Unmasking The Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption In The Home
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption in the Home
Related Articles: Unmasking the Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption in the Home
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption in the Home. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption in the Home

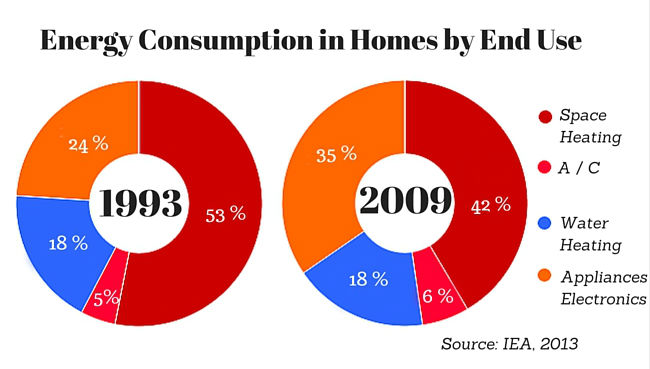
The modern home is a complex ecosystem of devices and appliances, each drawing power from the electrical grid. While the convenience and comfort they offer are undeniable, it’s crucial to understand the energy demands of these devices to make informed choices about their use and optimize our energy consumption. This article delves into the world of household electricity consumption, identifying the top energy-consuming appliances and exploring the factors that contribute to their high energy usage.
The Big Players: Identifying the Energy Guzzlers
Certain appliances stand out as major contributors to household electricity bills. These "energy hogs" are often characterized by their frequent use, high wattage, or inefficient design. Understanding their energy demands is the first step towards reducing our environmental footprint and saving money on our energy bills.
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
The heating and cooling systems, often referred to as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), are the undisputed champions of energy consumption in most homes. These systems account for a significant portion of household energy use, particularly in climates with extreme temperatures.
- Heating: Heating systems, whether fueled by natural gas, propane, oil, or electricity, consume substantial energy to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature during cold months. Electric furnaces, space heaters, and heat pumps are particularly energy-intensive.
- Cooling: Air conditioning units, responsible for keeping homes cool during summer months, draw significant amounts of electricity. The size and efficiency of the unit, as well as the temperature settings, play a crucial role in determining energy consumption.
2. Water Heating:
Heating water for showers, baths, dishwashing, and laundry is another major energy drain.
- Tank-style Water Heaters: Traditional tank-style water heaters continuously heat a large volume of water, resulting in significant energy consumption, even when not in use.
- Tankless Water Heaters: Tankless water heaters, also known as on-demand water heaters, offer greater efficiency by heating water only when needed. However, their initial cost is higher than tank-style heaters.
3. Refrigeration and Freezing:
Refrigerators and freezers are essential for food preservation but contribute significantly to household energy consumption.
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators work continuously to maintain a constant cold temperature, drawing a steady flow of electricity. Older models are generally less efficient than newer models with energy-saving features.
- Freezers: Freezers, especially chest freezers, consume even more energy than refrigerators due to their larger size and lower temperature settings.
4. Cooking Appliances:
Cooking appliances, including ovens, stoves, and microwaves, are substantial energy consumers.
- Electric Ovens: Electric ovens, particularly those with self-cleaning features, draw a significant amount of electricity during operation.
- Gas Ovens: While gas ovens are generally more efficient than electric ovens, they still consume energy for their operating components.
- Microwaves: Microwaves are generally more efficient than traditional ovens, but their energy consumption varies depending on the wattage and length of use.
5. Clothes Dryers:
Clothes dryers, especially electric dryers, are notorious energy hogs.
- Electric Dryers: Electric dryers consume a substantial amount of electricity, particularly during extended drying cycles.
- Gas Dryers: While gas dryers are more efficient than electric dryers, they still require energy for their operating components.
6. Lighting:
Lighting accounts for a considerable portion of household electricity consumption, particularly if outdated incandescent bulbs are used.
- Incandescent Bulbs: Incandescent bulbs are known for their high energy consumption and short lifespan.
- Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs): CFLs offer significantly improved energy efficiency compared to incandescent bulbs but contain mercury, which requires proper disposal.
- Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): LEDs are the most energy-efficient lighting option, offering significant energy savings and a long lifespan.
7. Electronic Devices:
The proliferation of electronic devices, such as computers, televisions, gaming consoles, and smartphones, has significantly increased household electricity consumption.
- Computers: Computers, especially desktop computers, consume a considerable amount of electricity, especially when running demanding applications.
- Televisions: Televisions, particularly large screen models, can draw significant amounts of electricity, especially when left on standby mode.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles, known for their high processing power, consume a significant amount of electricity during operation.
- Smartphones: While smartphones consume relatively little electricity compared to other devices, their widespread use and continuous charging contribute to overall household energy consumption.
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
Several factors contribute to the energy consumption of household appliances:
- Appliance Size and Wattage: Larger appliances generally consume more energy than smaller appliances. The wattage rating of an appliance indicates its power consumption.
- Efficiency Rating: Appliances with higher energy efficiency ratings consume less energy to perform the same task. Look for Energy Star labels, which indicate energy efficiency.
- Usage Patterns: The frequency and duration of appliance use significantly impact energy consumption. For example, using a clothes dryer less frequently or air conditioning only when necessary can save energy.
- Environmental Factors: Climate conditions, such as temperature and humidity, can influence energy consumption, particularly for heating and cooling systems.
FAQs: Demystifying Household Electricity Consumption
Q: What are the most energy-efficient appliances?
A: Energy-efficient appliances typically have Energy Star labels, indicating that they meet specific energy efficiency standards. Look for appliances with high efficiency ratings and features like programmable thermostats, energy-saving modes, and insulation.
Q: How can I reduce my household electricity consumption?
A: There are several ways to reduce your household electricity consumption, including:
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: Replace older, less efficient appliances with newer models that have higher energy efficiency ratings.
- Reduce appliance usage: Use appliances only when necessary and avoid leaving them on standby mode.
- Adjust appliance settings: Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature, use the cold water setting on your washing machine, and avoid preheating your oven unless necessary.
- Unplug unused devices: Unplug chargers, electronics, and appliances when not in use to avoid "phantom load" consumption.
- Use energy-efficient lighting: Replace incandescent bulbs with LEDs or CFLs to significantly reduce lighting energy consumption.
Q: What are the benefits of reducing my electricity consumption?
A: Reducing your electricity consumption offers several benefits, including:
- Lower energy bills: Saving energy translates to lower electricity bills, putting more money in your pocket.
- Reduced environmental impact: Lower energy consumption reduces your carbon footprint and contributes to a healthier environment.
- Increased energy security: Reducing your reliance on the electrical grid enhances energy security and reduces vulnerability to power outages.
Tips for Minimizing Energy Consumption
- Optimize your thermostat: Program your thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures based on your schedule, reducing energy consumption during unoccupied periods.
- Seal air leaks: Seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and other areas to prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Insulate your home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce energy consumption by preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer.
- Use natural light: Maximize natural light during the day to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
- Wash clothes in cold water: Most laundry detergents are effective in cold water, saving energy used for heating water.
- Air-dry clothes: Consider air-drying clothes instead of using a dryer, especially during warmer months.
- Use a power strip: Plug multiple devices into a power strip and turn off the strip when not in use to avoid "phantom load" consumption.
Conclusion
Understanding the energy demands of household appliances is crucial for making informed decisions about their use and minimizing our energy consumption. By identifying the energy hogs in our homes and implementing energy-saving measures, we can reduce our environmental impact, save money on our energy bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Remember, every small step towards energy efficiency makes a difference.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Energy Hogs: Understanding Electricity Consumption in the Home. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!