Understanding Wattage: The Power Behind Your Household Appliances
Related Articles: Understanding Wattage: The Power Behind Your Household Appliances
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Wattage: The Power Behind Your Household Appliances. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Wattage: The Power Behind Your Household Appliances

Wattage, a measure of electrical power consumption, is a fundamental concept in understanding the energy demands of our everyday appliances. It quantifies the rate at which an electrical device converts electrical energy into other forms, such as heat, light, or mechanical motion. Understanding wattage allows for informed decisions regarding appliance selection, energy efficiency, and overall household energy consumption.
This article delves into the wattage of common household items, providing a comprehensive overview of their energy demands and the factors influencing them. It explores the implications of wattage for energy efficiency, cost optimization, and safety considerations.
A Spectrum of Power Consumption
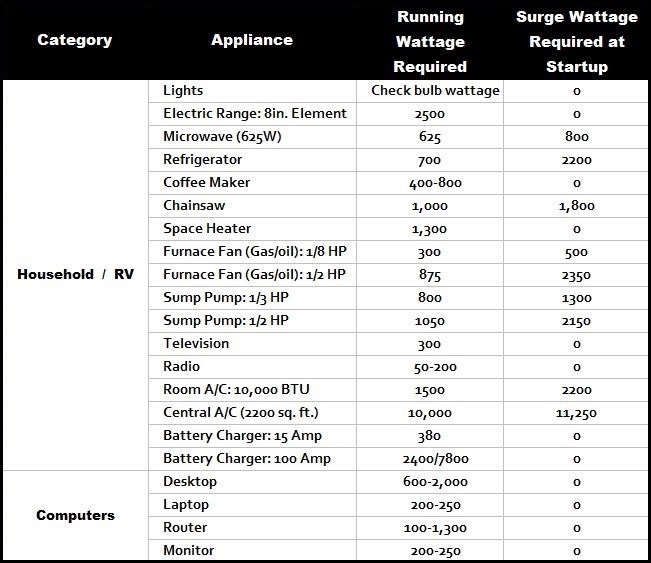
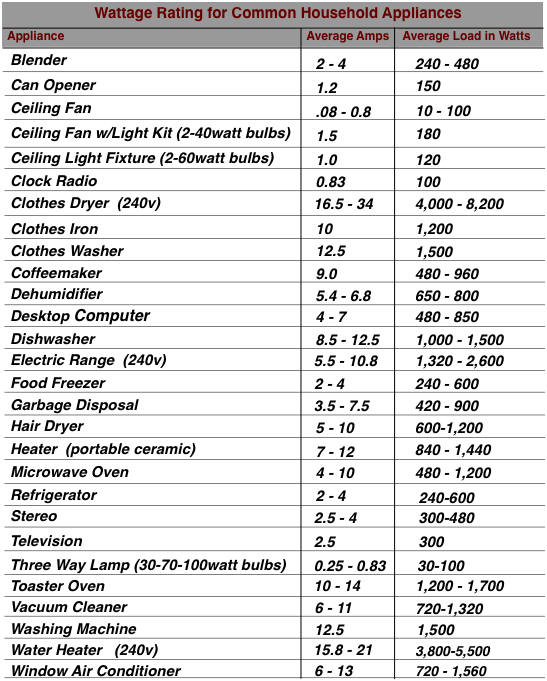
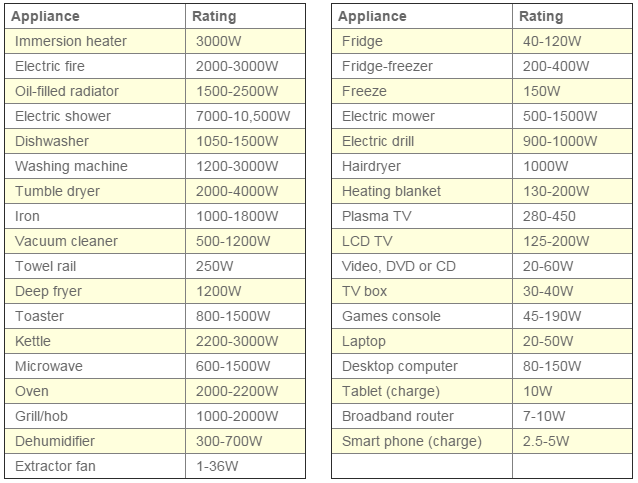
Household appliances exhibit a wide range of power consumption, ranging from a few watts for simple devices to thousands of watts for high-power appliances. This variation is directly linked to the appliance’s function and the amount of energy it requires to operate.
