Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Deep Dive into Home Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Deep Dive into Home Electricity Consumption
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Deep Dive into Home Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Deep Dive into Home Electricity Consumption

Our homes are havens of comfort and convenience, powered by a silent yet essential force: electricity. While we often take this energy source for granted, understanding its consumption patterns within our homes is crucial for responsible energy management and environmental sustainability. This article delves into the key appliances and systems that account for the largest electricity consumption in residential settings, providing a comprehensive analysis of their energy usage and strategies for optimizing their efficiency.
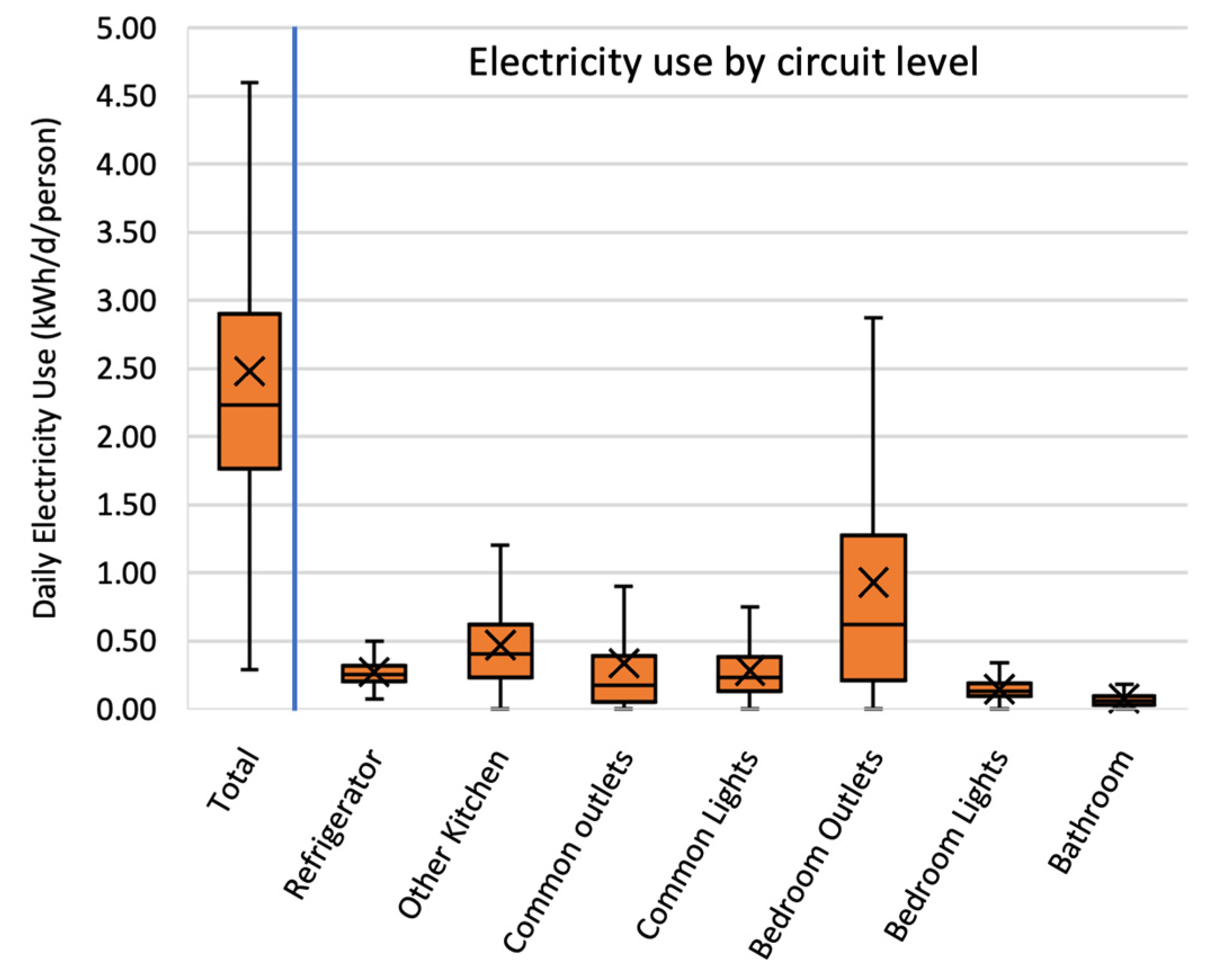
The Big Players: Appliances Leading the Charge
Several appliances and systems within our homes consistently rank among the highest electricity consumers. These include:
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
- Air Conditioners: In warmer climates, air conditioners are the undisputed champions of home energy consumption. Their operation relies on powerful compressors and fans to cool the air, drawing substantial electrical power. The size and efficiency of the unit, along with factors like room size and insulation, significantly influence energy consumption.
- Heating Systems: During colder months, heating systems, particularly electric furnaces and heat pumps, become major energy consumers. Electric furnaces use resistance heating elements to generate heat, while heat pumps utilize a refrigerant cycle to transfer heat from outside air or the ground into the home.
