Understanding Your Home’s Power Consumption: A Guide to Wattage Charts
Related Articles: Understanding Your Home’s Power Consumption: A Guide to Wattage Charts
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Your Home’s Power Consumption: A Guide to Wattage Charts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Your Home’s Power Consumption: A Guide to Wattage Charts
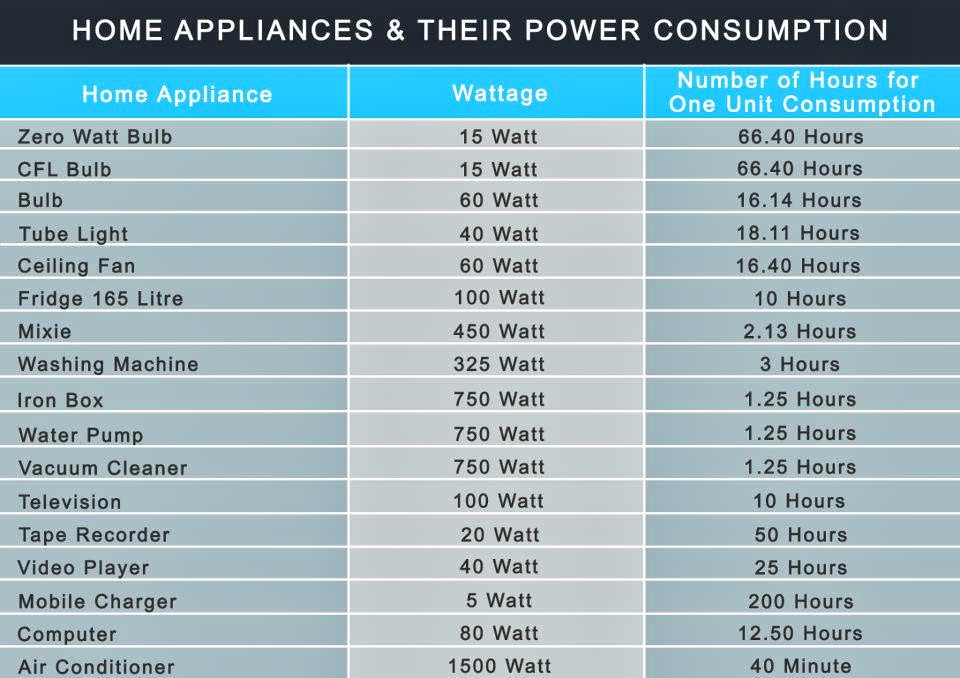
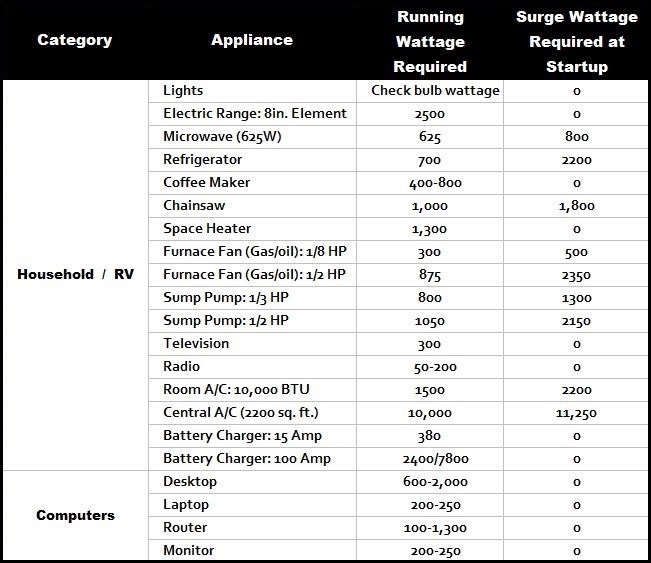
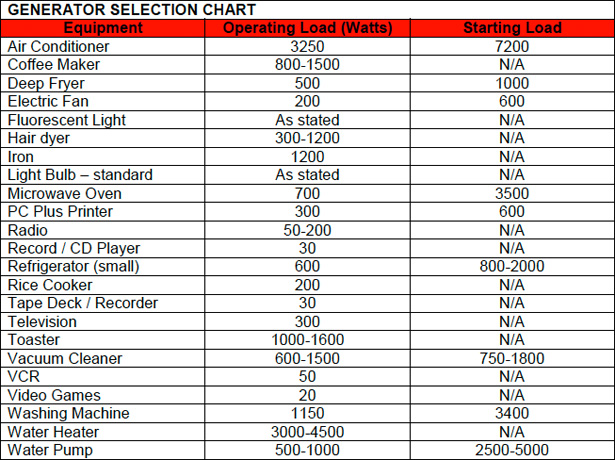
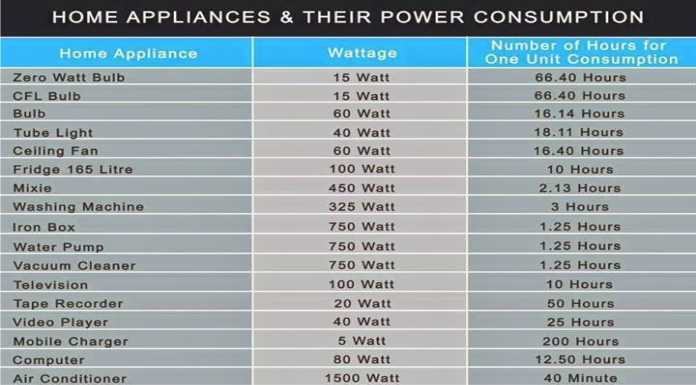
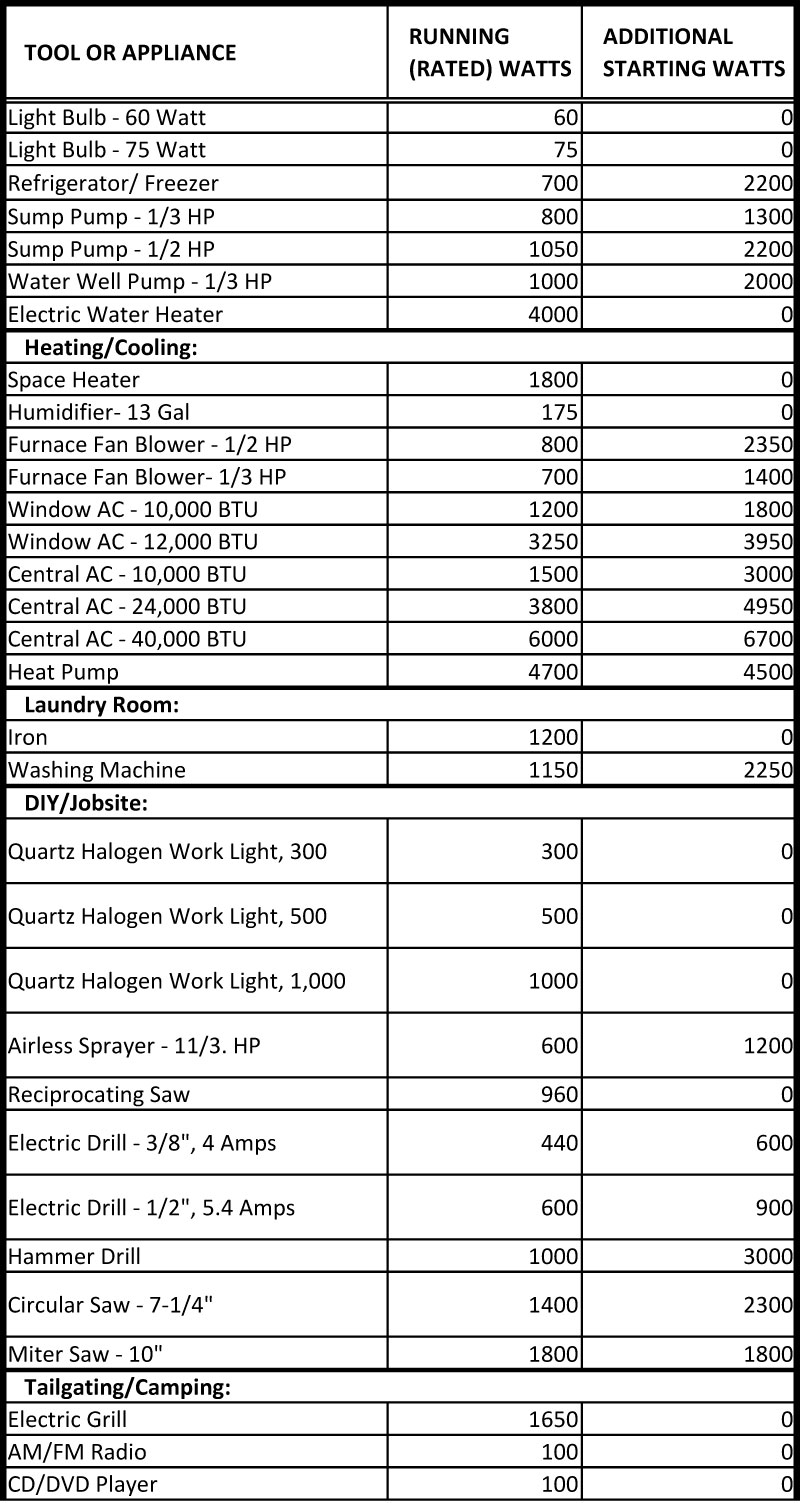
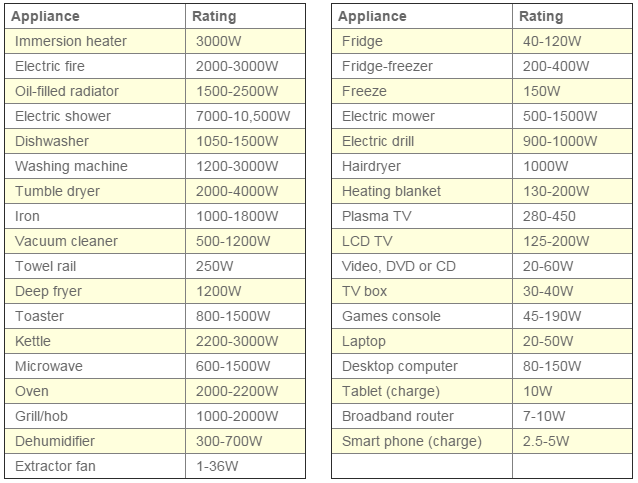
Every household appliance, from the humble light bulb to the powerful refrigerator, consumes electricity. This consumption is measured in watts (W) and kilowatts (kW), with the latter representing 1,000 watts. Understanding the wattage requirements of your appliances is crucial for efficient energy management, preventing electrical overload, and making informed decisions about your energy usage.
What is a Wattage Chart and Why is it Important?
A wattage chart provides a comprehensive overview of the power consumption of all electrical appliances and devices within your home. It lists each item, its wattage rating, and the average daily or weekly usage time. This information allows homeowners to:
- Assess overall energy consumption: By analyzing the wattage requirements and usage patterns of various appliances, homeowners can gain a clear understanding of their total energy consumption.
- Identify energy-hungry appliances: The chart highlights appliances with high wattage ratings and frequent usage, enabling homeowners to prioritize energy-saving measures for these devices.
- Optimize energy usage: The information on wattage and usage time allows for strategic scheduling of appliance use, minimizing energy consumption during peak hours and maximizing efficiency.
- Calculate electricity bills: By knowing the wattage and usage time, homeowners can estimate their electricity consumption and predict their energy bills more accurately.
- Plan for electrical upgrades: The chart reveals the total wattage load on the electrical system, helping homeowners determine if upgrades are necessary to accommodate future appliances or increased power demands.
