Unmasking The Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Electricity Consumption
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption

Understanding where our household electricity goes is crucial for making informed decisions about energy consumption and reducing our environmental footprint. This article delves into the key appliances and systems that contribute the most to our electricity bills, offering insights into their energy usage and potential for optimization.
The Big Players: Demystifying Household Energy Consumption
While every household’s energy consumption pattern varies depending on factors like size, climate, and lifestyle, certain appliances consistently emerge as major electricity consumers. Here’s a breakdown of the top contenders:
1. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC):
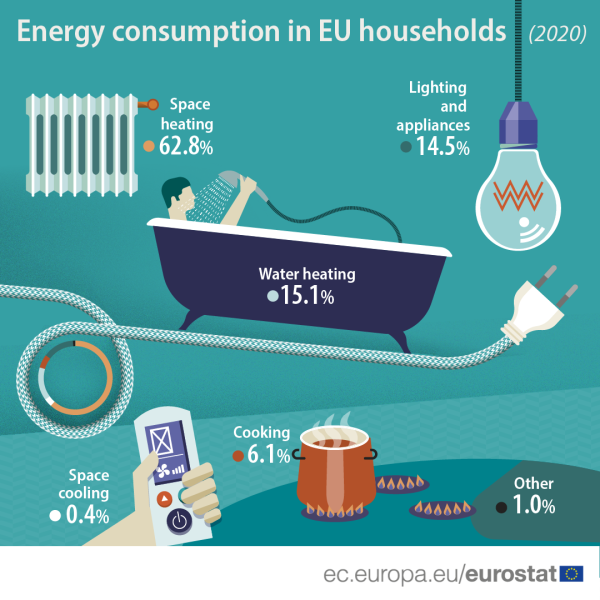
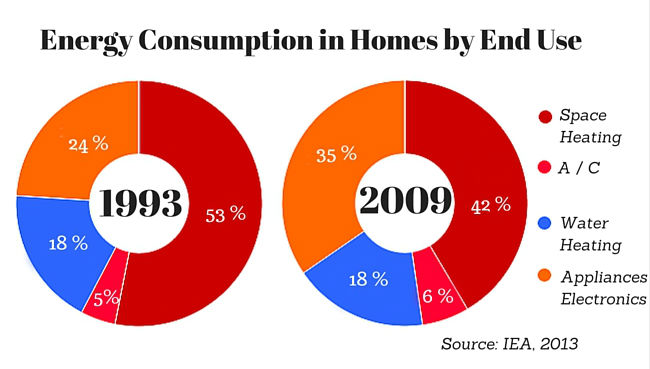
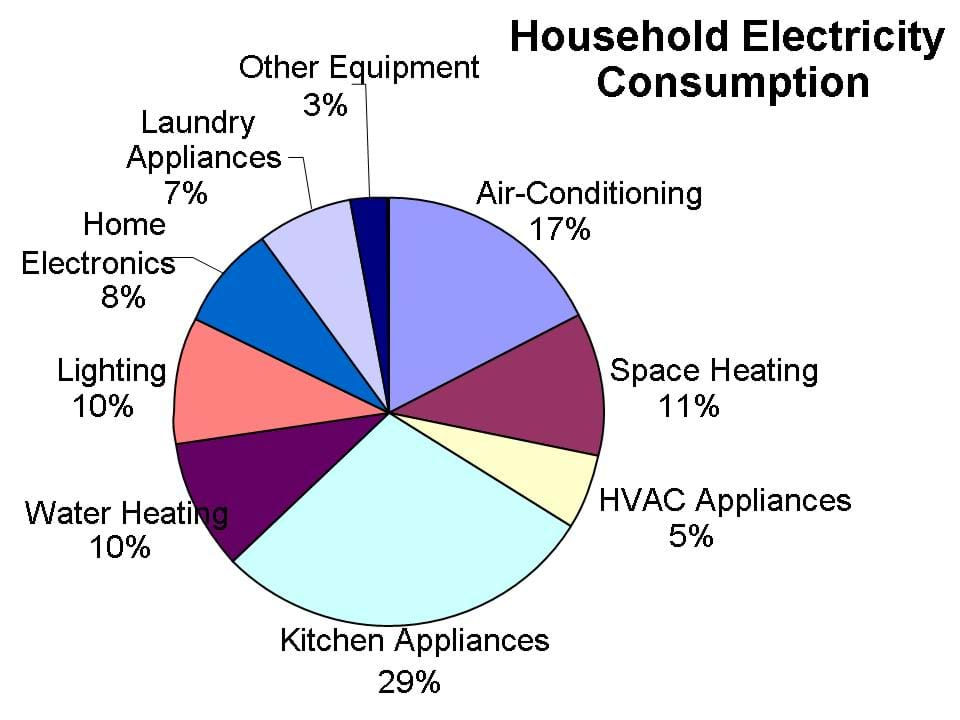
HVAC systems are often the single largest contributor to household energy consumption, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures. Heating and cooling systems utilize significant amounts of electricity to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, accounting for up to 40% of a home’s energy use.
