Unveiling The Composition Of Borax: A Comprehensive Look At A Versatile Compound
Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound
Related Articles: Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound
- 3.1 The Chemical Composition of Borax
- 3.2 The Borate Anion: The Heart of Borax’s Versatility
- 3.3 The Importance of Borax: A Multifaceted Compound
- 3.4 FAQs: Exploring the Composition and Uses of Borax
- 3.5 Tips for Using Borax Safely and Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion: Borax – A Versatile Compound with Diverse Applications
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound
Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is a naturally occurring mineral compound with a wide range of applications. From cleaning and laundry to manufacturing and agriculture, borax plays a significant role in various industries. Understanding its composition is crucial for appreciating its diverse uses and potential implications.
The Chemical Composition of Borax
At its core, borax is a hydrated sodium salt of boric acid. Its chemical formula is Na2B4O7·10H2O, indicating that it comprises:
- Sodium (Na): This alkali metal contributes to the ionic nature of the compound and plays a role in its solubility and reactivity.
- Boron (B): A metalloid element, boron forms the basis of the borate anion, which is the key to borax’s unique properties.
- Oxygen (O): Oxygen atoms bind to both sodium and boron, forming the structural framework of the compound.
- Water (H2O): Ten molecules of water are incorporated into the crystal structure of borax, giving it its characteristic white, crystalline appearance and contributing to its solubility.
The Borate Anion: The Heart of Borax’s Versatility
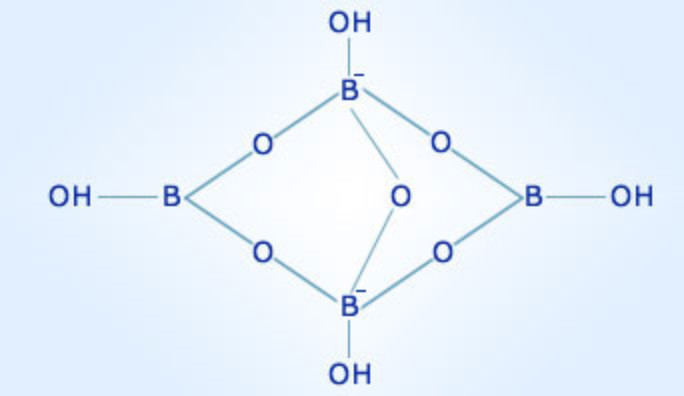
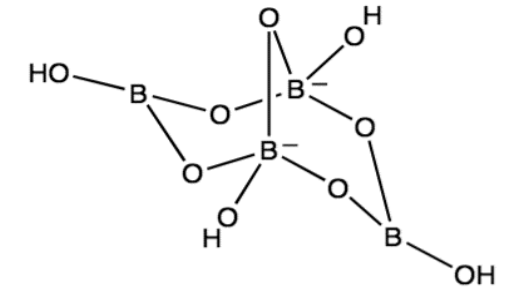
The borate anion, [B4O5(OH)4]2-, is the defining feature of borax. This complex anion, composed of four boron atoms, five oxygen atoms, and four hydroxyl groups, is responsible for many of borax’s unique properties.
- Acidity and Buffering: Borax exhibits amphoteric behavior, meaning it can act as both an acid and a base. This property allows it to buffer solutions, maintaining a relatively stable pH level.
- Complex Formation: Borate ions can form complexes with metal ions, leading to the formation of various borates. This complexation ability is crucial in applications like leather tanning and metal cleaning.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Borax’s ability to disrupt the cell membranes of microorganisms makes it an effective antimicrobial agent, particularly against fungi and bacteria. This property has led to its use in laundry detergents and cleaning products.
The Importance of Borax: A Multifaceted Compound
Borax’s diverse chemical composition and unique properties contribute to its widespread use in various industries:
- Cleaning and Laundry: Borax is a common ingredient in laundry detergents, acting as a booster to enhance cleaning power and soften water. Its antimicrobial properties also contribute to its effectiveness in tackling stains and odors.
- Manufacturing: Borax is used in the production of glass, ceramics, enamels, and fiberglass. Its ability to form borates with metal ions is essential in these processes, contributing to the desired properties of the final products.
- Agriculture: Borax serves as a micronutrient for plants, promoting healthy growth and development. It is also used as a fungicide and insecticide, effectively controlling pests and diseases.
- Water Treatment: Borax can be used to adjust the pH of water, making it suitable for various purposes. It is also used in the production of boric acid, a common disinfectant and antiseptic.
FAQs: Exploring the Composition and Uses of Borax
Q: Is borax safe for human use?
A: While borax is generally considered safe when used in small quantities and for specific purposes, it is important to handle it with caution. Excessive exposure can lead to health issues, and ingestion should be avoided.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with borax?
A: Ingestion of borax can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal problems. Prolonged exposure to borax dust can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
Q: What are the alternatives to borax?
A: Several alternatives exist for specific applications of borax. Baking soda and washing soda can be used for cleaning and laundry, while other fungicides and insecticides are available for agricultural use.
Q: How can I safely handle and dispose of borax?
A: Always wear gloves and a mask when handling borax powder. Avoid contact with eyes and skin. Dispose of borax in a sealed container and follow local regulations for waste disposal.
Tips for Using Borax Safely and Effectively
- Follow product instructions: Always read and adhere to the instructions provided on borax-containing products.
- Use in moderation: Avoid excessive use of borax, as it can be harmful if ingested or inhaled.
- Store properly: Keep borax in a cool, dry place, out of reach of children and pets.
- Ventilate well: When using borax, ensure adequate ventilation to minimize dust exposure.
Conclusion: Borax – A Versatile Compound with Diverse Applications
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral compound, offers a range of applications due to its unique chemical composition and properties. From cleaning and laundry to manufacturing and agriculture, borax plays a significant role in various industries. While its versatility is undeniable, it is crucial to handle borax with caution and use it responsibly, understanding its potential risks and employing appropriate safety measures.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Comprehensive Look at a Versatile Compound. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