Creating a Wattage Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
Constructing a wattage chart is a straightforward process. It involves gathering information about each appliance, its wattage rating, and its typical usage duration.
-
Inventory of Appliances: Begin by making a list of all electrical appliances and devices in your home, including:
- Major appliances: Refrigerator, washing machine, dryer, dishwasher, oven, microwave, air conditioner, etc.
- Smaller appliances: Toaster, blender, coffee maker, hair dryer, vacuum cleaner, etc.
- Electronic devices: Television, computer, laptop, gaming console, smartphone charger, etc.
- Lighting: Light bulbs, ceiling fans, lamps, etc.
-
Wattage Rating: Locate the wattage rating of each appliance. This information is usually found on a label or sticker attached to the appliance or its user manual. If the wattage rating is not readily available, you can use online resources or consult an electrician.
-
Usage Time: Estimate the average daily or weekly usage time for each appliance. Consider the frequency and duration of use for each device. For example, a refrigerator runs continuously, while a microwave is used for short bursts.
-
Data Organization: Create a table or spreadsheet to organize the information gathered. The chart should include columns for:
- Appliance name
- Wattage rating (in watts or kilowatts)
- Usage time (in hours per day or week)
Analyzing and Interpreting the Wattage Chart
Once the wattage chart is complete, you can analyze the data to identify areas for energy savings.
- High-Wattage Appliances: Focus on appliances with high wattage ratings and frequent usage, as they contribute significantly to your energy consumption. For example, a refrigerator running 24/7 consumes considerably more power than a microwave used for a few minutes each day.
- Usage Patterns: Observe the usage patterns of different appliances. Appliances used during peak hours (typically between 5 pm and 9 pm) contribute more to your electricity bill than those used during off-peak hours.
- Potential for Savings: Identify appliances with high wattage ratings and frequent usage that can be replaced with energy-efficient alternatives. For example, replacing traditional incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Tips for Reducing Energy Consumption
The wattage chart provides valuable insights into your home’s energy usage, enabling you to implement energy-saving strategies.
- Unplug Unused Appliances: Unplug appliances and electronics when not in use, as they continue to draw power even in standby mode.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Invest in energy-efficient appliances with higher Energy Star ratings, as they consume less energy and can save you money on your electricity bill in the long run.
- Smart Power Strips: Use smart power strips to turn off multiple devices with a single switch, reducing phantom power consumption.
- Lighting Choices: Opt for LED light bulbs, as they consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last longer.
- Proper Appliance Maintenance: Regularly clean and maintain appliances to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
- Optimize Thermostat Settings: Adjust your thermostat to reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Weatherization: Seal air leaks and insulate your home to reduce energy loss and improve energy efficiency.
FAQs about Wattage Charts
Q: What is the average wattage of a typical household?
A: The average wattage consumption of a household varies depending on factors such as the size of the home, the number of appliances, and the lifestyle of the occupants. However, a typical household may use between 5,000 and 10,000 watts per day.
Q: How do I convert watts to kilowatts?
A: To convert watts to kilowatts, divide the wattage by 1,000. For example, 1,000 watts equals 1 kilowatt.
Q: Is it necessary to create a wattage chart for every appliance?
A: While it is beneficial to have a comprehensive chart, you can prioritize appliances with higher wattage ratings and frequent usage.
Q: Can I use a wattage chart to determine my electricity bill?
A: The wattage chart provides information about your energy consumption, but it does not directly calculate your electricity bill. You will need to consult your energy provider’s rates and billing structure to determine your bill.
Conclusion
Understanding your home’s power consumption is essential for efficient energy management and financial savings. A wattage chart provides a comprehensive overview of your appliances’ energy requirements and usage patterns, allowing you to identify areas for energy savings and make informed decisions about your energy usage. By implementing energy-saving strategies based on the insights gained from the chart, you can reduce your electricity bill, minimize environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Your Home’s Power Consumption: A Guide to Wattage Charts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!