Factors Influencing HVAC Energy Consumption:
- System Efficiency: Newer, high-efficiency HVAC systems consume less energy than older models.
- Home Insulation: Poorly insulated homes lose heat or cool air faster, forcing HVAC systems to work harder.
- Climate: Homes in hot or cold climates require more frequent and prolonged HVAC operation.
- Occupancy: The number of people living in a home and their activity patterns influence the need for heating or cooling.
2. Water Heating:
Water heating accounts for a significant portion of household energy consumption, typically ranging from 14% to 25%. Electric water heaters, in particular, are known for their high energy demand.
Factors Influencing Water Heating Energy Consumption:
- Water Heater Size: Larger water heaters consume more energy, even if they are not fully utilized.
- Water Heater Efficiency: Newer, high-efficiency water heaters offer significant energy savings compared to older models.
- Water Usage Patterns: Frequent hot showers, dishwashing, and laundry contribute to increased water heating demand.
3. Lighting:
While lighting may seem like a minor energy consumer, the cumulative impact of numerous light bulbs can be substantial. Traditional incandescent bulbs are notorious for their energy inefficiency, while newer LED bulbs offer significant energy savings.
Factors Influencing Lighting Energy Consumption:
- Bulb Type: LED bulbs consume significantly less energy than incandescent bulbs, providing substantial savings.
- Lighting Usage Patterns: Leaving lights on in unused rooms or using high-wattage bulbs unnecessarily contributes to higher energy consumption.
4. Cooking Appliances:
Electric ovens, ranges, and cooktops contribute to household energy consumption, particularly during meal preparation and baking.
Factors Influencing Cooking Appliance Energy Consumption:
- Appliance Efficiency: Newer, energy-efficient models offer significant savings compared to older appliances.
- Cooking Habits: Frequent use of high heat settings and preheating can increase energy consumption.
- Appliance Size: Larger ovens and ranges consume more energy than smaller models.
5. Refrigerators and Freezers:
These appliances run continuously, consuming significant amounts of electricity to maintain their internal temperature.
Factors Influencing Refrigerator and Freezer Energy Consumption:
- Appliance Efficiency: Newer, energy-efficient models offer significant savings compared to older appliances.
- Door Opening Frequency: Frequent door openings allow cold air to escape, forcing the refrigerator to work harder.
- Placement: Placing refrigerators and freezers in warm areas or near heat sources increases their energy consumption.
6. Electronics and Appliances:
While individual electronic devices like televisions, computers, and gaming consoles may seem to consume relatively little energy, their combined impact can be substantial, especially when left on standby mode.
Factors Influencing Electronic and Appliance Energy Consumption:
- Energy Efficiency: Choosing energy-efficient models can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Usage Patterns: Leaving electronics on standby mode or charging devices unnecessarily contributes to energy waste.
- Device Power Consumption: Different electronic devices consume varying amounts of energy, with some being more energy-intensive than others.
Beyond the Top Consumers: Unveiling Other Energy Drains
While the aforementioned appliances are major contributors to household energy consumption, several other factors play a role. These include:
- Laundry: Washing machines and dryers consume significant amounts of electricity, particularly when using hot water or high heat settings.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers consume energy for both heating water and running the wash cycle.
- Other Appliances: Appliances like hair dryers, coffee makers, and electric kettles contribute to household energy consumption, although their individual impact may be smaller.
Navigating the Energy Maze: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I determine my household’s energy consumption patterns?
