Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral compound, has long been recognized for its diverse applications, ranging from cleaning and laundry to industrial processes. Understanding its chemical composition and the ingredients that contribute to its unique properties is crucial for appreciating its versatility and potential uses.
Delving into the Chemical Composition of Borax
Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is a chemical compound with the formula Na2B4O7. It typically exists in hydrated forms, with the most common being decahydrate (Na2B4O7·10H2O), which is the form commonly found in household products.
The Building Blocks of Borax:
The fundamental components of borax are:
- Sodium (Na): A highly reactive alkali metal that plays a crucial role in the formation of the borate anion.
- Boron (B): A metalloid element that forms the core of the borate anion.
- Oxygen (O): The most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, oxygen combines with boron and sodium to form the borate anion.
- Water (H2O): In hydrated forms of borax, water molecules are incorporated into the crystal structure, influencing its solubility and physical properties.
The Borate Anion: The Key to Borax’s Properties
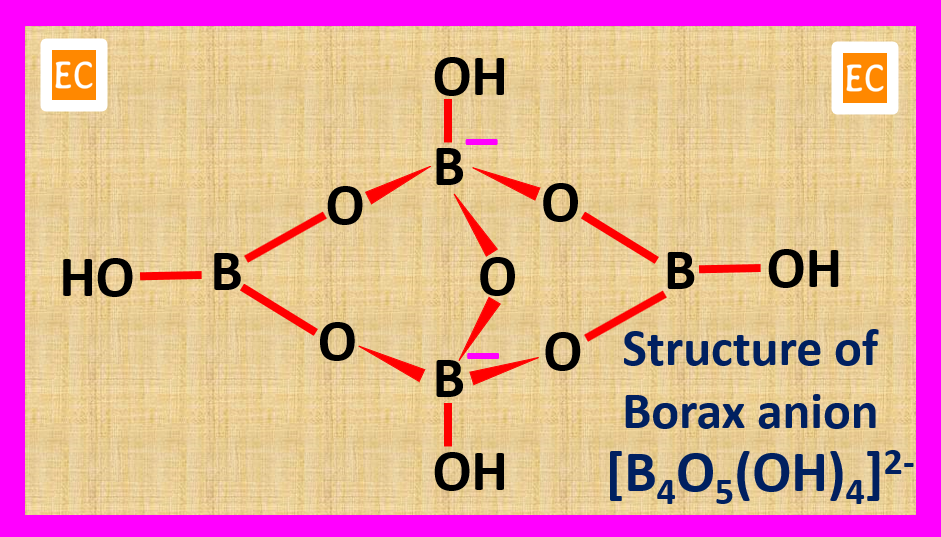
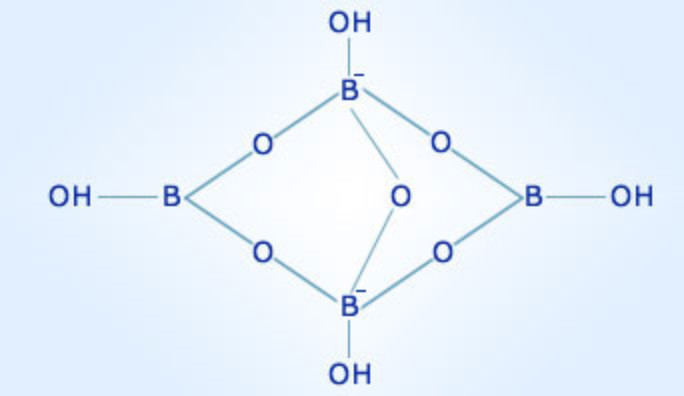
The borate anion (B4O7²⁻) is the heart of borax’s chemical structure. It comprises four boron atoms linked together by oxygen atoms, forming a complex tetrahedral structure. This anion, with its unique bonding arrangement, is responsible for many of borax’s distinct characteristics.
Exploring the Importance of Borax’s Ingredients
The precise combination of sodium, boron, oxygen, and water in borax gives rise to its numerous properties, making it valuable in various applications.
Sodium:
- Solubilizing Agent: Sodium contributes to borax’s solubility in water, making it readily available for use in solutions and cleaning products.
