Understanding Watts: Powering Our Everyday Lives
Related Articles: Understanding Watts: Powering Our Everyday Lives
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Watts: Powering Our Everyday Lives. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Watts: Powering Our Everyday Lives
The wattage of an appliance, a measure of its power consumption, is often overlooked despite its crucial role in our daily lives. It dictates how much energy an appliance uses, influencing factors like operating cost, safety, and even the efficiency of our homes. This article delves into the world of watts, exploring their relevance in everyday household items, shedding light on their importance, and providing valuable insights for making informed decisions about energy consumption.
A Primer on Watts:
Watts (W) represent the rate at which energy is consumed by an appliance. Higher wattage signifies greater energy consumption, translating to a higher electricity bill. For instance, a 100-watt light bulb consumes energy at a rate of 100 joules per second. This seemingly simple concept has significant implications for our daily lives, particularly when it comes to understanding and managing household energy consumption.
Decoding Watts in Common Household Appliances:
Understanding the wattage of various appliances provides valuable insights into their energy consumption patterns. Here’s a breakdown of wattage ranges for common household items:
1. Lighting:
- Incandescent Bulbs: 40-100 watts (Traditional bulbs, known for their high energy consumption)
- Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs): 5-15 watts (Energy-efficient alternatives to incandescent bulbs, offering significant savings)
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): 1-10 watts (Highly efficient and long-lasting, offering significant energy savings)
2. Kitchen Appliances:
- Refrigerators: 100-200 watts (Energy consumption varies depending on size and features)
- Freezers: 100-250 watts (Similar to refrigerators, with energy consumption influenced by size and features)
- Microwave Ovens: 700-1200 watts (Powerful appliances that consume significant energy during operation)
- Dishwashers: 1200-1800 watts (Energy consumption varies based on model and wash cycle)
- Ovens: 1500-3000 watts (High-wattage appliances requiring significant power)
- Stoves: 1200-3000 watts (Wattage varies depending on the type of stove and burner size)
- Coffee Makers: 500-1500 watts (Wattage depends on size and brewing method)
- Blenders: 300-1000 watts (Wattage influences blending speed and power)
3. Laundry Appliances:
- Washing Machines: 500-1500 watts (Energy consumption varies based on model and wash cycle)
- Dryers: 2000-4000 watts (High-wattage appliances requiring significant power)
4. Entertainment Systems:
- Televisions: 50-200 watts (Energy consumption varies based on size and features)
- Audio Systems: 50-200 watts (Wattage depends on the size and power of the speakers)
5. Heating and Cooling Systems:
- Air Conditioners: 1000-2000 watts (Energy consumption varies based on size and cooling capacity)
- Heaters: 1000-2000 watts (Wattage depends on the type and heating capacity)
6. Other Appliances:
- Computers: 50-200 watts (Energy consumption varies based on size and processing power)
- Printers: 10-50 watts (Wattage depends on the type and printing speed)
- Vacuum Cleaners: 500-1500 watts (Wattage influences suction power and cleaning efficiency)
Understanding the Significance of Watts:
- Energy Efficiency: Choosing appliances with lower wattage translates to lower energy consumption, leading to cost savings on electricity bills.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Higher wattage appliances consume more energy, resulting in higher electricity bills.
- Environmental Impact: Lower wattage appliances contribute to reduced carbon footprint, promoting sustainability.
- Safety: Appliances operating at their designated wattage ensure optimal performance and prevent potential hazards.
FAQs by Watts for Common Household Items:
1. How do I determine the wattage of an appliance?
The wattage of an appliance is typically found on its label, usually on the back or bottom. Look for a sticker or a plate containing information about the appliance’s specifications, including wattage.
2. Why does wattage matter for my light bulbs?
Wattage plays a crucial role in light bulb efficiency and energy consumption. Higher wattage bulbs consume more energy, leading to increased electricity bills. Choosing energy-efficient bulbs, such as LEDs, with lower wattage can significantly reduce energy consumption and save money.
3. How does wattage affect the performance of my refrigerator?
The wattage of a refrigerator influences its energy consumption and cooling efficiency. A higher wattage refrigerator might offer faster cooling but will consume more energy, leading to higher electricity bills. Choosing a model with a lower wattage can help save energy and reduce costs without compromising on performance.
4. What is the significance of wattage in my air conditioner?
Wattage determines the cooling capacity of an air conditioner. A higher wattage air conditioner offers faster cooling but consumes more energy. Choosing an air conditioner with the appropriate wattage based on the size of the room can ensure optimal cooling while minimizing energy consumption.
5. How can I reduce the wattage of my appliances?
While you cannot directly change the wattage of an appliance, you can make choices that indirectly reduce its energy consumption. For instance, opting for energy-efficient appliances with lower wattage ratings, using appliances sparingly, and utilizing energy-saving features can contribute to lower energy consumption.
Tips by Watts for Common Household Items:
- Lighting: Opt for LEDs or CFLs instead of traditional incandescent bulbs to significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Refrigerators: Choose models with Energy Star certification, which indicates high energy efficiency. Keep the refrigerator at the recommended temperature and avoid keeping it overly full.
- Dishwashers: Use the energy-saving cycle and ensure the dishwasher is fully loaded before running it.
- Washing Machines: Wash clothes in cold water and air-dry them whenever possible.
- Dryers: Use the dryer only when necessary and choose the energy-saving settings.
- Computers: Turn off your computer and monitor when not in use and use the power-saving settings.
Conclusion by Watts for Common Household Items:
Understanding the role of watts in our daily lives is essential for making informed decisions about energy consumption. By choosing appliances with lower wattage ratings, utilizing energy-saving features, and practicing energy-conscious habits, we can significantly reduce our electricity bills, contribute to environmental sustainability, and promote a more efficient and responsible approach to energy consumption. Recognizing the power of watts empowers us to make informed choices that benefit both our wallets and the planet.






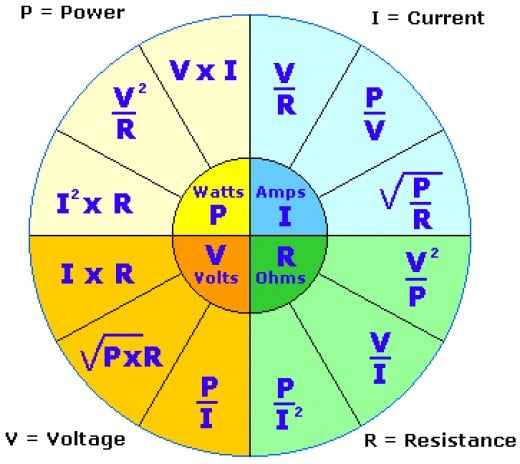
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Watts: Powering Our Everyday Lives. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