- Water Heaters: Electric water heaters, whether tank or tankless, consume significant electricity to maintain a consistent supply of hot water. The size of the water heater and its energy efficiency rating play a crucial role in its energy consumption.
2. Appliances with Powerful Motors:
- Refrigerators and Freezers: These appliances operate continuously, using electric motors to maintain a constant temperature. Larger models and those with features like ice makers and water dispensers consume more energy.
- Washing Machines and Clothes Dryers: Washing machines utilize electric motors for agitation and spin cycles, while dryers rely on electric heating elements for drying clothes. Both appliances contribute significantly to home energy consumption, particularly with frequent use.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers employ powerful motors and heating elements for washing and drying dishes, making them significant electricity consumers, especially when used multiple times a day.
3. Lighting Systems:
- Incandescent Bulbs: Though gradually being replaced by more efficient alternatives, incandescent bulbs remain a notable energy consumer. Their inefficiency, converting only a small percentage of energy into light and emitting the rest as heat, makes them a significant contributor to electricity bills.
- Other Lighting Fixtures: While newer LED and CFL bulbs are significantly more efficient, other lighting fixtures, such as halogen lamps and older fluorescent bulbs, still contribute to overall energy consumption.
4. Electronics and Entertainment Systems:
- Televisions and Monitors: Modern TVs and computer monitors, even when in standby mode, consume a small but continuous amount of electricity.
- Computers and Laptops: Computers and laptops, particularly those with powerful processors and multiple peripherals, draw significant electricity, especially when in use for extended periods.
- Gaming Consoles and Streaming Devices: These devices, while generally less energy-intensive than computers, still contribute to overall electricity consumption, especially when used for extended gaming sessions or streaming.
Understanding the Importance of Energy Consumption
Understanding the electricity consumption patterns within our homes is crucial for several reasons:
- Reducing Energy Bills: By identifying the most energy-intensive appliances and systems, we can implement strategies to reduce their consumption, resulting in lower energy bills and financial savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing electricity consumption contributes to a more sustainable environment by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resource Conservation: By using energy efficiently, we conserve valuable resources, ensuring their availability for future generations.
Strategies for Efficient Energy Consumption
Several strategies can be employed to optimize home electricity consumption:
- Upgrade Appliances to Energy-Efficient Models: Opting for appliances with high Energy Star ratings significantly reduces energy consumption.
- Use Appliances Wisely: Utilize appliances like dishwashers and washing machines only when fully loaded, and avoid unnecessary use of ovens and dryers.
- Maximize Natural Light: Utilize natural light whenever possible, reducing reliance on artificial lighting during the day.
- Turn Off Unnecessary Appliances and Electronics: Ensure that appliances and electronics are completely turned off when not in use, rather than left in standby mode.
- Implement Smart Home Technology: Utilize smart thermostats, lighting controls, and other smart home technologies to automate energy-saving measures.
FAQs: Demystifying Home Electricity Consumption
1. What is the biggest energy consumer in a typical home?
The largest energy consumers vary depending on factors like climate, home size, and individual usage patterns. However, heating and cooling systems are often the most significant contributors, followed by appliances with powerful motors, such as refrigerators and washing machines.
2. How can I track my home electricity consumption?
Many utility companies offer online portals or smart meters to monitor real-time electricity usage. Additionally, energy monitoring devices can be installed to track individual appliance consumption.
3. How often should I replace appliances to improve energy efficiency?
The lifespan of appliances varies, but generally, replacing older models with newer, more energy-efficient versions every 10-15 years can significantly reduce energy consumption.
4. Is it better to use a tankless water heater or a tank water heater?
Tankless water heaters are generally more energy-efficient than tank water heaters, as they only heat water on demand. However, tankless heaters may have a higher upfront cost.
5. What are the benefits of using LED bulbs?
LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, lasting longer and consuming less electricity while producing the same amount of light.
Tips for Energy-Efficient Living
- Unplug unused electronics: Even when turned off, many devices continue to draw small amounts of electricity, known as "phantom load." Unplugging these devices when not in use can save energy.
- Use power strips: Power strips with on/off switches allow you to easily disconnect multiple devices at once, reducing phantom load.
- Lower thermostat settings: Adjusting the thermostat by just a few degrees can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Wash clothes in cold water: Most laundry detergents are effective in cold water, reducing the energy needed to heat water.
- Air dry clothes: Line-drying clothes outdoors or using a clothes rack indoors eliminates the energy consumption of a dryer.
- Seal air leaks: Check for drafts around windows and doors and seal them with weather stripping or caulk.
Conclusion: Embracing Energy Efficiency
By understanding the major contributors to home electricity consumption and implementing strategies for efficient energy usage, we can significantly reduce our environmental footprint, minimize energy costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Embracing energy efficiency is not only a responsible choice but also a rewarding one, leading to financial savings, a lighter environmental impact, and a more conscious approach to energy consumption within our homes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Deep Dive into Home Electricity Consumption. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
