Unveiling The Composition Of Borax: A Journey Into The Chemistry Of A Versatile Compound
Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Journey into the Chemistry of a Versatile Compound
Related Articles: Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Journey into the Chemistry of a Versatile Compound
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Journey into the Chemistry of a Versatile Compound. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Journey into the Chemistry of a Versatile Compound
Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, is a naturally occurring mineral compound with a rich history of human use. Its versatility extends across various industries, from household cleaning and laundry detergents to industrial applications like glassmaking and ceramics. Understanding the elements that constitute borax is crucial to appreciating its unique properties and diverse applications.
The Building Blocks of Borax: Boron, Sodium, Oxygen, and Hydrogen
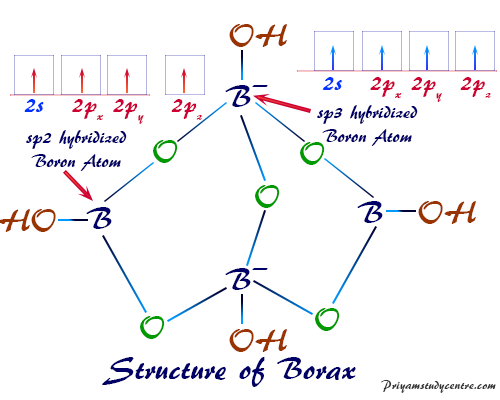
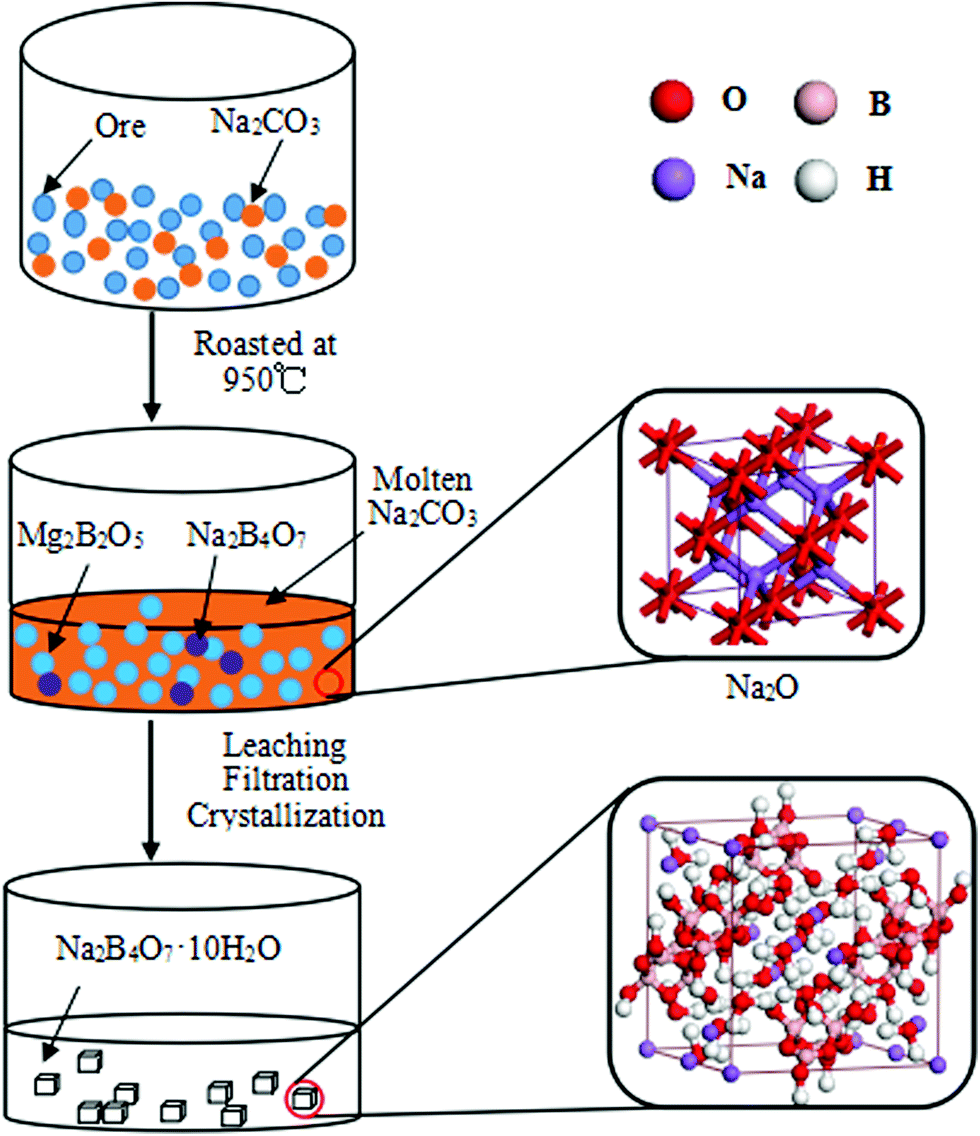
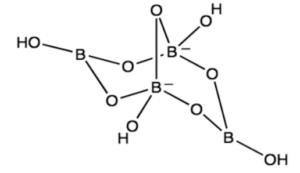
Borax is a fascinating chemical compound composed of four key elements: boron (B), sodium (Na), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H). These elements combine in a specific ratio to form the chemical formula Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O. This formula reveals the intricate structure of borax, showcasing the presence of two sodium atoms, four boron atoms, seven oxygen atoms, and ten water molecules.
