Unraveling The Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look At Home Electricity Consumption
Unraveling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look at Home Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Unraveling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look at Home Electricity Consumption
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look at Home Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look at Home Electricity Consumption

The modern home is a complex ecosystem of energy-consuming appliances and devices. While we often focus on the obvious culprits like air conditioning and heating, understanding the full spectrum of electricity usage is crucial for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and sustainability. This article delves into the major electricity consumers in the typical home, analyzing their contributions and highlighting strategies for minimizing energy waste.
Heating and Cooling: The Unseen Giants
Heating and cooling systems are often the largest consumers of electricity in residential homes, accounting for up to 50% of total energy use. This is particularly true in regions with extreme climates, where maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures necessitates significant energy expenditure.
- Heating Systems: Gas furnaces are generally more energy-efficient than electric heating systems, but electric furnaces are still prevalent in many homes. Heat pumps are a promising alternative, offering both heating and cooling capabilities with higher energy efficiency.
- Air Conditioning: Air conditioners are essential for comfort in hot climates, but their energy consumption can be substantial. Energy-efficient models with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
Water Heating: A Silent Drainer
Water heating is another significant contributor to home energy use, consuming around 14% of the average household’s electricity.
- Tank-style Water Heaters: Traditional tank water heaters constantly heat water, even when not in use, leading to energy loss.
- Tankless Water Heaters: Tankless water heaters, also known as on-demand water heaters, only heat water when needed, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Appliances: The Everyday Contributors
While seemingly less impactful than heating and cooling, the cumulative energy consumption of everyday appliances can be substantial.
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators run continuously, making them significant energy consumers. Modern energy-efficient models with features like automatic defrost and LED lighting can significantly reduce electricity usage.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers are a convenient appliance, but their energy consumption can vary significantly depending on the model and usage habits. Energy-efficient models with features like sensors that adjust water usage and cycle length can save energy.
- Clothes Washers and Dryers: Clothes washers and dryers are substantial electricity consumers, particularly electric dryers. Using cold water for washing and air-drying clothes can significantly reduce energy use.
Lighting: The Shifting Landscape
Lighting has traditionally been a significant energy consumer, but advancements in technology have drastically reduced its energy footprint.
- Incandescent Bulbs: Incandescent bulbs are the least energy-efficient option, converting most of their energy into heat rather than light.
- Fluorescent Bulbs: Fluorescent bulbs are more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, lasting significantly longer. However, they contain mercury, requiring careful disposal.
- LED Bulbs: LED bulbs are the most energy-efficient option, offering significant energy savings and long lifespans.
Electronics: The Hidden Energy Vampires
While seemingly insignificant individually, the cumulative energy consumption of electronics can be substantial.
- Televisions: Modern flat-screen TVs are significantly more energy-efficient than older models, but their energy consumption still adds up over time.
- Computers: Computers, particularly desktops, can be energy-intensive. Using energy-saving settings and turning off devices when not in use can reduce consumption.
- Chargers: Phone and laptop chargers continue to draw power even when not in use, creating "phantom load." Unplugging chargers when not in use can save energy.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Electricity Consumption
Several factors influence home electricity consumption beyond the type of appliances and devices used:
- Climate: Regions with extreme temperatures require more energy for heating and cooling, significantly impacting overall energy consumption.
- Household Size: Larger households tend to consume more energy due to increased appliance usage and lighting needs.
- Lifestyle Habits: Energy-conscious behavior, such as turning off lights when leaving a room and using appliances efficiently, can significantly reduce electricity consumption.
FAQs: Demystifying Home Electricity Consumption
Q: What are the most energy-efficient appliances?
A: Energy-efficient appliances are typically labeled with Energy Star ratings. Look for models with high SEER ratings for air conditioners, high Energy Factor (EF) ratings for water heaters, and high efficiency ratings for refrigerators, dishwashers, and clothes washers.
Q: How can I reduce my home’s electricity consumption?
A: There are numerous ways to reduce home electricity consumption:
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: Replace older, inefficient appliances with newer, Energy Star-certified models.
- Insulate your home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce energy loss through walls, windows, and doors, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Use energy-efficient lighting: Replace incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs, which offer significantly higher energy efficiency.
- Unplug devices when not in use: Unplug chargers, electronics, and other devices when not in use to avoid phantom load.
- Adjust thermostat settings: Lower the thermostat in winter and raise it in summer to reduce heating and cooling needs.
- Use cold water for washing clothes: Most clothes can be washed in cold water, significantly reducing energy consumption.
- Air-dry clothes whenever possible: Avoid using the dryer whenever possible, opting for air-drying instead.
- Take shorter showers: Reducing shower time can significantly reduce water heating energy consumption.
Q: What are the benefits of reducing home electricity consumption?
A: Reducing home electricity consumption offers numerous benefits:
- Reduced energy costs: Lower electricity bills lead to significant cost savings.
