Unveiling The Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Electricity Consumption
Unveiling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Unveiling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption

The modern home is a complex ecosystem of devices and appliances that contribute to our comfort and convenience. However, this convenience comes at a cost – energy consumption. Understanding which household items consume the most electricity is crucial for both environmental sustainability and financial responsibility. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the energy usage of various household appliances and offers insights into minimizing electricity consumption without sacrificing comfort.
The Big Energy Consumers:
While many appliances contribute to overall energy consumption, certain devices stand out as significant energy hogs. These include:
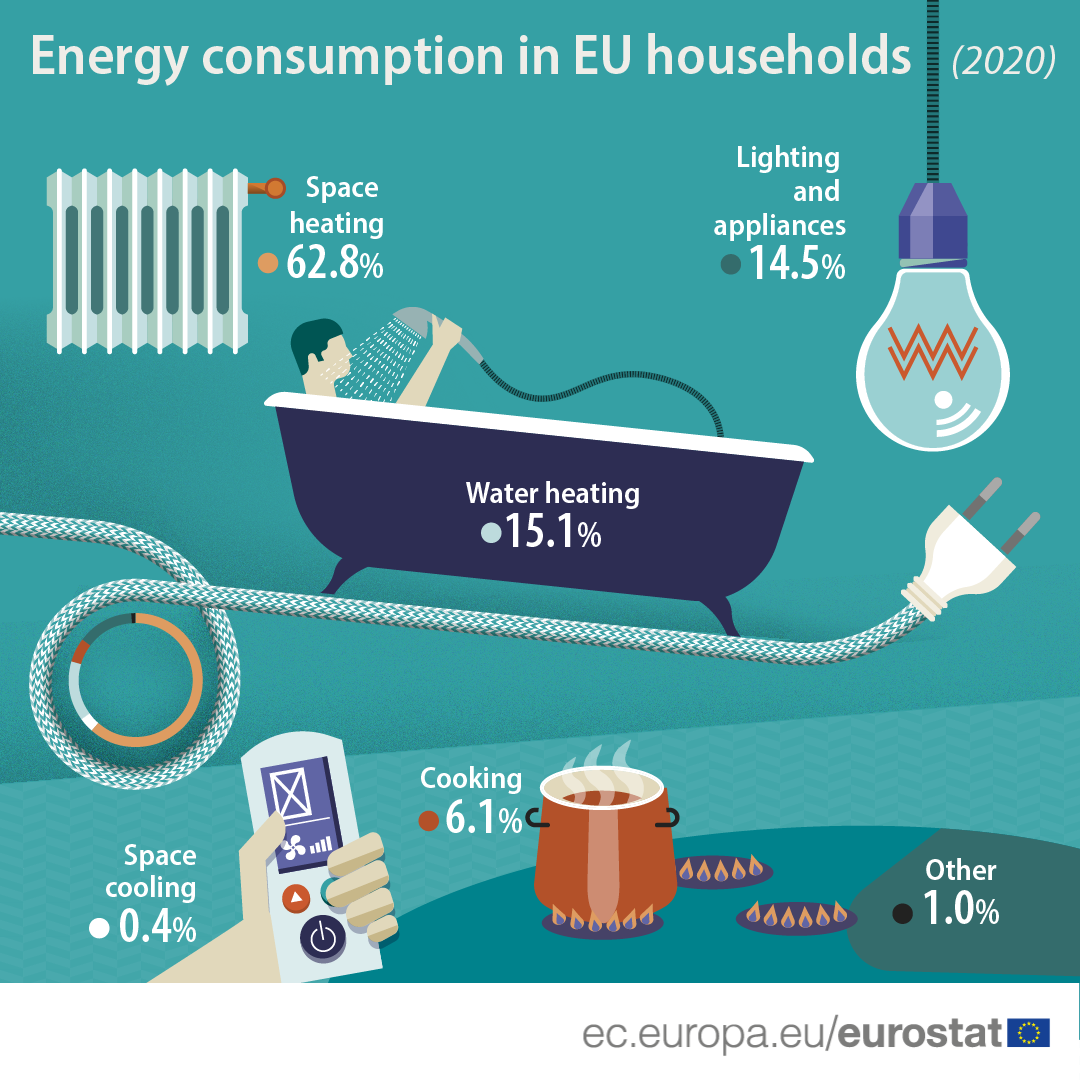
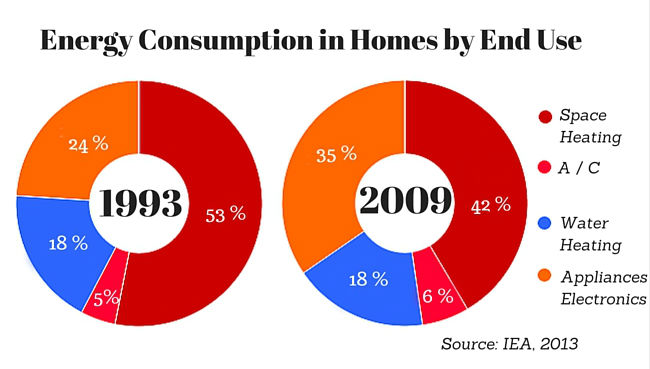
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
Heating and cooling systems, particularly air conditioners and furnaces, are often the biggest culprits in household electricity consumption. The energy required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, especially during extreme weather conditions, can significantly impact energy bills.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Climate: Regions with hot summers and cold winters experience higher heating and cooling demands.