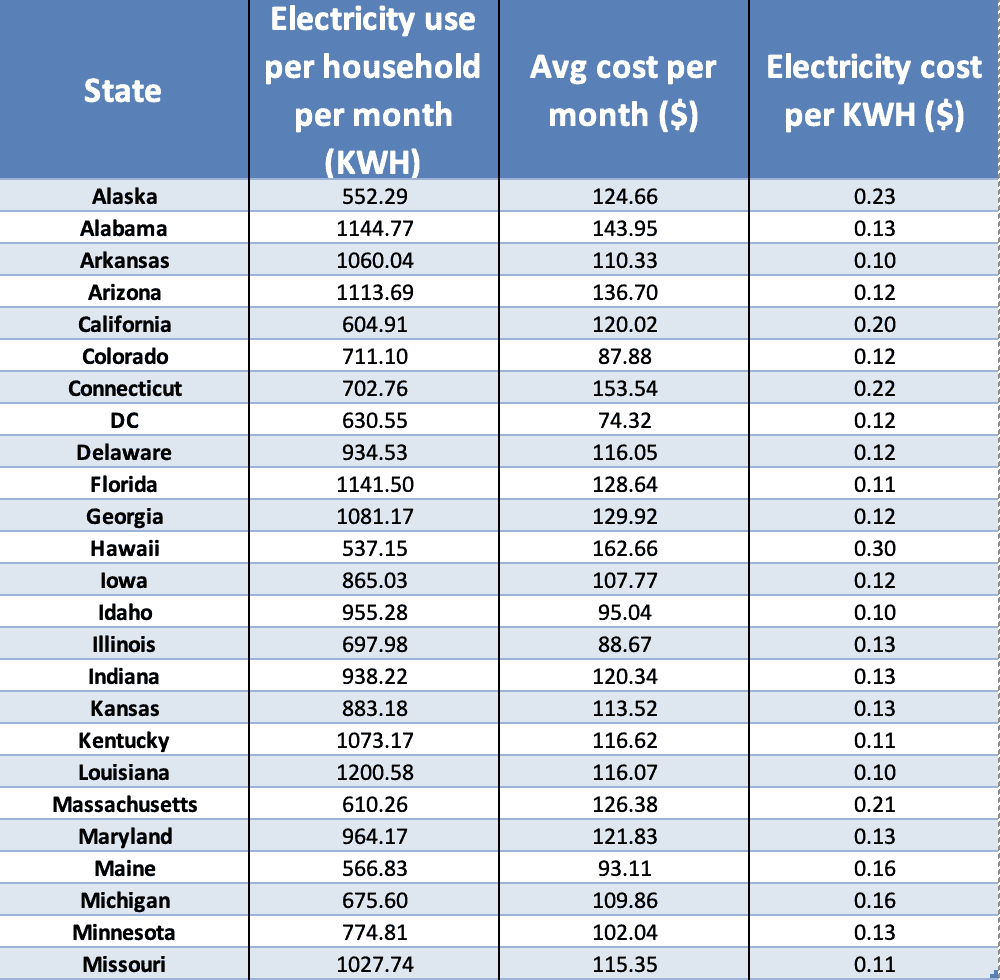
A: Many utility companies offer online portals or mobile apps that allow customers to track their energy usage in real-time. Additionally, installing a smart meter can provide detailed information about energy consumption by appliance.
Q: What are some practical ways to reduce my household’s energy consumption?
A: Implementing energy-saving strategies can significantly reduce your electricity bill. Some effective methods include:
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: Replace older, inefficient appliances with newer, energy-efficient models.
- Optimize HVAC usage: Set thermostats to comfortable temperatures, ensure proper insulation, and schedule regular maintenance.
- Adopt energy-saving lighting: Switch to LED bulbs, which consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Reduce water heating demand: Install a low-flow showerhead, use cold water for laundry whenever possible, and consider tankless water heaters.
- Unplug electronics when not in use: Avoid leaving electronics in standby mode, which can consume a surprising amount of energy.
- Practice energy-efficient cooking habits: Use the appropriate size pot for the burner, avoid preheating the oven unnecessarily, and use energy-efficient cooking methods like microwaving and slow cooking.
Q: Are there any government incentives or programs to encourage energy efficiency?
A: Many governments offer rebates, tax credits, and other incentives to encourage homeowners to adopt energy-efficient practices. Contact your local utility company or government agency for information about available programs.
Q: What is the role of renewable energy sources in reducing household energy consumption?
A: Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower energy bills. Installing solar panels, for example, can generate electricity directly from sunlight, reducing the need to draw power from the grid.
Tips for Energy-Efficient Living
- Conduct an energy audit: A professional energy audit can identify areas where your home is losing energy and recommend cost-effective improvements.
- Embrace smart home technology: Smart thermostats, smart lighting, and other smart home devices can automate energy-saving measures.
- Practice energy-conscious habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, unplug electronics when not in use, and avoid using appliances unnecessarily.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Future, One Household at a Time
By understanding the major contributors to household electricity consumption, we can make informed choices about our energy usage and implement practical strategies to reduce our environmental impact. From upgrading to energy-efficient appliances to adopting energy-saving habits, numerous opportunities exist to optimize our energy consumption and create a more sustainable future. As individuals and communities, we have the power to make a difference by embracing energy-efficient practices and contributing to a greener, more sustainable world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!