Low-Wattage Devices:
- LED Light Bulbs: Typically consume 5-15 watts, significantly less than traditional incandescent bulbs, which can consume 40-100 watts.
- Small Appliances: Devices like electric toothbrushes, hair dryers, and coffee makers generally consume between 50 and 1000 watts.
- Electronics: Laptops, tablets, and smartphones consume relatively low wattage, typically in the range of 10-100 watts.
- Clock Radios: These devices consume minimal power, usually around 5-10 watts.
Medium-Wattage Devices:
- Microwaves: These appliances consume around 700-1200 watts, depending on their power level and size.
- Refrigerators: Modern refrigerators typically consume between 100 and 200 watts, while older models may consume significantly more.
- Dishwashers: These appliances consume around 1200-1800 watts, depending on their features and efficiency.
- Washing Machines: Washing machines typically consume between 500 and 1500 watts, depending on the load size and wash cycle.
High-Wattage Devices:
- Electric Stoves and Ovens: These appliances consume substantial amounts of power, typically ranging from 2000 to 5000 watts or more.
- Electric Water Heaters: These devices can consume upwards of 4500 watts, depending on their capacity and heating elements.
- Air Conditioners: Air conditioners consume significant power, ranging from 1000 to 5000 watts depending on their size and cooling capacity.
- Electric Heaters: These devices consume a considerable amount of power, typically ranging from 1500 to 2500 watts or more.
Factors Influencing Wattage
Several factors contribute to the wattage of household appliances:
- Functionality: Appliances with more complex functions or higher power requirements naturally consume more energy.
- Size: Larger appliances, such as refrigerators or ovens, generally consume more power than smaller versions.
- Efficiency: Energy-efficient appliances are designed to consume less power while maintaining performance.
- Usage: The frequency and duration of appliance usage significantly impact overall energy consumption.
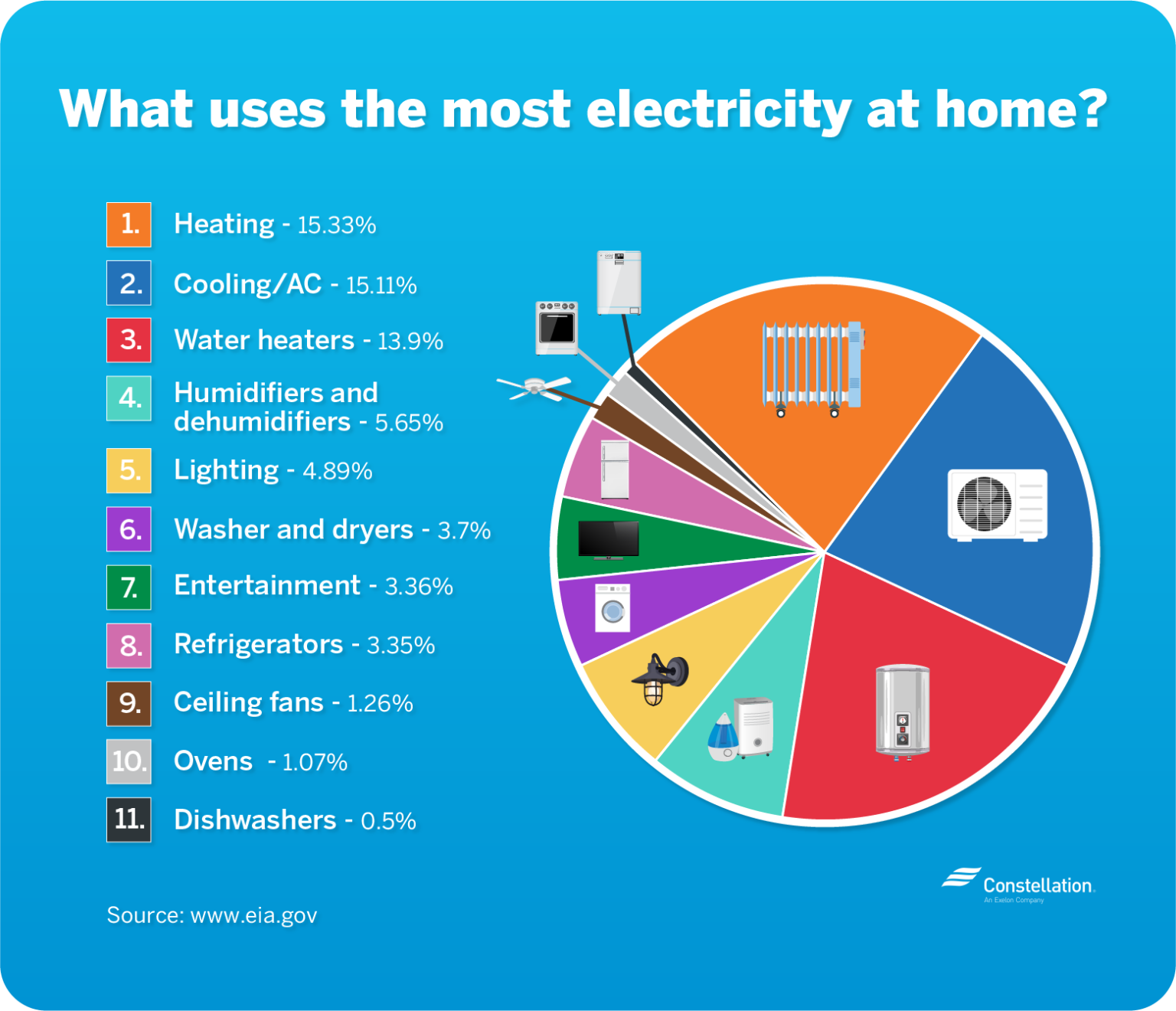
Wattage and Energy Efficiency
Understanding wattage is crucial for making informed decisions regarding energy efficiency. Appliances with lower wattage ratings generally consume less energy, leading to lower electricity bills and a reduced environmental footprint.
Cost Optimization
