Understanding Watt Usage: A Guide to Household Energy Consumption
Related Articles: Understanding Watt Usage: A Guide to Household Energy Consumption
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Watt Usage: A Guide to Household Energy Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Watt Usage: A Guide to Household Energy Consumption

Understanding the energy consumption of common household appliances is crucial for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. This article delves into the wattage of various household items, explaining the significance of this information and providing insights into its practical applications.
Watt Usage: A Measure of Power Consumption
Watts (W) are the units of power, representing the rate at which electrical energy is consumed. The higher the wattage, the more electricity an appliance uses. While wattage alone does not reflect total energy consumption, it provides a useful starting point for comparing the energy efficiency of different devices.
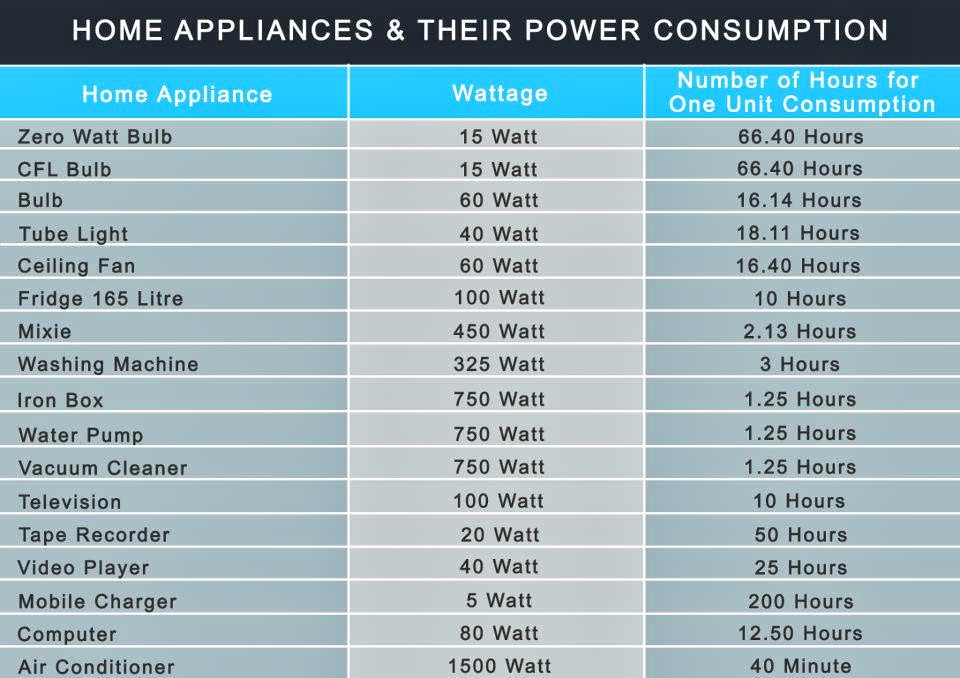
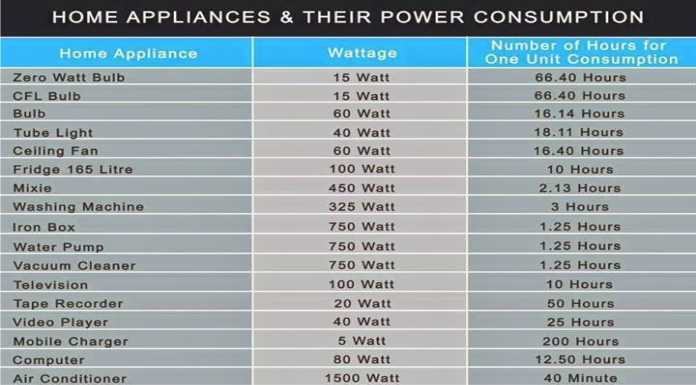
Common Household Appliances and Their Watt Usage
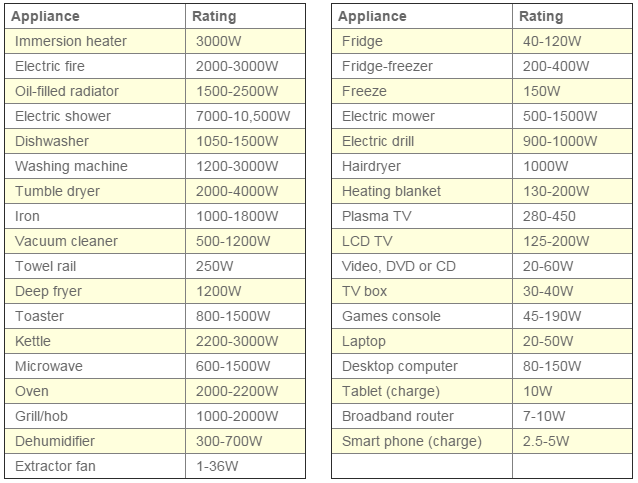
Here is a breakdown of the typical wattage of common household appliances:
1. Kitchen Appliances:
- Refrigerator: 75-200 W (varies significantly based on size and efficiency)
- Freezer: 100-250 W (similar to refrigerators)
- Dishwasher: 1200-1800 W (during operation, with significant variation based on model)
- Microwave: 700-1200 W (during operation)
- Oven: 2400-3000 W (during operation)
- Stovetop (electric): 1200-1800 W (per burner)
- Toaster: 800-1200 W
- Coffee Maker: 600-1000 W
- Blender: 300-500 W
2. Laundry Appliances:
- Washing Machine: 300-500 W (during operation)
- Clothes Dryer: 2000-3000 W (during operation)
3. Heating and Cooling:
- Air Conditioner: 1000-2000 W (varies based on size and efficiency)
- Heater: 1500-2000 W (varies based on type and size)
4. Electronics:
- Television: 50-200 W (varies based on size and technology)
- Computer: 100-300 W (varies based on configuration)
- Laptop: 20-50 W
- Smartphone: 5-10 W (during charging)
- Tablet: 10-20 W (during charging)
5. Lighting:
- Incandescent Bulb: 40-100 W (traditional bulb)
- LED Bulb: 5-15 W (highly efficient alternative)
- Fluorescent Bulb: 10-25 W (intermediate efficiency)
Understanding the Importance of Watt Usage
Knowing the wattage of appliances offers valuable insights into their energy consumption and its implications:
- Energy Costs: Higher wattage appliances generally consume more electricity, leading to higher energy bills. Understanding watt usage allows for informed choices about appliances, opting for those with lower wattage for potential cost savings.