Boron: The Heart of Borax
Boron, a metalloid element, plays a central role in the chemical structure of borax. It is a key component of the borate anion (B₄O₇²⁻), which forms the core of the borax molecule. Boron’s unique bonding properties allow it to form complex structures with oxygen, contributing to the versatility of borax.
Sodium: The Counterbalancing Force
Sodium, an alkali metal, balances the negative charge of the borate anion. Two sodium ions (Na⁺) are present for every borate anion, ensuring the overall molecule remains electrically neutral. This ionic bond between sodium and the borate anion is a fundamental aspect of borax’s chemical stability.
Oxygen: The Backbone of Borax
Oxygen, the most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, forms the backbone of the borate anion. Four boron atoms are linked to seven oxygen atoms through covalent bonds, creating a complex network of interconnected atoms. Oxygen’s ability to form multiple bonds with boron allows for the creation of the unique borate anion structure.
Water: The Hydration Factor
Water molecules play a crucial role in the structure of borax. Ten water molecules are associated with each borax molecule, forming a hydrated complex. These water molecules are not directly bonded to the borate anion but are held by hydrogen bonds, contributing to the compound’s solubility in water.
The Importance of Borax’s Composition: A Multifaceted Compound
The specific combination of elements in borax gives rise to its diverse properties and applications.
- Solubility: The presence of water molecules in the borax structure makes it readily soluble in water. This property is essential for its use in household cleaners and laundry detergents.
- Alkalinity: Borax’s chemical structure imparts alkalinity, making it an effective cleaning agent. It can neutralize acids and remove dirt and grime.
- Buffering Capacity: Borax acts as a buffer, helping to maintain a stable pH level in solutions. This property makes it valuable in industrial processes and biological systems.
- Antiseptic Properties: Borax exhibits weak antiseptic properties, making it useful as an antifungal and antibacterial agent in certain applications.
- Fire Retardant: Borax’s ability to decompose at high temperatures and release water vapor makes it an effective fire retardant.
Borax’s Role in Everyday Life and Industry
Borax’s unique composition enables its use in a wide range of applications, impacting our daily lives and industrial processes.
- Household Cleaning: Borax is a common ingredient in household cleaners, detergents, and laundry products. Its alkalinity and cleaning properties make it effective in removing dirt, grease, and stains.
- Laundry: Borax is used as a laundry booster to enhance the cleaning power of detergents and soften clothes. It can also help to remove odors and brighten whites.
-
Industrial Applications: Borax is essential in various industrial processes, including:
- Glassmaking: Borax acts as a flux, lowering the melting point of glass and improving its fluidity.
- Ceramics: Borax is used in glazes and enamels to enhance their properties and create unique finishes.
- Agriculture: Borax is a source of boron, an essential micronutrient for plant growth.
- Textile Industry: Borax is used in dyeing and printing processes to improve the adhesion of dyes to fabrics.
FAQs: Exploring the Chemistry of Borax
Q: What is the chemical formula of borax?
A: The chemical formula of borax is Na₂B₄O₇·10H₂O. It represents the composition of two sodium atoms, four boron atoms, seven oxygen atoms, and ten water molecules.
Q: What are the main elements that make up borax?
A: Borax is composed of four key elements: boron (B), sodium (Na), oxygen (O), and hydrogen (H).
Q: How does the composition of borax contribute to its properties?
A: The unique combination of these elements and their arrangement in the borax molecule contribute to its solubility, alkalinity, buffering capacity, antiseptic properties, and fire retardant characteristics.
Q: Why is borax important?
A: Borax is a versatile compound with diverse applications, ranging from household cleaning to industrial processes. Its unique properties make it a valuable resource in various industries and aspects of our daily lives.
Tips: Handling Borax with Care
- Always handle borax with caution. While generally considered safe for household use, it is important to follow product instructions and avoid direct contact with skin and eyes.
- Keep borax out of reach of children and pets.
- Store borax in a cool, dry place.
Conclusion: A Versatile Compound with a Rich History
Borax, a naturally occurring mineral compound, is a testament to the power of chemistry. Its unique composition, featuring boron, sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen, gives rise to a remarkable set of properties that have made it a valuable resource for centuries. From household cleaning to industrial applications, borax continues to play a significant role in our lives, showcasing the enduring impact of chemistry on human progress.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Composition of Borax: A Journey into the Chemistry of a Versatile Compound. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