- Home Insulation: Poorly insulated homes require more energy to maintain desired temperatures.
- System Efficiency: Older or inefficient HVAC systems consume more energy compared to newer, energy-efficient models.
2. Water Heating:
Water heating is another major energy consumer, especially in homes with large families or frequent hot showers.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Water Heater Size: Larger water heaters consume more energy to heat water.
- Water Heater Type: Tankless water heaters generally consume less energy than traditional tank-style water heaters.
- Water Usage: Frequent hot showers and baths contribute to higher energy consumption.
3. Refrigerators and Freezers:
Refrigerators and freezers are essential for food preservation but can consume significant energy over time.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Refrigerator Size: Larger refrigerators consume more energy.
- Refrigerator Age: Older refrigerators are less efficient and consume more energy.
- Door Opening Frequency: Frequent door openings allow cold air to escape, increasing energy consumption.
4. Clothes Dryers:
Electric clothes dryers are among the most energy-intensive appliances in the home.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Dryer Type: Electric dryers consume more energy than gas dryers.
- Dryer Efficiency: Older dryers are less efficient and consume more energy.
- Load Size: Drying smaller loads requires less energy.
5. Cooking Appliances:
Electric ovens, stovetops, and cooktops can consume significant energy, especially during prolonged cooking sessions.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Appliance Type: Electric ovens and stovetops generally consume more energy than gas counterparts.
- Cooking Habits: Frequent use and prolonged cooking times increase energy consumption.
- Appliance Efficiency: Older appliances are less efficient and consume more energy.
6. Lighting:
While individual light bulbs may seem insignificant, the cumulative energy consumption of multiple light fixtures can be substantial.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Bulb Type: Incandescent bulbs consume significantly more energy than LED or CFL bulbs.
- Usage Patterns: Leaving lights on unnecessarily contributes to higher energy consumption.
- Number of Fixtures: More light fixtures mean higher energy consumption.
Understanding the Importance of Energy Efficiency:
Minimizing electricity consumption is essential for several reasons:
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels and minimizes greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Financial Savings: Lower energy consumption translates to reduced electricity bills, saving money in the long run.
- Resource Conservation: By using energy more efficiently, we conserve valuable natural resources and reduce strain on the power grid.
FAQs about Household Electricity Consumption:
1. How can I determine my home’s energy consumption?
You can monitor your home’s energy consumption through your electricity bill or by installing a smart meter. Some utilities also offer online tools to track and analyze energy usage.
2. What are the most effective ways to reduce energy consumption in my home?
There are several effective strategies to reduce energy consumption, including:
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: Replace older, inefficient appliances with newer, energy-efficient models.
- Optimize HVAC system efficiency: Ensure proper insulation, seal air leaks, and consider upgrading to a more efficient HVAC system.
- Reduce water heating consumption: Install a tankless water heater, take shorter showers, and consider using cold water for laundry.
- Embrace energy-efficient lighting: Replace incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs, and utilize timers or motion sensors to minimize unnecessary lighting.
- Practice energy-saving habits: Turn off lights when leaving a room, unplug electronics when not in use, and avoid using appliances during peak hours.
3. Are there any government incentives for energy-efficient upgrades?
Many governments offer rebates and tax credits for purchasing energy-efficient appliances and implementing energy-saving upgrades. Consult your local utility company or government website for available programs.
4. How can I measure the energy consumption of individual appliances?
You can use a Kill-A-Watt meter to measure the energy consumption of specific appliances. This device plugs into an outlet and measures the power usage of the appliance connected to it.
5. What are the best practices for using appliances efficiently?
- Refrigerators: Ensure the refrigerator is properly sealed, keep the coils clean, and avoid overfilling the fridge.
- Water Heaters: Set the water heater temperature to 120 degrees Fahrenheit and consider using a timer to heat water only during peak hours.
- Clothes Dryers: Use the dryer’s automatic sensor setting to avoid over-drying, and consider air-drying clothes whenever possible.
- Cooking Appliances: Use the appropriate burner size for cooking, avoid preheating the oven unnecessarily, and consider using a slow cooker or microwave for energy-efficient cooking.
Tips for Minimizing Electricity Consumption:
- Embrace Energy-Efficient Technology: Invest in energy-efficient appliances, lighting, and electronics.
- Optimize Home Insulation: Ensure proper insulation and seal any air leaks to prevent heat loss or gain.
- Utilize Natural Lighting: Maximize natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds.
- Practice Energy-Saving Habits: Turn off lights and appliances when not in use, unplug electronics, and consider using energy-efficient power strips.
- Monitor Energy Consumption: Track your energy usage through your electricity bill or a smart meter to identify areas for improvement.
- Embrace Renewable Energy Sources: Consider installing solar panels or other renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on traditional electricity grids.
Conclusion:
Understanding the energy consumption of household items is crucial for making informed decisions about energy usage. By recognizing the biggest energy consumers and implementing energy-saving strategies, individuals can reduce their electricity bills, contribute to environmental sustainability, and conserve valuable resources. By adopting these practices, we can collectively create a more energy-efficient and environmentally conscious future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Electricity Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!