- Environmental Impact: Reduced energy consumption directly translates to a smaller carbon footprint. By choosing energy-efficient appliances and using them responsibly, individuals can contribute to a sustainable future.
- Optimizing Energy Usage: Understanding appliance wattage allows for strategic use of energy. For instance, using a microwave instead of an oven for reheating can significantly reduce energy consumption.
FAQs Regarding Watt Usage of Household Items
1. What is the relationship between wattage and energy consumption?
Wattage indicates the rate of energy consumption. Multiplying the wattage of an appliance by the duration of its use gives the total energy consumed in watt-hours (Wh).
2. How can I reduce my energy consumption?
- Choose energy-efficient appliances with lower wattage ratings.
- Use appliances sparingly and only when necessary.
- Unplug appliances when not in use, as they can consume "phantom" energy.
- Opt for LED lighting, which offers significant energy savings compared to traditional bulbs.
3. How can I calculate the cost of running an appliance?
To calculate the cost of running an appliance, you need to know its wattage, the duration of use, and the electricity rate per kilowatt-hour (kWh). The formula is:
Cost = (Wattage x Hours of Use x Electricity Rate) / 1000
Tips for Reducing Watt Usage in Your Home
- Unplug Unused Devices: Even when turned off, many electronics draw power in standby mode. Unplugging these devices can save energy and reduce your carbon footprint.
- Utilize Natural Light: Maximize the use of natural light during the day, minimizing reliance on artificial lighting.
- Use Power Strips: Power strips allow you to easily turn off multiple devices with a single switch, preventing phantom energy consumption.
- Invest in Energy-Efficient Appliances: Opt for appliances with Energy Star ratings, signifying their energy efficiency and potential cost savings.
- Consider Smart Plugs: Smart plugs allow you to remotely control and monitor the energy usage of connected devices, enabling you to optimize their use.
- Maintain Appliances Regularly: Regularly cleaning and maintaining appliances ensures they operate efficiently, reducing energy consumption and prolonging their lifespan.
Conclusion
Understanding watt usage is essential for making informed decisions about energy consumption in the home. By carefully considering the wattage of appliances and implementing energy-saving practices, individuals can significantly reduce their energy costs, minimize their environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future. By understanding the power consumption of common household items, we can make conscious choices that positively impact our energy usage and environmental responsibility.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Watt Usage: A Guide to Household Energy Consumption. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!