Wattage directly influences the cost of operating an appliance. Higher wattage appliances consume more electricity, leading to increased energy bills. By choosing energy-efficient appliances with lower wattage ratings, households can significantly reduce their electricity costs.
Safety Considerations
Wattage plays a crucial role in electrical safety. Appliances with high wattage ratings require appropriate electrical wiring and circuit breakers to handle the load. Improper wiring or overloaded circuits can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and electrical malfunctions.
FAQs by Wattage of Common Household Items
Q: What is the typical wattage of a standard incandescent light bulb?
A: Standard incandescent light bulbs consume a significant amount of power, ranging from 40 to 100 watts.
Q: How much power does a refrigerator consume on average?
A: Modern refrigerators typically consume between 100 and 200 watts, while older models may consume significantly more.
Q: What is the average wattage of an electric stove?
A: Electric stoves consume substantial amounts of power, typically ranging from 2000 to 5000 watts or more.
Q: How much power does an air conditioner consume?
A: Air conditioners consume significant power, ranging from 1000 to 5000 watts depending on their size and cooling capacity.
Tips by Wattage of Common Household Items
- Replace Incandescent Bulbs with LEDs: LEDs consume significantly less power than incandescent bulbs, saving energy and money.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, indicating high energy efficiency and lower wattage consumption.
- Unplug Unused Electronics: Even when turned off, some electronic devices consume small amounts of power, known as "phantom load." Unplugging unused devices can save energy.
- Use Appliances Efficiently: Optimize appliance usage by selecting appropriate settings, washing full loads, and using energy-saving features.
- Consider Energy Audits: Hire a qualified energy auditor to assess your home’s energy consumption and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding wattage is essential for navigating the complexities of modern household energy consumption. By recognizing the power demands of various appliances, individuals can make informed decisions regarding energy efficiency, cost optimization, and safety. By embracing energy-saving practices and selecting energy-efficient appliances, households can reduce their environmental impact and minimize electricity costs.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Wattage: The Power Behind Your Household Appliances. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!