption of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies.
Tips for Optimizing Stomach Acid Production
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume a variety of foods, including those mentioned above, that stimulate stomach acid production.
- Chew Food Thoroughly: Proper chewing helps break down food particles, making it easier for stomach acid to work its magic.
- Avoid Overeating: Large meals can overwhelm the stomach and lead to digestive discomfort.
- Manage Stress: Stress can negatively impact digestion. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like exercise, meditation, or deep breathing into your routine.
- Consider Supplements: If you suspect low stomach acid, consult with a healthcare professional about potential supplements like betaine hydrochloride.
FAQs
Q: Is it possible to have too much stomach acid?
A: Yes, excessive stomach acid production can lead to conditions like heartburn, gastritis, and ulcers.
Q: Can I increase my stomach acid production naturally?
A: Yes, consuming foods that stimulate stomach acid production and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help.
Q: What are the risks of low stomach acid?
A: Low stomach acid can lead to various digestive problems, including indigestion, bloating, constipation, and nutrient deficiencies.
Q: Should I take supplements to increase stomach acid?
A: Consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they may not be suitable for everyone.
Conclusion
Hydrochloric acid is an essential component of the digestive process, playing a vital role in breaking down food, killing bacteria, and absorbing nutrients. While the term "hydrochloric acid foods" is not technically accurate, certain foods can stimulate the production of this vital digestive fluid. Maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, and addressing any underlying medical conditions can contribute to optimal stomach acid production and overall digestive health. If you experience persistent digestive issues, seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Role of Stomach Acid in Digestion: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!