- Environmental sustainability: Reducing electricity consumption helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the environment.
- Increased energy independence: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels contributes to energy independence.
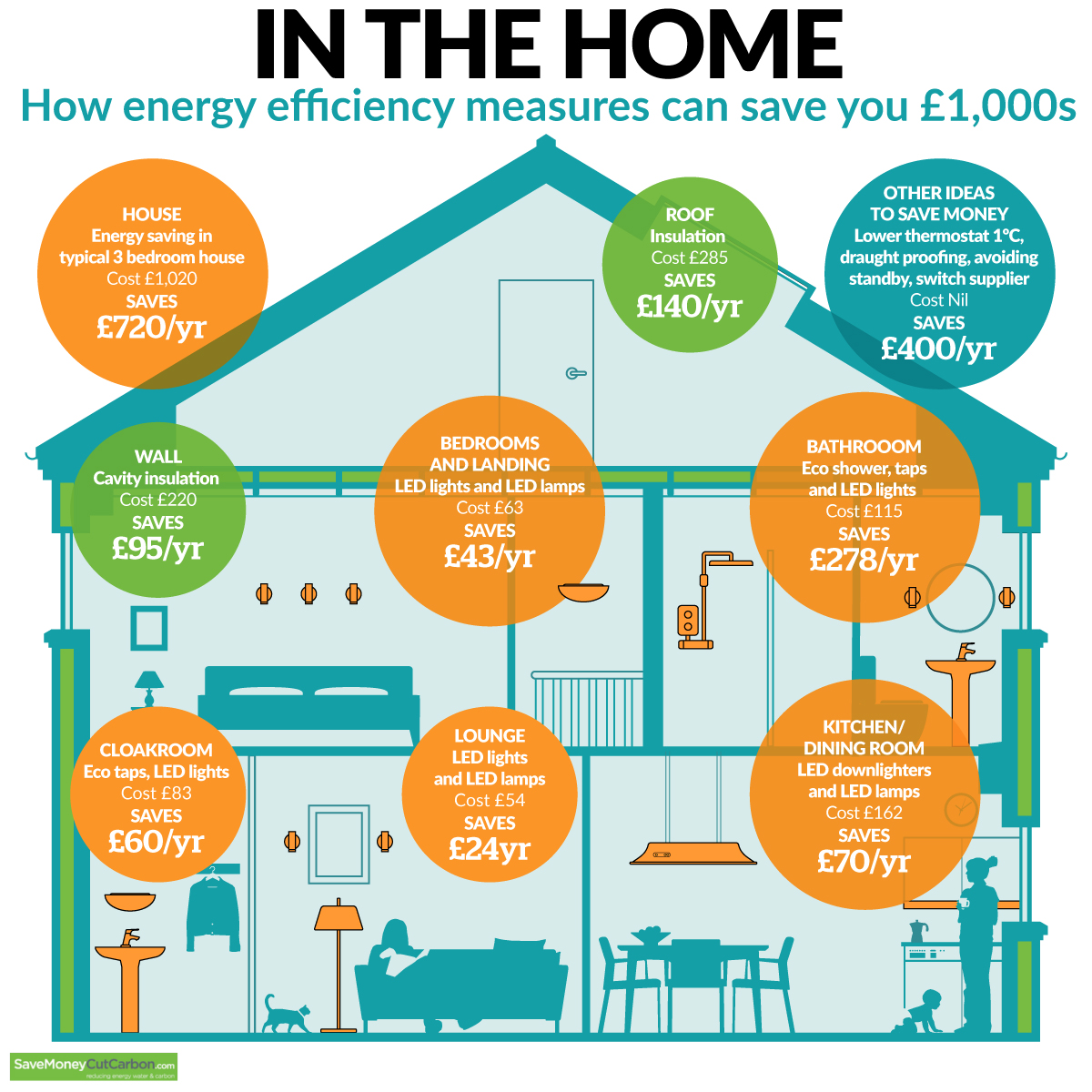
Tips for Optimizing Home Energy Efficiency
- Conduct an energy audit: A professional energy audit can identify areas where your home is losing energy and recommend solutions for improvement.
- Utilize smart home technology: Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances can automate energy-saving measures, reducing consumption without requiring constant effort.
- Participate in energy-saving programs: Many utility companies offer programs and incentives for energy efficiency upgrades, such as rebates for purchasing energy-efficient appliances.
- Make small changes: Even small changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room and unplugging chargers when not in use, can accumulate significant energy savings over time.
Conclusion: Embracing Energy-Conscious Living
Understanding the energy consumption patterns of our homes is essential for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and sustainability. By recognizing the significant energy consumers within our homes and adopting energy-saving strategies, we can reduce our environmental impact, lower our electricity bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future. The journey towards a more energy-conscious lifestyle begins with awareness and a commitment to making informed choices about our energy consumption habits.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Look at Home Electricity Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!