- Alkalinity: Sodium imparts alkalinity to borax solutions, enhancing their cleaning power and effectiveness in removing grease and grime.
Boron:
- Antimicrobial Properties: Boron-containing compounds exhibit antimicrobial activity, making borax effective against certain bacteria and fungi. This property is particularly relevant in its use as a disinfectant and in laundry detergents.
- Fire Retardant: Borax, as a source of boron, acts as a fire retardant by inhibiting the combustion process. This makes it suitable for use in fire-resistant materials and textiles.
Oxygen:
- Essential for Structure: Oxygen forms the backbone of the borate anion, contributing to its unique shape and reactivity.
Water:
- Hydration and Solubility: Water molecules incorporated into the crystal structure of borax influence its solubility and stability. Hydrated borax is more readily dissolved in water, making it easier to use in various applications.
- Flexibility and Malleability: The presence of water in hydrated forms of borax imparts flexibility and malleability, allowing it to be molded and shaped for specific purposes.
Applications of Borax: A Diverse Spectrum
Borax’s unique chemical composition and properties have led to its widespread use in various industries and applications, including:
- Cleaning Products: Borax is a popular ingredient in laundry detergents, dishwashing soaps, and all-purpose cleaners due to its alkalinity, cleaning power, and antimicrobial properties.
- Industrial Processes: Borax plays a vital role in various industrial processes, including glassmaking, ceramics, and the production of fertilizers, pesticides, and enamels.
- Textiles: Borax is used in the textile industry as a fire retardant, a mordant (a substance that helps dyes adhere to fibers), and a softener.
- Agriculture: Borax is used in agriculture as a micronutrient for plants, promoting healthy growth and increasing yields.
- Wood Preservation: Borax is used as a wood preservative to prevent rot, decay, and insect infestations.
Understanding the Benefits of Borax’s Ingredients
The unique combination of ingredients in borax results in a versatile compound with numerous benefits, including:
- Effective Cleaning: Borax’s alkalinity and antimicrobial properties make it a highly effective cleaning agent, capable of removing grease, grime, and even mold and mildew.
- Fire Retardancy: Borax’s boron content provides fire retardant properties, reducing the risk of fires and protecting materials from damage.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Borax’s antimicrobial properties make it a valuable tool for disinfecting surfaces and controlling the growth of bacteria and fungi.
- Versatility: Borax’s diverse properties allow it to be used in a wide range of applications, from cleaning and laundry to industrial processes and agriculture.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries About Borax
1. Is Borax Safe to Use?
Borax is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, it is important to note that borax is a salt and can be toxic if ingested in large quantities. It is essential to keep borax out of reach of children and pets and to use it with caution.
2. What are the Potential Health Risks Associated with Borax?
Exposure to high levels of borax can cause health problems, including skin irritation, respiratory problems, and digestive issues. Long-term exposure to borax may also be linked to certain health risks, such as reproductive problems and cancer. However, it’s crucial to note that these risks are associated with high levels of exposure and are not typically observed with normal, everyday use.
3. Is Borax a Natural Product?
Borax is a naturally occurring mineral compound, extracted from deposits found in the Earth’s crust. It is not a synthetically produced chemical.
4. What are the Alternatives to Borax?
There are several alternatives to borax, including baking soda, washing soda, and vinegar. However, these alternatives may not offer the same range of properties as borax.
5. Where Can I Buy Borax?
Borax is widely available in grocery stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
Tips for Using Borax Safely and Effectively
- Always follow the instructions on the product label.
- Use borax in well-ventilated areas.
- Avoid contact with eyes and skin.
- Wash hands thoroughly after handling borax.
- Keep borax out of reach of children and pets.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Power of Borax’s Ingredients
Borax, with its unique chemical composition and diverse properties, has proven itself to be a valuable compound with applications spanning various industries and aspects of daily life. Understanding its ingredients and their contributions to its remarkable versatility allows us to appreciate its potential benefits and use it responsibly and effectively. While borax has its potential risks, its numerous advantages, when used appropriately, make it a valuable resource for cleaning, industrial processes, and a range of other applications.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!